
3 minute read
Desk Research
The desk research comprised of 3 phases viz. research, understanding and conclusion. Phase 1 - Research I researched the organisations involved in neurological rehabilitation. Some of the organisations like headway and MND Scotland are doing tremendous work in this sector. They have immense resources related to neurological diseases, which helped us gain insights about patients & carers and their action. It also provided information about the fundings a carer gets from the government to look after the patient. The insight from this exercise was that carers find it challenging to avail themselves of the funding services from the government. The information regarding the funding is not accessible to the public. I also went through many patient interviews and carer testimonies available on the respective organisation’s websites. These interviews were very beneficial to understand the journey of a patient right from the diagnosis to treatment. The interviews also highlighted how a rehab centre plays a vital role in the recovery of the patients. We also learnt about the delays in the system, which makes the patients more vulnerable.
We listed down all the possible questions we had in mind regarding the referral process, communication channels, the possibility of engaging with the patients for ethnographic research, how carers are involved in the process and how does a rehab centre looks like. We narrowed it down to five major questions: How is the communication between the doctors and the family? 1. How can we help rehab practitioners collaborate well? 2. How can we build trust and reduce delays in the system? 3. How to design a long term guide for patient recovery? 4. How to empower the patients to be in control of their rehabilitation? From this activity, we also listed down the questions which we had related to the DGRC.

Phase 2 - Understanding

After the introduction session with the staff of NHS Ayrshire and Arran, we decided to reflect on the understanding of the current working of the DGRC centre. We divided the work into NHS, neurology and tools. NHS: We listed down the stakeholders involved at the centre. We investigated the location of the rehab centre. We analysed the rehab centre pictures available on the web. We learned about the accessibility of the DGRC ward. Neurology: We studied the different types of neurological diseases that are being cured at the DGRC: We learnt about Parkinson’s disease, motor neurone diseases and Huntington’s disease. I listed down the symptoms of these diseases and how it affects a patient. Understanding the service offerings of the DGRC helped us to understand the shortcomings in the services.
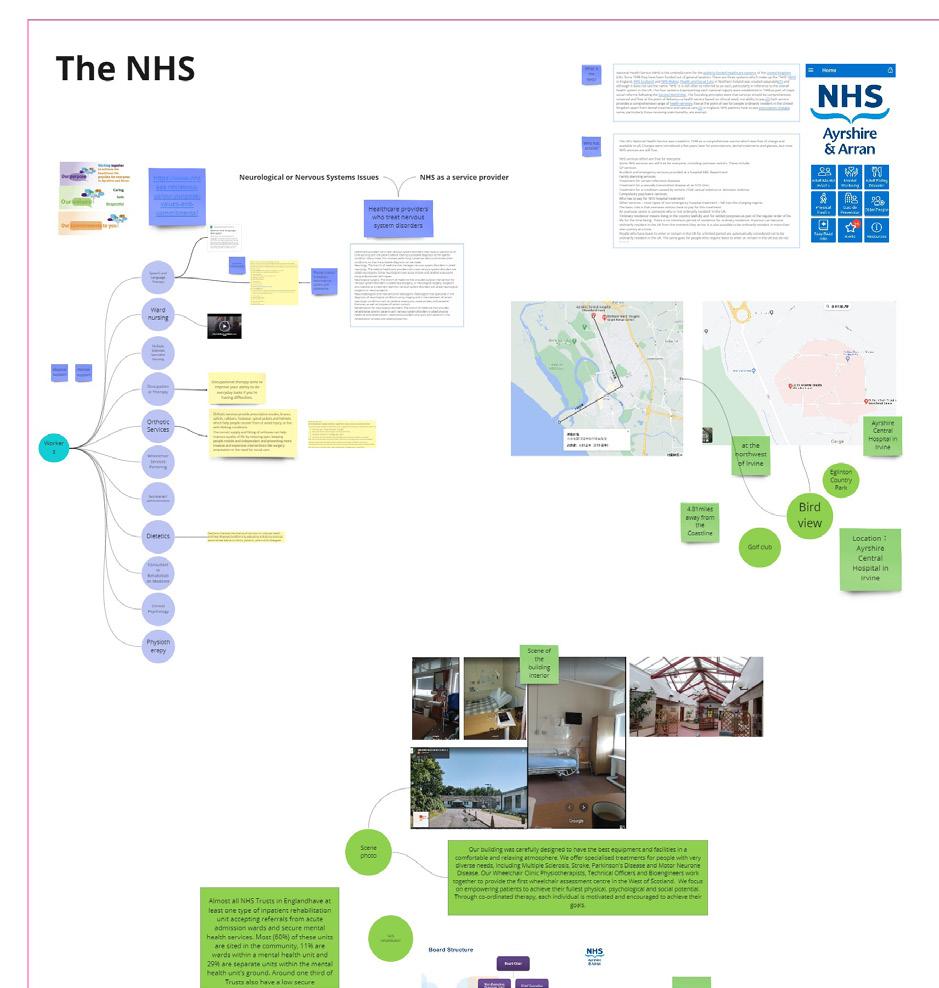
Tools: After researching the tools, we earned about the variety of tools involved in the process and how they are used based on the requirement. It also highlights how technology is being used to make accessible tools for the patients to make them less vulnerable and make them more empowered.
Phase 3 - Conclusion Desk research helped us to understand the working of the DGRC centre. The led us to insights related to patient expectations and communication. The research also led us to find our initial opportunities, which helped us design our interviews with the patients, carers and practitioners. From the research, we also gathered stats like • 28% of respondents disagree that their treatment and condition are effectively passed between the different people who care for them. • Only 10% of respondents have been offered a care plan. • 23% of respondents had not explained their diagnosis, that they understood when they were first told they had a neurological condition. • 48% were not given written information when they were told they had a neurological condition Checking the rehab centre videos, we understood the patients’ dependency on the carers and the therapists. It also highlighted the communication gap between the patients and the practitioners. Opportunities and hypothesis Based on the desk research analysis, we found out various gaps in the system related to • Communication • Building trust













