
















































































































































































According to the Markets and Markets agency, the global cocoa market as per revenue was estimated to be worth $21.1 billion by 2022 and is poised to reach $26.3 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 4.5% from 2022 to 2027. The global chocolate market as per revenue was estimated to be worth $127.9 billion by 2022 and is poised to reach $160.9 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 4.7% from 2022 to 2027.
Increasing sales of chocolate confectionery products to be consumed as comfort food is responsible for making it a regular grocery items in households. Chocolate is considered a traditional gift on special occasions and festivals such as Christmas, Easter, Halloween, and Valentine’s Day in American and European countries, a trend which is now adopted in some Asian countries such as India, China, and Japan.
The seasonal and festive sales of chocolate products highly impact the market as a large portion of chocolate products are consumed in this segment. The cocoa and chocolate market has been growing in accordance with the rising demand for health benefits of cocoa in chocolate products are the key drivers for the chocolate market. In addition to this, chocolates are being consumed as a premium and comfort food which is a rising trend among consumers, further proliferating the market growth.
Chocolates have a long history of being used as a health food. In the 18th century, a chocolaty drink was used in England to prevent and cure stomach aches. Today, ORAC (Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity) is used to compare the antioxidant capacity of different foods. Chocolates, along with apples and blueberries, are considered to be one of the best ORAC rating foods.
Instead of relying on medication, consumers prefer to incorporate ingredients that improve their health into their normal diet. Dark chocolate is becoming more popular among consumers due to its high cocoa content and flavonoids, especially a subtype known as flavanols that is linked to a lower risk of heart disease. Additionally, those who consume dark chocolate or high cocoa content have a lower chance of developing insulin resistance and high blood pressure. Thus, the health benefits associated with cocoa and its products are the biggest driver for the cocoa and chocolate market.
Chocolate prices are highly dependent on raw materials. Cocoa and sugar are the most important raw materials in chocolate manufacturing and constitute over 80% of the raw material cost for chocolate production. Hence, the rising cost of raw material will impact the market for chocolate. According to the International Cocoa Organization, the world largest supplier of cocoa is Africa, which accounts for 72% of the global production of cocoa. Ivory Coast and Ghana are the major countries producing cocoa, but these countries are also facing certain issues such as fair trade discrepancies, environmental issues, spells of government unrest, and reducing labor force as more population is leaving farming as an occupation and opting other professions.
Developing countries such as India and China offer a great opportunity for growth to major chocolate companies due to low penetration rates in these markets. In these countries, chocolate is mostly used for confectionery. The market for premium chocolates is almost undeveloped in such countries. However, the scenario is about to change, with major companies such as Kraft Foods, Ferrero, and Mars launching their premium products in Asian countries.
A major cause for the rising demand for chocolates is the rising disposable income of customers in Asia Pacific’s developing nations. Over the past several years, the availability of local brands has boosted chocolate sales in South Korea, Japan, India, and China. Due to evolving taste preferences and rising brand loyalty, international brands such as Ghirardelli, Mars, Ferrero, and Hershey’s have also seen growth in these countries.
A major threat to the chocolate industry is the changing consumer preferences of chocolates. Chocolates were consumed as a confectionery item, but now there is a growing demand for the healthy chocolate option, with an inclination toward dark chocolate, a rich source of polyphenols. As per a recent survey conducted by Barry Callebaut, 36% of Europeans
want chocolates with health benefits, while 38% would like chocolates with reduced sugar content.
Such consumer trends have forced companies such as Hero Nutritional and Barry Callebaut to launch chocolates with health benefits. Companies will have to make sure that their new product launches are in accordance with consumer tastes and preferences. Since chocolate is a perishable product, any decrease in the demand for a particular product could result in large inventories with very limited time for disposal.
Chocolate is considered a traditional gift on special occasions and festivals such as Christmas, Easter, Halloween, and Valentine’s Day in American and European countries, a trend which is now adopted in some Asian countries such as India, China, and Japan. Chocolate sales shoot up during festive seasons. Keeping this seasonal effect of sales in mind, companies trying to venture into developing econ-

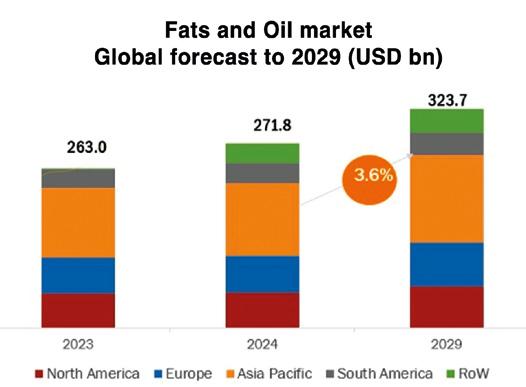
According to the latest market analysis published by MarketsandMarkets agency, the fats and oils market size is projected to reach USD 323.7 billion by 2029 from USD 271.8 billion in 2024, at a CAGR of 3.6% during the forecast. Growing consumer demand for healthier options in their diet and increasing adoption of fats and oils in various foodstuffs are boosting the fats and oils market growth. Better awareness of the nutritional value of specific oils and developments regarding processing and refining techniques act as drivers. Moreover, the expansion of culinary practices and increasing development of functional oils boasting health benefits add to the growth. Long-term investments in increasing production capacity and enhancing supply chains also uphold this growth trend.
Increasing oilseeds production
The ever-growing global demand for edible oils, important for both food and industrial applications, more than significantly expanded oilseed cultivation. According to the National Research Center in Egypt, oilseed crop areas have surged 82 percent

For instance, consider the palm oil industry, where large-scale extraction requires enormous capital to set up palm oil mills capable of processing vast quantities of fresh fruit bunches. These mills need specialized machinery like sterilizers, digesters, and centrifuges, each of which represents a considerable upfront cost.
Moreover, ensuring these facilities meet environmental regulations adds another layer of complexity and cost.
Key players within this market consist of reputable and financially robust fats & oils manufacturers. These entities boast extensive industry tenure, offering diversified product portfolios, cutting-edge technologies, and robust global sales and marketing networks. Prominent fats and oils manufacturers are ADM (US), Wilmar International Ltd (Singapore), Cargill, Incorporated (US), Bunge (US), Kaula Lumpur Kepong Berhad (Malaysia), Olam Agri Holdings Pte Ltd (India), Mewah Group (Singapore), Associated British Foods plc (UK), United Plantations Berhad (Malaysia), and Ajinomoto Co., Inc. (Japan).
Vegetable sources enjoy the largest share in the fats and oils market due to the intrinsic value in their
versatility, health benefits, and wide availability. Vegetable oils, such as soybean, palm, sunflower oil, and others, find broad use in cooking and processing due to consumer preference based on varied uses. They provide essential fatty acids while they are perceived as healthier than animal fats. Moreover, with the advent of improvements in agricultural practices and biotechnology, the production of vegetable oils increased, hence making their supply continuous and at low costs to consumers. Their versatility in food and industrial uses cements their leading market position.
Food application holds the largest share of the market for fats and oils since it is an integral part of enhancing flavor, texture, and preservation in various food products. Not only this, but also, fats and oils play a huge role in terms of cooking and baking, adding definite desirable properties like crispiness and richness. Apart from this, they also work as carriers for fat-soluble vitamins and flavors, which are important for consumer acceptance. Thus, the growing demand for processed and convenience foods and increasing consumer preference for varied gastronomic experiences further drives food applications domination within this market segment.
The increasing pace of urbanization processes, rise in disposable incomes, and changing dietary patterns toward processed and convenience foods place the Asia-Pacific region at the top position with the highest CAGR in the fats and oils market. Given the growing population and expanding middle class, there is an increasing demand for edible oils for use in cooking and food processing. Growing fast food consumption and a developing food service industry further add to the growth in the market. Strong economic development and improvement in distribution networks also aid the leading position of the region in the global fats and oils market.
www.marketsandmarkets.com
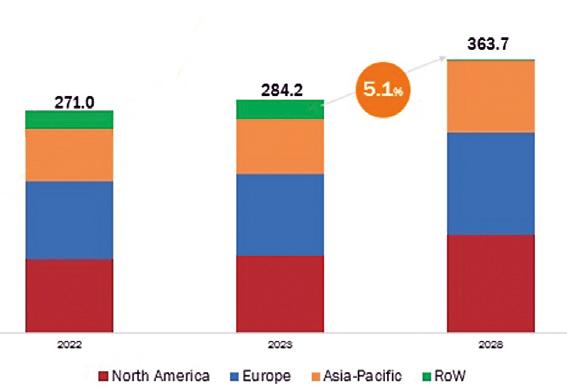
According the latest market analysis published by MarketsandMarkets agency, the frozen foods market is estimated at USD 284.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 363.7 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 5.1% from 2023 to 2028. The primary key factor contributing to the growing demand for frozen foods is convenience.
In today’s fast-paced world, consumers are constantly seeking time-saving solutions that fit their busy lifestyles. Frozen foods offer a hassle-free way to put meals on the table without the lengthy preparation associated with fresh ingredients. This convenience factor resonates with a wide spectrum of consumers, from working professionals and busy families to students and seniors. Frozen foods provide a quick and efficient means of meal preparation, allowing individuals to enjoy a wide variety of options without sacrificing taste or nutritional value. The ease of storage and longer shelf life compared to fresh foods further enhances their appeal. As a result, the convenience factor remains the driving force behind the sustained and growing demand for frozen foods in the market.
Packaged Food & Beverage Drives Growth in the Frozen Foods Market
The rapid growth in the packaged food and beverage industry is significantly fueling the expansion of the frozen foods market. This synergy can be at-
tributed to several key factors. Firstly, the packaged food and X beverage sector is experiencing increasing demand due to changing consumer lifestyles and preferences. Convenience, portability, and longer

ious dietary preferences, such as vegan, paleo, and gluten-free diets, making them inclusive and adaptable. In an era where health consciousness and convenience intersect, raw frozen foods align perfectly, allowing consumers to prepare fresh, wholesome meals with minimal effort. This appeal is driving their popularity, ensuring that raw frozen food remains the largest share of the frozen food market.
The retail segment is anticipated to witness the highest growth
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the trend of consumers stocking up on frozen essentials due to their longer shelf life, providing a boost to the retail frozen food segment. Additionally, as consumers become more health-conscious, frozen foods are evolving to offer a wider range of healthier options, including organic and low-calorie choices, further appealing to a health-focused demographic.
Furthermore, retail channels provide a convenient and accessible distribution network, making it easier for consumers to purchase frozen foods. With the ongoing expansion of e-commerce and online grocery shopping, retail frozen foods are well-positioned to capture a significant share of the market as they cater to the evolving preferences and needs of today’s consumers.
The online segment is projected to experience the highest growth
The online distribution channel is poised to experience the fastest growth in the frozen food market due to a confluence of factors. Firstly, the digital transformation of the retail landscape has seen an exponential increase in e-commerce and online grocery shopping, driven by changing consumer preferences and convenience. This shift has been further accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which prompted many consumers to turn to online platforms for their shopping needs, including frozen foods.
Secondly, online channels offer a wider variety and selection of frozen food products compared to brick-and- mortar stores, catering to diverse dietary preferences, including vegan, gluten-free, and organic options. This variety attracts a broader customer base, appealing to health-conscious and adventurous consumers.
Moreover, the ease of doorstep delivery and the ability to compare prices and products online makes it an attractive option for time-pressed consumers. As technology continues to advance and online platforms become more user-friendly, the online distribution channel is primed for rapid growth in the frozen food market, providing unparalleled convenience and accessibility for consumers.
Health and Wellness: Consumers are increasingly seeking healthier frozen food options, including those with organic ingredients, fewer additives, and lower sodium content. There’s a growing demand for frozen fruits, vegetables, and lean protein options as people become more health-conscious.
Plant-Based Alternatives: With the rise in vegetarianism, veganism, and flexitarian diets, there’s a surge in demand for plant-based frozen foods. This includes plant-based meat substitutes, dairy-free ice creams, and vegetable-based frozen meals, catering to the needs of diverse dietary preferences.
Convenience and Time-Saving: Busy lifestyles and hectic schedules have fueled the demand for convenient meal solutions. Frozen foods offer quick and easy meal options without compromising on taste or nutrition. Single-serve frozen meals, microwaveable snacks, and pre-cut frozen produce are gaining popularity among consumers seeking hassle-free meal solutions.
Premiumization: Consumers are willing to pay more for higher-quality frozen food products. Brands
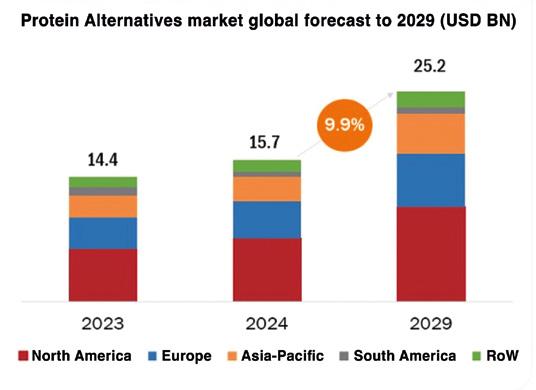
According to the latest market analysis published by MarketsandMarkets agency, the global protein alternatives market is estimated at USD 15.7 billion in 2024; it is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.9% to reach USD 25.2 billion by 2029. The protein alternatives market has experienced rapid growth and diversification in recent years, driven by increasing consumer demand for sustainable, health-conscious, and ethically produced food options. Key drivers of this market include rising concerns over the environmental impact of traditional animal agriculture, health benefits associated with plant-based diets, and ethical considerations regarding animal welfare. Major segments within the protein alternatives market include plant-based proteins, insect-based proteins, microbial protein. Companies like Beyond Meat, Impossible Foods, and Oatly have become household names, reflecting the mainstream acceptance and expanding consumer base for these products. Technological advancements and significant investments from both food industry giants and venture capitalists have further accelerated the development and accessibility of innovative protein alternatives.
The increasing global population underscores the necessity for alternative protein sources. Over the past decade, significant efforts have focused on develop -

with 14.7% experiencing multiple reactions. Notably, 46.2% of those affected had pre-existing food allergies exacerbated by insect consumption. Gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea and vomiting were commonly reported. This underscores the significant allergy-related challenges facing insect protein adoption, particularly in Western cultures.
The global population’s expansion is placing heightened strain on limited resources, with escalating energy prices and raw material expenses impacting food costs, particularly affecting lower-income demographics. Additionally, the strain on food resources is being intensified by water scarcity, notably prevalent across Africa and Northern Asia. Within the Asia Pacific region, there exists a cost advantage in terms of both production and processing, fostering high demand and offering favorable conditions for dairy alternative suppliers and manufacturers to target this market.
As lifestyles evolve rapidly, there’s a noticeable shift towards more nutritious and health-conscious food options. The distinction between fast food and junk food is anticipated to grow, with consumers increasingly seeking quick yet wholesome alternatives. Recognizing naturally rich nutritional products presents a significant opportunity for suppliers and manufacturers to meet evolving consumer preferences.
Furthermore, the rise in disposable incomes is driving demand for convenient, healthy, and highly nutritious products across Asia Pacific nations. Emerging economies within the region present substantial opportunities for growth within the protein alternatives market.
Developing plant-based proteins that convincingly replicate the taste, texture, and mouthfeel of traditional meat and dairy products is a multifaceted challenge in the protein alternatives market. Meat and dairy products are deeply ingrained in culinary cultures worldwide, and consumers have well-established expectations regarding their sensory experi-
ences. Mimicking the savory umami flavor, juicy texture, and tender bite of meat, for example, requires intricate formulation of plant proteins and other ingredients. Achieving a similar experience to dairy products like cheese or yogurt involves not just replicating taste but also mimicking the creamy texture and richness that dairy fats impart.
Texture plays a crucial role in consumer acceptance of plant-based alternatives. The fibrous structure of meat or the smooth consistency of dairy products is often difficult to replicate with plant-derived ingredients alone. Innovations in food science have led to the development of techniques such as extrusion, fermentation, and blending of proteins to enhance texture and mouthfeel. However, balancing these efforts with clean label requirements and natural ingredient preferences adds another layer of complexity. Moreover, ensuring that these products remain stable during cooking or processing without compromising taste or texture is a continuous challenge that requires ongoing research and development.
Prominent companies in this market include well-established, financially stable manufacturers of protein alternatives. These companies have been operating in the market for several years and possess a diversified product portfolio, state-of-the-art technologies, and strong global sales and marketing networks. Prominent companies in this market include ADM (US), Cargill Incorporated (US), International Flavors & Fragrances Inc. (US), Roquette Frères (France), Ingredion (US), Wilmar International Ltd. (Singapore).
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) recently released a report on the global coffee market where the world coffee production for 2024/25 is forecast to rebound 7.1 million bags from the previous year to 176.2 million due primarily to continued recovery in Brazil and rebounding output in Indonesia. With additional supplies, global exports are expected up 3.6 million bags to 123.1 million primarily on strong shipments from Indonesia and Brazil. Consumption is seen 3.1 million bags higher to 170.6 million. Ending stocks are expected to rise 1.9 million bags to 25.8 million following 3 years of decline.
The production is forecast nearly unchanged at 29.0 million bags, with over 95 percent of total output remaining as Robusta. The rainy season was slightly delayed and above average temperatures were recorded in many areas, adversely affecting yields. Similar conditions lowered yields and output the previous 2 harvests. Bean exports are forecast to drop nearly 500,000 bags to 24.4 million due to reduced total supply and rising domestic consumption.
Reduced groundwater and forest cover pose long term challenges as many coffee growers in Vietnam rely on wells for irrigation and forest cover helps slow evaporation. In response, the provincial Department of Agriculture and Rural Development and Western Highland Agriculture and Forest Science Institute have implemented strategies to encourage sustainable coffee production. These plans include replacing old coffee trees with new varieties, intercropping to increase shade and water retention, adopting water saving irrigation systems, and helping coffee farmers certify their farms for sustainable practices. According to Ministry of Agriculture and Rural
Development statistics, approximately 30 percent of coffee area has been certified to meet sustainability standards. For more information, read the Coffee Annual Report – 2024 from FAS Post in Hanoi, Vietnam.
Combined Arabica and Robusta harvest is forecast up 3.6 million bags to 69.9 million in 2024/25. Arabica output is forecast to improve 3.3 million bags to 48.2 million and the Robusta harvest is expected to rebound

Additive manufacturing is gaining significance in the industrial sector and is poised to become a standard component of series production. What benefits can 3D printing bring to systems and mechanical engineering within the food and beverage industry? What challenges still need to be addressed?
Layer by layer to the finished component
“3D printing, alongside robotics, digitalization, and machine learning, stands as a key technology of the future. In this process, also known as additive manufacturing, a 3D model created using CAD is converted into two-dimensional layers, which are then applied one after the other during printing. The benefits of this method include the swift exe-
cution of innovative concepts, extensive design flexibility, and minimal geometric constraints, all while using resources efficiently and generating little waste.”
Disruptive technology shows its advantages especially in bionic lightweight structures,
which are difficult to realise using traditional production methods such as CNC milling or turning. For example, honeycomb or grid structures are particularly suitable. They not only impress with their high stability, they are also significantly lighter in

ference to commercially available filaments lies in a polyamide optimised for the FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling) printing process. The material is food-safe and can be detected with a metal detector. It also exhibits good mechanical properties and high temperature resistance. This allows very smooth surfaces to be achieved in the printing process.
The examples show: 3D printing enables customised, tool-free production of complex geometries. A technology of the future, but one that poses challenges for use in hygiene-critical areas such as the food industry. With metallic 3D printing, such as laser beam melting, the resulting surfaces often do not have the necessary hygienic surface prop-
Tecno3’s latest marvel is the new GFS nut granulator, innovative, adaptable, intuitive, a true leap in quality for nut granulation (hazelnuts, almonds, pistachios, peanuts, and cashews), seeds, and nougat.
The new Granulator is the result of 4 months of intense technical development, a record time that demonstrates Tecno3’s commitment to constant innovation. Thanks to the direct collaboration with their clients and partners, they have identified and implemented significant improvements, exceeding expectations and offering a unique solution on the market.
The secret of its strength: freedom of movement
• Total disassembly: for quick cleaning without the need for tools, ensuring efficiency and independence from internal maintenance.
• Oxidation prevention: preserving the freshness of nuts by avoiding the rancidification process, thanks to the quick and easy disassembly of parts that come into contact
with the product for thorough cleaning and residue removal.
• Modular configuration: for optimal arrangement in the industrial layout, with movable parts that facilitate maintenance.
The easy format change allows for versatile and adaptable production, enabling quick and easy transitions between different products.
At Tecno3, the vision is driven by the constant pursuit of improvement and by teamwork. This spirit of collaboration extends to their partners, with
erties due to their high degree of roughness. The development and validation of special finishing strategies to perfect surfaces that come into contact with the product is another obstacle that needs to be overcome in additive manufacturing for the food industry in the coming years.
www.anugafoodtec.com
whom they wish to share every achievement.
The company has invested in a newly renovated and expanded test area for this very reason: to explore together the potential of each system. Here the customers have the opportunity to test specific recipes, develop projects, and consult with dedicated technicians.
Collaboration is the key to turning ideas into reality.
(Tecno3 - Via Mastri Cestai 2 - 12040 Corneliano d’Alba - CN - Italy - Tel. +39 0173 610564email: a.mattis@tecno-3.it - www. tecno-3.it)

Homogenisation is a widely used technique in manufacturing powdered milk with a direct impact on product solubility, and the homogenisation pressure is a central attribute of this process. Brazilian Researchers aimed to understand the effect of increasing homogenisation pressures (0/0, 15/5, and 75/5 MPa, 1st/2nd stages) on particle-size distribution during homogenised whole milk powder manufacture and rehydration of the final product.
The fluid milk was thermally treated, homogenised, concentrated by rotary evaporation, and then dried using a spray dryer. Particle size (Dv90) was monitored at all stages of the manufacturing process. The final product (milk powder) was analysed using particle-size distribution, electronic scanning microscopy, water activity, and isotherms. The results demonstrated that increasing the homogenisation pressure leads to milk powder with smaller particle size when rehydrated (Dv90 values: 6.08, 1.48 and 0.64 mum for 0, 20 and 80 MPa, respectively). Furthermore, the volume (%) of the particles in the ‘sub-micro’ region (smaller than 1.0 mum) presented an inversely proportional profile to the homogenisation pressure (homogenised fluid milk: 86.1, 29.3 and 2.4%; concentrated milk: 86.1, 26.5 and 5.7%, and reconstituted milk powder: 84.2, 31.8 and 10.9%). Surprisingly, this pattern was not observed in the SPAN value (which corresponds

to the width or range of the size distribution based on the volume). Additionally, the increase in the homogenisation pressure did not affect the sorption isotherm pattern.
These results published in the Journal of Dairy Research
demonstrate that increasing the homogenisation pressure decreases the particle size of the reconstituted powdered milk, indicating the potential for future studies on how this phenomenon affects its physicochemical and final product properties.
German Researchers have published in LWT - Food Science and Technology a work in which it was investigated whether the current state (roasting level) of the coffee beans during the roasting process can be detected by acoustic monitoring.
To answer this question, an experiment was carried out with a sample drum roaster (Hottop KN–8828B– 2K+) in which the
airborne sound pressure was recorded for five different roasting methods and then examined. The methods used differed in the inner temperature of the roaster when the coffee beans were inserted (75°C, 100°C, 150°C, 175°C, 200°C). The recording of the roasting processes has been made by two microphones placed in front of the drum, with each process being repeated five
ProSweets Cologne is the top address for all sweets and snacks producers, who want to organise their packaging processes more environmentally-friendly, more economically and thus more contemporarily, also to combat food waste
From hard caramels, jelly babies, chocolate and liquorice, through to pretzels, gluten-free, vegan and fat-reduced snacks - today’s sweets and snacks market is as diversified as the trends that drive it. Even beyond the most important seasonal occasions like carnival, Easter, Halloween or Christmas, the brightly packed products entice the customers to buy. A glance at the shelves in the supermarket shows: Brand names and the trade are increasingly opting for sustainable packaging, whether in the form of recyclable materials or by dispensing with plastic.
The latest innovations include cardboard packaging that completely does without glue as well as cardboard monofilm hybrid solutions, which allow the use of plastic to be reduced considerably. This is accompanied by intelligent packaging design, which leads to a smaller volume. This enables more and also lighter packaging to be stacked, stored and trans-
ported, which reduces the energy requirement for transportation and cooling.
With regards to sustainability, above all laminates are problematic, because they are heavy or

possible if the packaging can be filled without any quality loss. The packaging machine builders are offering the sweets and snacks producers innovative technologies to support them in preparing for these market conditions and in remaining competitive.
This is realised among others by pick-and-place robots, which play an increasingly more important role in the packaging lines in the course of the ongoing digitalisation and automation. They pick up the sweets and place them in trays, cartons or thermoformed trays with millimetre precision. A continually gentle handling and portioning is indispensable par-

ticularly when processing sensitive products like biscuits or crackers to protect these against mechanical stress or breakage – and thus minimise the waste. Intelligent pick-and-place technology and particularly gently operating feed modules ensure a continual synchronisation of the products even at the highest speed and thus contribute towards a reliable process. Because ultimately practically every unplanned stoppage means that the discharged products can no longer be sold. With a view to ProSweets Cologne, it becomes clear that sustainability doesn’t stop at environmentally-friendly materials.
In addition to the demonstrations at the stands, ProSweets Cologne 2025 is presenting itself as Europe’s leading content platform for the suppliers of the sweets and snacks industry. With a firstclass specialised programme on the Expert Stage and Sweet Week -Talks & Tasting Stage, it presents solutions and future-oriented examples of best practice for the current challenges of the industry, such as the rising costs for raw materials and energy, high personnel costs, a lack in skilled labour and the slow rate of digitalisation of the production processes.
Furthermore, a special highlight is the Sweets & Snacks Production Summit that is being organised for the first time and which brings production managers, CEOs and owners of the production companies exhibiting at ISM together with the supplier industry (exhibitors of ProSweets Cologne) in a targeted manner. First-class examples of best practice on the implementation of AI tools for a cost-efficient and future-proof production will be showcased here. Threeminute pitch sessions of the supplier industry by ProSweets Cologne exhibitors will also be held here followed by a matchmaking forum in the Networking Area to promote concrete solutions and business relations.
www.prosweets.com

The new EU funded ReBioCycle project provides a portfolio of bioplastic sorting and recycling technologies within three complementary wasteprocessor-centric hubs. These hubs will be established for different technologies and technology readiness levels (TRL) in the Netherlands, Italy, Spain and partly in Ireland. They will be focusing on mechanical recycling, chemical recycling, enzymatic recycling and microbial recycling.
The ReBioCycle project kickoff took place at the University College Dublin on 2-3 October 2024. European Bioplastics and its members, including TotalEnergies Corbion, AIMPLAS, Novamont, Corbion, Sulapac, and Kaneka are amongst the 20 partners that have joined forces for developing and implementing “A new European blueprint for circular bioplastics upcycling solutions”, under the lead of the University College Dublin and BiOrbic Bioeconomy SFI Research Centre.
At a demonstrative scale and in the real operational environment for the effective and efficient recycling of three types of bioplastics: PLA, PHA and Composites, the project aims to demonstrate the higher impact of obtaining the same or superior grade of recycled polymers in higher-value applications.
Jan Pels CTO and Managing Director of TORWASH, leader of the Dutch hub, indicates that currently “The current recycling technologies available for recycling biodegradable plastics are limited, but with this project we are going to make them widely available. Then nobody can claim that the switch to biodegradable plastics cannot be made, because they cannot be recycled”.
Prof. Kevin O’ Connor, coordinator of the project, expects that “ReBioCycle will scale up and demonstrate biobased biodegradable plastics recycling technologies: Biobased biodegradable plastics can be kept in the material cycle for as long as possible through innovative recycling technologies thus demonstrating that end-of-life biobased biodegradable plastics can be used in the circular bioeconomy.”
ReBioCycle will verify the industrial grade specifications by biopolymer brand owners and via demonstration of real-world products: durable and mul-
The EU Packaging & Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) sets extensive targets for the quality, properties and recyclability of packaging. Meeting these requirements presents manufacturers with challenges. Schubert supports customers with state-of-the-art packaging technology and comprehensive consulting services to find the very best packaging for every application.
Less waste and a greater circular economy – this is the objective of the European Union’s Packaging & Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR). In March 2024, the representatives of the European Parliament and member states agreed on the proposal for regulation by the Council Presidency. Formal confirmation by the EU Parliament is now required before it enters into force.
The PPWR will be applied 18 months after this date.
The directive’s extensive content covers the entire life cycle of packaging and primarily affects packaging manufacturers. The regulation includes:
• A restriction of hazardous substances
• Criteria for recycling-friendly design (Design for Recycling)
• Minimum requirements for recycled content
• Specifications for avoiding unnecessary packaging and empty space
• Targets for the gradual reduction of packaging waste
• Labelling and information obligations
• Regulations on reuse, deposit and take-back systems
Unlike EU directives, the regulation does not need to be implemented in the national legislation of member states, but applies immediately in all EU countries once it comes into force. This
gives packaging manufacturers very little time to adapt to the new requirements. In practical terms, this means that manufacturers who produce plastic packaging will have to fulfil mandatory requirements regarding the proportion of recycled material in their products in just a few years’ time. Design for Recycling requirements, on the other hand, apply to all materials. They are intended, for example, to prevent material composites from ending up unseparated in waste and not being properly recycled.
“In light of the tightening legislation across the EU, we ad-


3070 L ERGON palletizer; conveyor belts, labelling machine, encoder and control systems.
Main advantages
ECOBLOC® ERGON HEVF blowing-filling-capping system:
• compact solution for the blowing and filling of 0.6 L and 1.5 L PET containers: rinsing machine and air conveyors between the blower and the filler are not required
• reduced energy consumption
• high-efficiency rotary stretchblow moulding system equipped with motorized stretch rods, for productions up to 36,000 bottles/hour
• precise management of the stretch rod stroke and accurate control of its position, as well as significant energy saving
• preform heating module with energy-efficient IR lamps
• two-stage air recovery system, which enables to reduce energy costs
• easy management of the format changeover
• filling system with high-precision flow meters installed near each tap
• walk-in frame to easily access the filler and capper
• filling chamber completely isolated from transmissions that do not come into contact with any type of liquid
• the machine frame is inclined towards the drainage points resulting in a higher level of hygiene
wrap-around case packer:
• continuous packaging through a wrap-around system: smooth production process, without jerky movements
• ideal solution for packaging in impact-resistant 4x5 cases (0.6 bottles) and 3x4 cases (1.5 L bottles): higher protection of the product during transport
• better pack quality and reduced mechanical wear
• possibility to graphically customize the cardboard box
• extremely ergonomic machine structure
• easy and safe maintenance operations
• sliding POSYC® control panel, which allows the operator an easy and efficient use of the system
• highly intuitive, graphical interface, touch-sensitive screen and advanced real-time diagnostics and technical support.
automatic palletizing system
• single-column system with two Cartesian axes for palletizing cardboard boxes arriving from the WP 600 ERGON in 1000x1200 mm pallets
• extremely flexible modular structure, easily adaptable to the logistical conditions of the line
• ergonomic system that allows the operator to easily and safely carry out all activities related to the use, cleaning and maintenance of the system
• high operational flexibility that allows the creation of multiple palletizing patterns
• eco-sustainable solution, thanks to the use of ICOS motors equipped with integrated digital servo-drive (driver), able to simplify the wiring of the machine and ensure greater energy efficiency, lower noise and reduced wear of the components
• optimized TCO (Total Cost of Ownership) thanks to low management and maintenance costs.
(SMI Group - Via Carlo Ceresa, 10 - 24015 San Giovanni BiancoBG - Italy - Tel. +39 0345 40111
- email: info@smigroup.it - www. smigroup.it)

Commercial cheese brines are used repeatedly over extended periods, potentially for years, and can be a reservoir for salt-tolerant pathogens, such as Listeria monocytogenes. The objective of the US Researchers was to determine the inactivation of L. monocytogenes in cheese brines treated with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) (0, 50, and 100 ppm) at holding temperatures representing manufacturing conditions.
In experiment one, four fresh cheese brines were prepared with 10 or 20% salt and pH 4.6 or 5.4
(2x2 design; duplicate trials). Brines were inoculated with L. monocytogenes, treated with H2O2, and stored at 10 and 15.6°C. For experiment two, seven used commercial brines (representing five cheese types, 15-30% NaCl, pH 4.5-5.5; three seasonal trials) were inoculated with L. monocytogenes or S. aureus, treated with H2O2, and stored at 12.8°C (both L. monocytogenes and S. aureus), 7.2 and 0°C (L. monocytogenes only). Each treatment was assayed on Days 0, 1, and 7 for microbial populations and residual H2O2. Data

revealed that pathogen populations decreased <=1 log in cheese brines with no hydrogen peroxide stored for 7 days, regardless of the storage temperature. In fresh brine treated with 50 or 100 ppm of H2O2, populations of L. monocytogenes were reduced to less than the detectable limit by 7 days at 10 and 15.6°C (>4 log reduction). For unfiltered used brines, H2O2 had no effect on L. monocytogenes populations in Brick J (pH 5.4, 15% NaCl) due to rapid inactivation of H2O2, likely by indigenous yeasts (~3-log CFU/ ml). For the remaining brines, the addition of 100 ppm H2O2killed >4 log L. monocytogenes when stored at 7.2 or 12.8°C for 1 week, but only 3-4 log reduction when stored at 0°C. The addition of 50 ppm H2O2had similar lethal effects at 12.8°C but was less effective at 7.2 or 0°C. Inactivation rates of S. aureus were similar to that of L. monocytogenes
This study, published in the Journal of Food Protection, confirmed that high salt, warmer temperature, and 100-ppm H2O2 accelerated the inactivation of L. monocytogenes in cheese brines. Data also suggest that the presence of catalase-positive indigenous microorganisms may neutralize the effect of H2O2
The extraction of bioactive compounds from food wastes or by-products with natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) could be an attractive alternative to traditional hydroalcoholic extraction but needs to be optimized taking advantage of modeling. An Italian work, published in Journal of Food Process Engineering, aims to propose, develop, and discuss a new model for the extraction of phenolic compounds from spent coffee grounds (SCGs) using NADES to overcome some gaps related to the kinetic extraction models and the surface response methodology.
The model presented is based on the same assumption as the
kinetic model, but improving it to be able to predict phenolic extraction changing different process parameters (e.g., water content, time of extraction, temperature, etc.) using betaine: triethylene glycol (molar ratio 1:2). The model was validated on the extraction of total phenolic compounds from SCG as a function of water content of NADES ranging from 30 to 60% v/v. There was good agreement between experimental and simulated data and even, in some cases, better than with the second-order kinetic models. In addition, the new model needs fewer parameters to be regressed concerning the specific case investigated in this work. This model

and methodology can be the basis for further modeling applicable to other bioactives, and/or other NADES and feedstocks.
Natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES) can be a potential sustainable solvent for the valorization of food by-products as they can be used to extract bioactive compounds with high added value. This extraction process needs to be optimized depending on several factors like water content in NADES solution, solids ratio, extraction time, and temperature. The model validated in this work on spent coffee ground (SCG) could be used for this purpose, improving the gaps related to the kinetic extraction models and the surface response methodology (RSM).
The new model enables predicting the behavior of the process as a function of the parameters previously mentioned and reduces the number of experimental trials required compared with RSM. In particular, the new model was validated on the variation of water content in NADES solution. Certainly, this model will need to be further validated, but, once further studies are conducted, this model could be used for scale-up calculation and design optimization of the industrial process.
A Brazilian study aimed to evaluate the use of freezing/ thawing as a way of accelerating the aging processes of beef from Nellore animals.

Non-frozen (NF) or freezing/ thawing (FT) strip loins were aged (for 14 and 28 days) using two systems: bone-in dry-aging (DA); boneless wet-aging (WA). FT-treated samples had greater weight losses (P<0.05) during aging than NF-treated samples, especially using the DA process. However, the weight loss of the FT 14-days DA beef samples was comparable to that of NF 28-days DA. FT beef had lower fragmentation index and shear force values (P<0.05), as well as its maximum sensorial tenderness was achieved earlier (P<0.05) than the NF counterpart. With 28 days of aging, DA beef showed higher (P<0.05) tenderness and juiciness scores and lower lightness values than WA beef. The FT process decreased the reducing capacity of
meat samples, generating more metmyoglobin and lower amounts of chroma than NF. The expected volatile profile of DA beef was achieved faster in FT-treated samples, but the freezing treatments did not compromise the microbial count for either aging system. Their findings, published in Meat Science journal, indicate
that accelerated DA by the FT process could improve the palatability of Nellore beef, allowing the desired tenderness and flavor profile to be achieved in a shorter time, without increasing costs with weight losses or adversely affecting physicochemical, chemical, and microbial characteristics.
Carboxylates such as volatile fatty acids (VFA) can be produced by acidogenic fermentation (AF) of dairy wastes including cheese whey, a massive residue produced at 160.67 million m3 of which 42% are not valorized and impact the environment. In mixed-culture fermentations, selection pressures can favor AF and halt methanogenesis.
Inoculum pre-treatment was evaluated by Dutch Researchers as a selective pressure for AF demineralized cheese whey in batches. Alkaline (NaOH, pH 8.0, 6h) and thermal (90°C for 5 min, ice-bath until 23°C) pre-treatments were tested with batch operations runs at initial pH 7.0 and 9.0, food-to-microorganism (F/M) ratios of 0.5 to 4.0 g COD g-1 VS, and under pressurized (P) and nonpressurized (NP) headspace, in experiments duplicated in two different research institutes.
Acetic acid was highly produced on both Unicamp and TU
Delft samples (1.36 and 1.40 g CODAcOH L-1, respectively), at the expense of methanogenesis by combining a thermal pre-treatment of inoculum with a NP batch operation started at pH 9.0. Microbial communities comprising VFA and alcohol producers, such as Clostridium, Fonticella and Intestinimonas, and fermenters such as Longilinea

Soy protein can be an effective fat substitute in ice cream due to its contribution to viscosity and foaming ability.
In the study published in the Journal Food Hydrocolloids, Dutch researchers analyzed the individual effect of soy protein

particle size and mixture viscosity on the physical, rheological, tribological and sensory properties of fat-free ice cream. The particle size was varied by homogenization and subsequent separation of the dispersible and non-dispersible fractions. Three series of ice cream mixes were made in which (i) particle size and viscosity were varied, (ii) particle sizes were varied with a constant viscosity, and (iii) the ratio of dispersible and non-dispersible protein fractions, particle size and viscosity was varied. Results showed that dispersible protein particles (0.25 μm) led to lower hardness and greater palatability, as their presence correlated with increased overrun and reduced non-airborne thickness between air cells. In comparison,
the large non-dispersible particles (3.8-145 μm) improved the melt strength and stability of the ice cream by forming a network in the serous phase. Therefore, the size of the protein particles determined their functionality in ice cream. Based on sensory evaluation, samples with a protein particle size of about 4 μm showed a relatively denser consistency, lower melting rate, and better lubrication behavior (less friction), as well as a sensory profile similar to that of full-fat ice cream.
This study indicates that the texture and sensory properties of fat-free ice cream can be improved by manipulating the size of the plant proteins and the viscosity of the mixture.
Using lentil protein as an innovative ingredient for the production of texturized proteins (DVTs) may offer new opportunities for the production of next-generation hybrid meat products. In a Canadian paper published in the Journal of Food Science, TVPs from lentil protein isolate were produced using low-moisture extrusion cooking with different combinations of speed (SS), food moisture content (MC), and temperature profile (BT). In total, seven different combinations of processing treatments were
tested and the DVTs obtained were characterized for physical (rehydration ratio, texture profile analysis, color and mass density), techno-functional (oil and water holding capacity) and microstructural properties.
The processing conditions of higher SS and lower MC resulted in an increase in the values of several texture profile attributes (elasticity, texture, and resilience), an increase in water holding capacity (WHC), and a decrease in bulk density. Compared to raw lentil proteins, DVTs showed a higher oil-holding capacity, while WHC decreased or remained constant. Extrusion response parameters (die pressure, torque and specific mechanical energy) showed positive correlations with different physical properties (texture, WHC and total colour variation), revealing their potential as important quality indicators of TVPs.
TVPs produced at SS, MC and BT at 450 rpm, 30% and 140°C respectively showed relatively better overall physical and techno-functional quality and can be used as meat extenders in hybrid meat patties. Overall, this research highlighted the feasibility of lentil protein as a potential ingredient for the production of low-moisture products.

The objective of the US Researchers was to compare the influence of beef production systems using additive combinations of growth-promotant technologies on meat quality.
Steer calves (n = 120) were assigned to 1 of 4 treatments: 1) no technology (NT; control), 2) antibiotic treated (ANT; NT plus therapeutic antibiotics, monensin, and tylosin), 3) implant treated (IMP; ANT plus a series of three implants), and 4) beta-agonist treated (BA; IMP plus ractopamine-HCl). Muscle biopsy samples from the longissimus lumborum were extracted from a subset (n = 4 per treatment) of steers to evaluate expres-

sion of calpain-1, calpain-2, and calpastatin using real-time RTPCR. Following carcass chilling, objective color (L*, a*, and b*) was evaluated. The right strip loin was removed from each carcass, portioned into 2.54cm steaks, and designated to 7, 14, or 21 d postmortem aging periods for analysis of cook loss and Warner-Bratzler shear force (WBSF). The anterior face of each strip loin was used for analysis of crude fat and moisture. Treatment influenced ( P < 0.001) L*, a*, and b*. The NT and IMP treatments had greater ( P < 0.01) L* values, ANT was intermediate, and BA had the lowest ( P < 0.01) L* values. The NT and IMP treatments had higher ( P < 0.01) a* and b* values compared with ANT, which were higher ( P < 0.01) than BA. Steaks from implanted steers (IMP and BA) tended ( P <= 0.067) to exhibit higher a* and b* than steaks from nonimplanted steers. Cattle in the NT and ANT treatments produced steaks with increased ( P < 0.01) crude fat per-
centage compared with the IMP and BA treatments, which were similar ( P > 0.05). Percent moisture of NT steaks was lower ( P < 0.01) than all other treatments, ANT was intermediate, and IMP and BA were similar ( P > 0.05) and had the highest ( P < 0.01) moisture content. Cook loss tended to be greater ( P = 0.088) for implanted steers (IMP and BA) compared to nonimplanted steers (NT and ANT). Steaks from NT and ANT treatments were more tender ( P < 0.05) than IMP and BA, which were similar ( P > 0.05). Thus, WBSF was lower ( P < 0.001) in nonimplanted than implanted steaks. Expression of calpastatin was increased (P <= 0.025) in ANT and BA treatments, and there was a tendency for expression of calpain-2 to be increased ( P = 0.081) in ANT compared to NT.
These results, published in Translational Animal Science journal, suggest that production systems with limited use of growth promoting technology produced strip loins with more crude fat, less moisture and cook loss, and improved tenderness.
For the sustainable production of cultured meat, Japanese researchers propose a new circular cell culture (CCC) system in which microalgae are used as a source of nutrition for the culture of mammalian cells and as waste recyclers.
In the study published in Archives of Microbiology littoral Chlorococcum, RL34 hepatocytes and C2C12 myoblasts were used as cell sources for microalgae, growth factor-producing cells and muscle cells, respectively. In the first cycle, C2C12 cells were amplified 4.0-fold after 48 hours of culture in a medium conditioned
by RL34 cells. In the second cycle, C2C12 cells were cultured in the waste medium of the C. littorale culture to which nutrients derived from C. littorale were added. The proliferation rates of coastal C. and C2C12 and the nutrient extraction efficiency from coastal C. were the same in the first and second cycles. Therefore, this CCC system, which works without the addition of nutrients derived from animal grains and whrums, will help to drastically reduce the environmental burden, resource/ energy consumption and costs of future cultured meat production.
Informa Markets (world leader in the trade fair industry) and Ipack Ima S.r.l. (international benchmark for process and packaging exhibitions, a joint venture between Ucima and Fiera Milano) have publicly announced the agreement they signed a few months ago to establish a new strategic alliance. The deal aims to promote joint international initiatives and enhance cross-sell-
ing activities across their trade fair portfolios, including Informa Markets’ Propak and Fispal platforms, as well as the events organized by Ipack Ima. The agreement is intended to ensure a global presence for trade fairs centered around processing and packaging technologies, packaging materials, and to target key sectors such as the food industry – with a particular emphasis

on grain-based and liquid food products – as well as pharmaceuticals.
This agreement will allow Ipack Ima to further consolidate its global position as a reference point for the technologies it deals with, thus strengthening key markets. With Informa’s support, the presence of exhibitors from strategic markets like India and the United States will be enhanced, in addition to further consolidating its penetration in important European countries like France, Germany, Spain, the Netherlands, and Belgium, supporting Ipack-Ima’s already established sales network.
The collaboration between Informa and Ipack Ima will therefore guarantee processing and packaging businesses increased visibility on the markets in all the continents, supported by vertical skills tied to these industries. www.ipackima.com