This combination of Eastern red cedar and rhododendron on the north side of two townhomes preserves views into the meadow. Once fully grown, these plants would reduce annual heating costs by an estimated total of $79 each year. Energy savings are estimated using the US Forest Service iTree tool.
This row of Eastern red cedars on the northern side of two townhomes would block views into the meadow, but it would provide excellent protection from cold winds, reducing heating costs by an estimated $137 each year once trees reach maturity. Energy savings are estimated using the US Forest Service iTree tool.
Common Name
Latin Name
Type
Height at Maturity
Eastern redbud
Cercis canadensis
deciduous
12-25’
red mulberry
Morus rubra
deciduous
15-30’
serviceberry
Allegheny laevis
deciduous
15-25’
musclewood
Carpus carolinia
deciduous
20-35’
river birch
Betula nigra
deciduous
25-45’
tulip tree
Liriodendron tulipeferia
deciduous
60-90’
sweet gum
Liquidambar styracifula
deciduous
60-90’
red maple
Acer rubrum
deciduous
35-50’
American holly
Ilex opaca
evergreen
12-30’
Eastern red cedar
Juniperus virginiana
evergreen
15-30’
red spruce
Picea rubens
evergreen
30-60’
baslam fir
Abies balsamesa
evergreen
35-60’
mountain laurel
Kalmia latifolia
evergreen
4-10’
rhododendron
Rhododendron spp.
evergreen
5-15’
Eli Bloch and Allison Mason Spring 2020
In this rendering birch (Betula nigra) trees are aligned next to the gables and placed farther from the structures to minimize shading. This design of three birch trees would reduce summer cooling costs by an estimated $74 each year once the trees reach maturity. The cooling effect would also improve the efficiency of rooftop PV panels. Energy savings are estimated using the US Forest Service iTree tool.
Plantings for Energy Efficiency
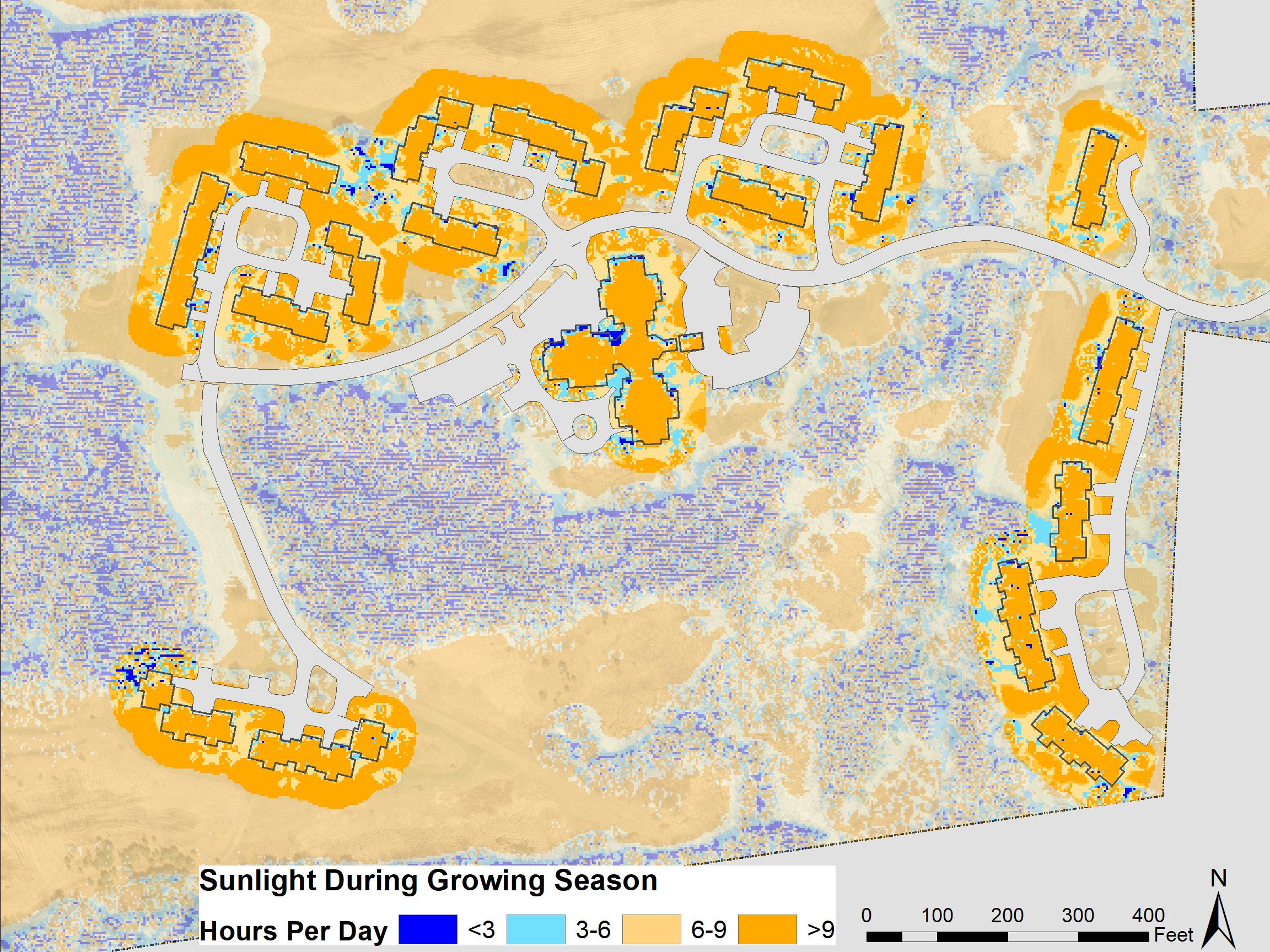
Trees can also reduce energy needs for winter heating by partially blocking cold winter winds from hitting the walls of a building, reducing the loss of thermal energy. Since winter winds in this region generally travel from the north or northwest to south or southeast, it is best to plant trees to the north or northwest of a home. Evergreen trees with a dense branching structure are most effective at protecting buildings from cold winds. When these trees are positioned to the northern side of a building, blocking solar panels is not a concern.
Northampton and Easthampton, Massachusetts
Tree planting in a way that blocks rooftop solar panels would be counterproductive. If planting next to a townhome that has or is suitable for solar panels, plant a species that grows to a maximum of 10 feet or for every foot over 10 place it an extra foot away from the home. For example a 30-foot tree could be planted 20 feet away from a structure with solar panels or a 50-foot tree planted 40 feet away. Planting to the west of structures also provides valuable cooling as it shades the home during the afternoon, and since it would not interfere with solar panels, larger species can be used.
Lathrop Retirement Community Landscape Master Plan
Trees are natural temperature regulators and can reduce the need for both winter heating and summer cooling in buildings. Trees cast shade, protecting surfaces from the sun, and cool the air around them through the process of evapotranspiration. The combination of shading and evapotranspiration leads to dramatic reductions in the need for mechanical cooling systems. Various studies have measured that suburbs with mature trees are 4 to 6 degrees Fahrenheit cooler than suburban areas without significant tree cover (EPA). This reduces the need for cooling , and creates safer conditions to be outside. Planting trees anywhere near a home will contribute some summer cooling effect; however, to get the most shade on a building it is best to plant on the southern side. Deciduous trees should always be used for this purpose because they provide cooling during the summer when it is most needed but allow sunlight through the canopy in the winter when heating is needed. Evergreen trees, if planted to the south of buildings, can actually increase winter heating needs.
DESIGN DIRECTION
THE CONWAY SCHOOL
Design Direction: Plantings for Energy Efficiency
18
Not for construction. Part of a student project and not based on a legal survey.