





Academic Authors: Jatinder Kaur, Ayushi Jain
Creative Directors: Bhavna Tripathi, Mangal Singh Rana, Satish
Book Production: Rakesh Kumar Singh
Project Lead: Jatinder Kaur
VP, Learning: Abhishek Bhatnagar
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited
First published 2025
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the above-mentioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: Hexa Computer Science Teacher Manual 1
ISBN: 978-81-985754-6-3
Published by Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address:
85, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2017PTC322986
Illustrations and images: www.shutterstock.com, www.stock.adobe.com and www.freepik.com
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, computer science has become an essential field of study, shaping the world around us in countless ways. From the smartphones in our pockets to the vast networks that connect people across the globe, computer science drives innovation and progress in nearly every aspect of modern life. In today’s fast-paced digital world, understanding the basics of computer science is as important as learning to read, write, or solve maths problems.
Recognising this imperative, the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 has strongly recommended the integration of coding skills, computational thinking, critical analysis, and problem-solving abilities into the curriculum.
Inspired by these insights, Uolo has introduced a comprehensive program, Hexa, for grades 1 to 8, to empower young minds with the knowledge and skills they need to thrive in the digital age. From the basics of how computers function to the tools that shape our digital landscape, this series opens the door to a world of endless possibilities.
We believe that learning computer science should be an engaging and accessible experience for all children. This series takes a project-based approach, allowing students to learn by way of concurrently applying acquired knowledge and skills. As they progress through the course, they will build strong foundations in computational thinking, coding basics, and digital literacy. Our program focuses on three key areas:
1. Computer Science Fundamentals: Core concepts are introduced step by step, ensuring a solid grasp of how computers function, and how information is processed and stored.
2. Latest Computer Tools: Various computer tools relevant to today’s world are included, equipping students with the confidence to thrive in the digital age.
3. Introduction to Coding: The series offers an introductory look into coding, preparing students for more advanced learning in the future.
To support teachers in delivering effective and engaging lessons, we offer a thoughtfully designed Teacher Manual to enhance the teaching and learning experience. Rather than prescribing teaching methods, the manual provides examples and demonstrates how and why teachers can apply these examples in their classes.
Each chapter in this manual is structured to provide a comprehensive lesson plan. The chapters are divided into multiple sessions, each following the Warm up, Engage, Build, and Sum up (WEBS) strategy.
• The Warm up phase sets the stage for learning by connecting to prior knowledge and building curiosity.
• The Engage phase captures the students’ attention and motivates them to participate actively.
• In the Build phase, questions from various sections are discussed to build the understanding of the students.
• Finally, the Sum up phase reinforces learning through easy-to-recall activities and questions. Time duration for each section has been suggested based on the requirements of the students. Additionally, an answer key for every chapter is provided to assist teachers in assessing their students’ understanding and guiding their learning effectively.
We hope this Teacher Manual empowers educators to implement the curriculum effectively, support diverse student learning, and create interactive, engaging environments tailored to their students’ needs and interests.
1 Fun with Computers ������������������������� 1
Natural and Human-made Things
What Are Machines?
Computers
Types of Computers
2 Know Your Computer ��������������������� 10
What Computers Do
Places Where Computers Are Used
Main Parts of a Computer
Devices
3 Operating a Computer ������������������ 18
Starting a Computer
Shutting Down a Computer
Rules for Using Computers
4 Playing with Mouse ������������������������ 24
Computer Mouse and Its Parts and Uses
Holding and Using a Computer Mouse
5 Let Us Type!�������������������������������������� 29
Keyboard, Alphabet Keys and Number Keys
Special Keys
6 Getting Started with Paint ������������ 34
Introduction to Paint
Drawing in Paint
Colouring in Paint and Saving a Drawing
7 Fun with Coding ������������������������������ 41
What Is Coding?
Block-based Coding
Problem Solving: Example 1
Problem Solving: Example 2
8 A Tour to Code�org �������������������������� 49
Exploring Code.org
Puzzles 1 and 2
Puzzles 3 and 4
Coding Challenge
9 Following Commands and Sequences ���������������������������������������� 57
Command 1
Command 2
Sequence 1
Sequence 2
Coding Challenge

This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Natural and Human-made Things
2. What Are Machines?
3. Computers
4. Types of Computers
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe natural things.
● describe human-made things.
Keywords
● Natural Things: Some things like trees, animals, mountains, and rivers are present in nature. These are called natural things.
● Human-made Things: Humans make things like buildings, cars, and umbrella. These are called human-made things.
Ask the students about different things around them.
Discuss a few examples of things such as buildings, cars, trees, etc., and then describe them as natural and human-made things.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students about different things around them.
● Now, build the concept by asking the students if they know whether these things are created by humans or nature. Then introduce them to natural and human-made things.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
15 mins
Describe natural things. Tell the students that things present in nature like trees, animals, mountains, and rivers are called natural things as given on page 1.
Describe human-made things.
Tell the students that things made by humans are called human-made things as given on page 1.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 1A Question 1 section and encourage students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:

Build
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic “What is the difference between natural and man-made objects?” as mentioned in the Discuss section on page 1.
Correct Response: Some things are present in nature like trees, animals, mountains, and rivers. These are called natural things.
Some things are made by humans like buildings, cars, and umbrella. These are called human-made things.
3 mins
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that things that are present in nature like trees, animals, mountains, and rivers are called natural things and things made by humans such as buildings, cars, umbrella, etc., are called human-made things.

● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in classroom.
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 1
C. Who Am I?: Question 1
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 4
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 1
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe machines.
Keyword
● Machines: Machines are human-made things that help us do different kinds of work.
Ask the students about the machines they have seen at home such as washing machine, refrigerator, microwave.
Tell them what machines are. Group discussion Conclude the concepts 5 mins 15 mins 7 mins 3 mins
5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students about the machines they have seen at home such as washing machine, refrigerator, microwave, etc. Then tell what functions some of these machines perform. For example, a washing machine helps us wash our clothes.
15 mins
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Explanation
Describe machines. Tell the students what a machine is. Also, tell them that some machines need electricity, some need fuel and some need human power to run, as given on page 2.
Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding.
● Name three machines you see every day around you.
Possible Responses: Car, mobile, rickshaw

● Categorise the given machines on the basis of whether they require electricity, fuel or human power to run: Aeroplane, cycle, television.
Correct Responses:
Aeroplane: Fuel
Cycle: Human power
Television: Electricity
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic ‘My Favourite Machine’.
Possible Responses: Calculator, mobile, refrigerator
● Conclude the session by summarising that machines are human-made things that help us do different kinds of work. Machines run on electricity, fuel, and human power.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 1
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 2
C. Who Am I?: Question 2
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 2
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1 and 3
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe a computer and do things using a computer.
● describe how are computers different from us.
Keyword
Ask the students to name some machines that run on electricity. Explain to the students what a computer is. Tell them things we can do using a computer. Also, tell them how are computers different from us.
● Computer: A computer is a machine. It needs electricity to work. 5 mins Warm
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts
● Ask students to name some machines that run on electricity. Now, build the concept by discussing computer is also a machine that runs on electricity.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Describe a computer and what things can be done using a computer.
Describe how are computers different from us.
Explanation
Tell the students that a computer is a machine that needs electricity to work. Also, tell them computers are used to learn new things, listen to music, etc., as given on page 3.
Tell them that a computer is a smart machine that works very fast, never gets tired, etc., as discussed on page 4.

● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 1A Question 2 section and encourage students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses: 2. a. F b. T c. T Build 7
● Ask the students to answer the question “What can be other things you can do using a computer?” asked in the Think and Tell section given on page 3.
Possible Responses: see our pictures, watch cartoons, make drawing, etc. Sum
● Conclude the session by summarising that a computer is a machine that needs electricity to work. Computers are used to learn new things, listen to music, etc. Also revise with them that a computer is a smart machine that works very fast, never gets tired, does not make any mistakes, and can store pictures, letters, and videos.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 2 and 3
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 3
C. Who Am I?: Question 3
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 3
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe different types of computers.
Ask the students where they have seen computers. Describe different types of computers.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
● Ask the students where they have seen the computers.
● Now, build the concept of types of computers by asking students if they know that a smartphone is also a type of computer.
● Also tell them that a desktop, laptop, tablet, and a smartphone are different types of computers.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Explanation
Describe different types of computers. Tell the students that there are many different types of computers such as desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. Also, tell them about the features of each of these types of computers, as given on page 5.

● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 1B section and encourage students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their book. Correct Responses:
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic “Can computers be smaller than smartphones?” as mentioned in the Discuss section on page 5.
Yes/No
● Conclude the session by summarising that there are many different types of computers such as desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 4
C. Who Am I?: Question 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1, 2, and 3
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 4
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 2
This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. What Computers Do
2. Places Where Computers Are Used
3. Main Parts of a Computer
4. Devices
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe about the activities we can do on a computer.
Ask the students what a computer is.
Ask them to name a few things that they keep in their school bag.
Describe to them what activities we can do on a computer.
Action Plan
Warm Up
● Ask the students what a computer is.
● Ask them to name a few things that they keep in their school bag.
● Tell them as we do different kinds of work with each item in our school bag like books, bottles, pencils, and crayons. In the same way, a computer also has many things in it that lets us do different activities.

Explain the following concepts:
Describe about the activities we can do on a computer.
Describe to the students that we can draw and colour, learn new things, play games, etc., on a computer, as given on page 9.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 2A Question 1 section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses: 1. a. T b. F c. T
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic “What are some of the new things you wish to learn on a computer?” provided in the Discuss section, as mentioned on page 9.
Possible Responses: Learn block-based coding, touch typing, etc. Sum Up 3
● Conclude the session by summarising that we can use a computer to do different activities such as learn new things, draw and colour, listen to music, send messages, watch videos, etc.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1 and 2
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 2
E. Answer the following questions: Question 1
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
Ask the student to name the places where they have seen computers.
● describe the uses of computers at different places. 5
Warm Up
Describe uses of computers at different places.
Group Discussion Conclude the concepts
● Ask the students to name the places where they have seen computers.
● Tell them that computers are used at various places, such as offices, schools, shops, airports, etc.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Describe the uses of computers at different places.
Explanation
Describe to the students that we go to different places like restaurants, shopping malls, and airports. People use computers at all these places for different kinds of work, such as at airports to check flight information, schools to teach, etc., as given on page 10.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 2A Question 2 section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.

Correct Responses:
2. a. To teach and learn.
b. To book tickets.
c. To play on the field.



● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic ‘Use of Computers at Home’. Possible Responses: Talk to friends and family, play games, watch cartoons, etc. Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that computers can be used at airports and railway stations to check flights and train information, offices to do important work and send messages, hospitals to keep information of the patients, etc.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 1
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1 and 2
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 3
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1 and 2
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe the four main parts of a computer: monitor, CPU, keyboard, and mouse.
Keywords
● Monitor: A monitor looks like a TV screen. It shows us what we are doing on a computer.
● CPU (Central Processing Unit): It is like the brain of a computer.
● Keyboard: A keyboard helps us write on a computer.
● Mouse: A mouse allows us point to and select different things on the monitor.
• Ask the students the names of different parts of the body.
• Ask the students how they write in their notebooks.
• Ask the students how they point to some words in their book.
• Relate our body parts to the computer’s parts and tell them about the monitor and the CPU.
• Tell the students that with the help of the keyboard we can write on a computer.
• Tell the students that on a computer, we point to a line or word with the help of a mouse. Group
Warm Up
● Ask the students the names of different parts of the body. Relate our body parts to the computer’s parts and tell them about the monitor and the CPU.
● Ask the students how they write in their notebooks.
● Ask the students how they point to some words in their book.
● Now, explain to them about the keyboard and the mouse.

Explain the following concepts:
Describe four main parts of a computer: monitor, CPU, keyboard, and mouse.
Describe to the students that the monitor looks like a TV screen. It shows us what we are doing on a computer, and the CPU is like the brain of a computer. Also tell them that the keyboard helps us write on a computer and the mouse allows us point to and select different things on the monitor, as given on pages 11 and 12.
Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 2B section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Response:

● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic ‘Have you seen a monitor before?’.
Correct Response: Yes. I have seen a monitor at home. I watch cartoons on it.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that the monitor, CPU, keyboard, and mouse are the four important parts of a computer. The monitor looks like a TV screen, and the CPU is the brain of a computer. The keyboard helps us write on a computer and the mouse allows us point to and select different things on the monitor.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to complete in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 4
C. Who Am I?: Questions 3 and 4
F. Apply your Learning: Question 4
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe the input devices.
● describe the output devices.
● describe the storage devices.
Keywords
● Input Devices: These devices help us tell the computer what to do.
● Output Devices: These devices help the computer to share information with us by displaying the final output.
● Storage Devices: These devices help the computer store information.
• Ask the students what a keyboard is.
• Ask the students where they store their clothes and books.
• Explain to them that a keyboard is an input device. Then explain to them the input and output devices by giving examples of each.
• Describe to the students that storage devices are like their wardrobe where they keep their toys, clothes, and books.
5 mins
● Ask them what a keyboard is and then build the concept by defining the input and output devices.
● Ask the students where they store their clothes and books. Describe to the students that storage devices are like their wardrobe where they keep their toys, clothes, and books.

Explain the following concepts:
Describe the input devices.
Describe the output devices.
Describe the storage devices of computers.
Explain to the students that input devices help us to tell the computer what we want to do. The keyboard and mouse are input devices, as given on page 13.
Explain to the students that output devices help the computer share information with us by displaying the final output. Monitor, speaker, and printer are output devices, as given on page 13.
Describe to the students that a computer stores information on storage devices. A compact disc, pen drive, hard disk, and memory card are some examples of storage devices, as given on pages 13 and 14.
● Read aloud the question provided in the Do It Yourself 2C section. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:



● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic ‘Give examples of input and output devices’.
Correct Responses: Input: Keyboard, mouse
Output: Monitor, speaker
● Conclude the session by summarising that the keyboard and mouse are input devices, whereas the monitor, printer, and speaker are output devices.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to complete in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 3
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 2
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1 and 4
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 2
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 3
This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Starting a Computer
2. Shutting Down a Computer
3. Rules for Using Computers
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● start a computer.
Ask the students if they know how to turn on the television at their homes.
Explain to the students the steps to start a computer. Think and Tell Conclude the concepts
● Ask the students if they know how to turn on the television at their homes.
● Now tell them that they can start the computers by following certain steps.

Explain the following concepts:
Start a Computer. Explain to the students that there are four steps needed to start a computer: Switching on the main power switch
Pressing the ON button on the CPU
Pressing the Power button on the monitor, and waiting till the Windows screen appears, as given on page 17.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 3A section. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
1. T 2. T
● Ask the students to give the answer to the question “What will happen if we just switch on the main power and then turn on the monitor? Will the computer start?” asked in the Think and Tell section, as given on page 17.
Correct Response: No, the computer will not start. We also need to switch on the CPU to start the computer.
Sum Up 3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that to start a computer, we need to switch on the main power switch, then press the ON button of the CPU and finally, press the ON button of the monitor.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1, 2 and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 1
C. Who Am I?: Question 1
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 5
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 1
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 4
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● shut down a computer.
Keyword
● Shut down: To shut down a computer means to turn it off.
Ask the students if they keep the television on for the whole day or they switch it off after watching it for some time.
Explain to the students how to shut down a computer. Also, explain to them why they should not turn off the computer directly.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Action Plan
Warm Up
● Ask the students if they keep the television on for the whole day or if they switch it off after watching it for some time.
● Now, tell them that they should shut down the computer when it is not in use.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Explanation
Shut down a computer. Describe the steps of shutting down a computer: clicking on the Start menu, clicking on the Power icon, and clicking on the Shut down option, as given on page 18. Also, explain to the students if they turn off the computer directly, then it may get damaged.

● Read aloud the question provided in the Do It Yourself 3B Question 2 section. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Response: 2. F
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic ‘Should we leave the computer on forever?’
Possible Responses: Yes/No
Correct Response: No, we should not leave the computer on forever. We should shut it down when it is not in use. Sum Up 3
● Conclude the session by summarising that we should shut down a computer properly and always use the mentioned steps to shut down a computer.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 3
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 2
C. Who Am I?: Question 3
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1 and 4
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 2
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 1
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● follow the do’s while using a computer.
● learn what not to do while using a computer.
Keywords
● Do’s: Do’s are the things we must do.
Warm Up
Ask the students if they follow some rules while playing in the playground.
Then tell them that while using a computer, they must follow some do’s and don’ts.
● Don’ts: Don’ts are the things we must never do. 5 mins
Warm Up
Engage Build Sum Up
Explain to the students the various do’s and don’ts one must follow while using a computer.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Action Plan
● Ask the students if they follow some rules while playing in the playground.
● Then tell them that while using a computer, they must follow some do’s and don’ts.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Follow the do’s while using a computer.
Learn what not to do while using a computer.
Explanation
Describe some do’s that must be followed while using a computer, such as keeping the computer clean and pressing the keyboard keys gently, etc., as given on page 19.
Describe some don’ts that must be followed while using a computer, such as not to switch off the CPU directly, not to touch the computer devices with wet and dirty hands, and not to pull the wires from the computer, etc., as given on page 19.

● Read aloud questions 1, 3 and 4 provided in the Do It Yourself 3B section. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
1. F 3. T 4. T
Build
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic ‘Is it necessary to follow rules to operate computers?’.
Correct Response: Yes, it is necessary to follow the rules to operate computers, as they function properly when we take good care of them.
3 mins
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that we should follow some do’s while using a computer, such as keeping the computer clean and pressing the keyboard keys gently, etc. We should also follow some don’ts while using a computer, such as not to switch off the CPU directly, not to touch the computer devices with wet and dirty hands, and not to pull the wires from the computer, etc.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 4
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 3
C. Who Am I?: Questions 2 and 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 2 and 3
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 3 and 4
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 2 and 3
This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Computer Mouse and Its Parts and Uses
2. Holding and Using a Computer Mouse
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe a computer mouse and a mouse pointer.
● identify parts of a computer mouse.
● describe the uses of a computer mouse.
Keywords
● Mouse: A computer mouse is a pointing device that is used to point at and select things on the computer screen.
● Mouse Pointer: It is a small arrow that appears on your computer screen.
Ask the students if they have ever tried pointing to the words using their fingers or a pencil while reading books.
Explain to the students what a computer mouse and a mouse pointer is. Also explain to them the parts and uses of a computer mouse.
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts

Warm Up
● Ask the students if they have ever tried pointing to the words using their fingers or a pencil while reading books. This helps to avoid getting lost in the words.
● In the same way, we use the computer mouse to point on the screen. 15 mins
Explain the following concepts:
Describe a computer mouse and a mouse pointer.
Identify parts of a computer mouse.
Describe the uses of a computer mouse.
Tell the students that a computer mouse is a pointing device that is used to point at and select things on the computer screen. Also, tell them about the mouse pointer, as given on page 23.
Explain to the students the parts of a computer mouse, namely, the left mouse button, the scroll wheel, and the right mouse button, as given on pages 23 and 24. Also explain the difference between wired and wireless mouse.
Tell the students that a mouse can be used to point and select, draw and colour, play games, open a file, etc., as given on page 25.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 4A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Responses:
mins
● Ask the students to give the answer to the question “Which type of mouse would you like to use— wired or wireless? Why?” asked in the Think and Tell section given on page 24.
Possible Response: Nowadays, we use mouse that have no wire, as they give us freedom of movement.
3 mins
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that a computer mouse is a pointing device that is used to point at and select things on the computer screen. A mouse pointer is a small arrow that appears on your computer screen. Parts of a computer mouse are the left mouse button, the scroll wheel, and the right mouse button. A mouse can be used to point and select, draw and colour, play games, open a file, etc.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 2 and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 3, 4, and 5
C. Who Am I?: Question 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1, 2, 3 and 5
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 1, 2, and 3

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● hold a mouse and use the mouse buttons.
Keyword
● Scroll Wheel: The scroll wheel helps you move up and down on the screen.
Ask the students if they have ever played games using a computer mouse. Also, ask them how they use the mouse to play games.
Explain to the students how to hold a mouse and use the mouse buttons. Group discussion
Conclude the concepts
● Ask the students if they have ever played games using a computer mouse. Also, ask them how they use the mouse to play games.
● Tell them that a mouse is held using different fingers and used by clicking its two buttons or using the scroll wheel.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Hold a mouse and use the mouse buttons.
Explanation
Tell the students that one must hold the left mouse button and the right mouse button with the index finger and the middle finger, respectively, as given on pages 47 and 48. Also, tell them what a left mouse button, a right mouse button, and a scroll wheel do, as given on pages 25 and 26.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 4B section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
1.

2. a. Right mouse button
b. Scroll wheel
c. Left mouse button
Build
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic ‘Uses of a Computer Mouse’. Possible Responses: A mouse helps us do many things: point and select, draw and colour, play games, open a file, etc.
3 mins
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that we put the index finger on the left mouse button and the middle finger on the right mouse button. The left mouse button opens the file, and the right mouse button pops up a list of items. The scroll wheel helps you move up and down on the screen.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1, 3, and 4
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1 and 2
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 4
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 4 and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5

This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Keyboard, Alphabet Keys and Number Keys
2. Special Keys
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe a keyboard.
● describe what the alphabet keys are.
● describe what the number keys are.
Keywords
● Keyboard: It is a part of the computer that helps us write on it.
● Typing: Writing on the computer using a keyboard is called typing.
● Cursor: The blinking line on the computer screen is called a cursor.
Ask the students how we can write on a computer. Explain to the students what a keyboard is. Also explain to them about alphabet keys and number keys.
Think and Tell Group discussion
Conclude the concepts
5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students how we can write on a computer.
● Tell them that just as we write on paper with a pencil, we can write on the computer using its part called the keyboard.
15 mins
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Describe a keyboard.
Describe what the alphabet keys are.
Describe what the number keys are.
Explanation
Tell the students that a keyboard is a part of the computer that helps us write on it. Tell them about typing and the cursor as well, as given on page 31.
Tell the students that for each letter of the alphabet, we have one key on the keyboard. These keys are called alphabet keys, as given on page 32.
Tell them that we can use the number keys to type numbers on the computer, as given on page 33.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 5A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.

Build
7 mins
● Ask the students to give the answer to the question “Which keys will you use to type your name?” asked in the Think and Tell section, as given on page 32.
Possible Response: Alphabet Keys/Number Keys
Correct Response: Alphabet Keys
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic “Which number keys will you use to type your age?”, as mentioned in the Discuss section on page 33.
Possible Responses: 5 or 6.

● Conclude the session by summarising that a keyboard is a part of the computer that helps us write on it. Writing on the computer using a keyboard is called typing. The alphabet keys are used to type words and sentences on a computer. We can type numbers using the number keys.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 3 and 5
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1 and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 4
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 1 and 3
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1 and 2
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
Warm Up Engage Build Sum Up
Ask the students if they know, while typing on the computer, which key helps them to move up, down, left, and right across various words.
Ask the students how they erase what they write on paper.
● describe what special keys are. 5 mins
Explain to the students what special keys are.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
● Ask the students if they know that while typing on the computer, which key helps them to move up, down, left, and right across various words, sentences, etc.
● Tell them that the up arrow key helps them move the cursor up, the left arrow key helps to move the cursor left, and similarly for the other keys.
● Ask how they erase what they write on paper.
● Tell them that similar to how they write on paper, they can erase text using the Backspace or the Delete key on the keyboard.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Explanation
Describe what special keys are. Tell the students about special keys such as the Spacebar, Enter, Backspace, Delete, and Arrow keys, as given on pages 34 and 35.

● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 5B section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.

Build
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic ‘Use of Backspace Key’. Correct Response: The backspace key helps us to erase mistakes while typing.
3 mins
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that the Spacebar, Enter, Backspace, Delete, and Arrow keys are some special keys on the keyboard.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1, 2, and 4
B. Identify the Keys Correctly: Question 1
C. Who Am I?: Questions 2, 3, and 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1, 2, and 3
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 2, 4, and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 3 and 4
This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Introduction to Paint
2. Drawing in Paint
3. Colouring in Paint and Saving a Drawing
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe what Paint is.
● start Paint.
● explain the different parts of the Paint window.
Keyword
● MS Paint: MS Paint or simply Paint lets us draw and colour on the computer.
Ask the students to draw their favourite fruit on a paper using a pencil.
Discuss what MS Paint is. Explain to them how they can start Paint. Also, get them familiar with the different parts of the Paint window.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts

5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students to draw their favourite fruit on a paper using a pencil.
● Now, build the concept by telling the students that we can draw on a computer as well, using MS Paint.
15 mins
Explain the following concepts:
Describe what MS Paint is. Tell the students that as we draw on paper using pencil and colours, we can also draw on the computer, as given on page 39.
Start Paint. Explain the steps to start MS Paint to the students, as given on page 39.
Explain the different parts of the Paint window.
Tell the students about different parts of the MS Paint window, such as the title bar, drawing area, tools, etc., as given on page 40.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 6A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
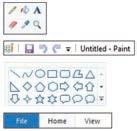
Ask the students the following questions to check their understanding:
● Name the space where you draw in MS Paint.
Correct Response: Drawing area
● Which bar shows the name of your MS Paint file?
Correct Response: Title bar
Build
Tabs
Title bar Shapes
Tools
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic ‘My Favourite Drawing in MS Paint’.
Possible Responses: Hut, robot, etc.
● Conclude the session by summarising that MS Paint lets us draw and colour on the computer. To start MS Paint, click on the Search bar, type “Paint” in it, and click on Paint in the menu. In MS Paint, you’ll see the title bar at the top, tabs like File, Home and View, different tools, different shapes, color options, and the drawing area where you can draw and colour.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 1
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1 and 3
C. Who Am I?: Question 1
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 1

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● draw an oval.
● draw a triangle.
Ask the students to give examples of some objects that are oval in shape. Discuss how to draw an oval and a triangle using the Shapes tool.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
● Ask the students to give examples of some objects that are oval in shape. Then, build on the concept by explaining how they can draw shapes using Paint.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Draw an oval. Tell the students the various steps to draw an oval, as given on page 41.
Draw a triangle. Tell the students the various steps to draw a triangle, as given on page 41.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 6B section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book. Possible Responses: Oval, Rectangle, Square, Triangle, etc.
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic, “Which is your favourite shape? Which shapes do you want to draw in Paint?” provided in the Discuss section, as mentioned on page 41.
Possible Responses: Triangle, star, diamond, etc.
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising the steps to draw an oval and a triangle in Paint.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 2
C. Who Am I?: Questions 2 and 3
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 2
3 mins

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● colour a drawing.
● save a drawing.
Ask the students if they would like to colour in the drawings they have created. Ask the students how they can see the same drawing again some days later.
Describe the steps to colour and save a drawing.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
● Ask the students if they would like to add colour to the drawings they have created. Tell them that they can make their drawings colourful by using the Fill with color tool.
● Ask the students how they can see the same drawing again some days later. Tell them that they can do so by saving their files.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Explanation
Colour a drawing. Tell the students the steps to colour a drawing, as given on page 42.
Save a drawing.
Tell the students the importance of saving a drawing and then tell them the steps to save a drawing, as given on page 43.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 6C and Do It Yourself 6D sections and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
Do It Yourself 6C: Draw a diamond shape and colour using your favourite colour. Do It Yourself 6D: 1. T 2. T
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic, “By what name should we save our drawing?”.
Possible Responses: Our name, favourite animal, superhero, etc.
Correct Response: We should give the file a name that reflects the content of the drawing. Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that saving a file helps us open our drawing again on Paint. Also, revise with them the steps to colour and save a drawing.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 3 and 4
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 2
C. Who Am I?: Question 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 3 and 4
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 1 and 2
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 1

This chapter is divided into the following sessions
What Is Coding?
Block-based Coding
Problem Solving: Example 2
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe what coding is.
Keywords
● Instruction: An instruction means telling someone what to do.
● Coding: Coding is a language used to give instructions to a computer.
Ask the students whether they like to solve the puzzles. Explain to the students what coding is.
● Ask the students if they like solving puzzles. Tell them, just like solving a puzzle, coding is putting the right instructions in the right order to tell the computer what to do. Then, connect this concept to define coding.
Explain the following concepts:
Describe what coding is. Tell the students that a computer does not understand human languages. That is why we need to learn coding to give instructions to a computer. Also ask the students to solve the puzzle to complete the image of a dog, as given on page 46.
Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding.
● Computers are smart, but they need instructions. Can you talk to a computer in any language? Do you think it will listen to you?
Possible Responses: Yes/No
Explanation: No. The computer does not understand all the languages. It will only understand our instructions if we use a language that the computer understands.
● How would learning coding help us?
Possible Response: Learning coding will help us to understand problems, think of solutions, make a computer do a task, and solve a question in many ways.
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic, ”How can you solve any puzzle?”.
Possible Responses: Sort by colour, trial and error method, looking at the solved picture, etc.
● Conclude the session by summarising that a computer does not understand human language. So, we use coding to give instructions to a computer.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 3
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1 and 2
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 2

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● explain block-based coding.
Keyword
Ask the students if they have ever played with Lego or physical colourful blocks.
Explain to the students what block-based coding is. Attempt the given activity Conclude the concepts
● Block-based coding: The coding language that uses blocks to give instructions is called block-based coding. 5 mins
Warm Up
Ask the students if they have ever played with Lego or physical colourful blocks.
Explain to them that, just like connecting the Lego blocks with each other, we need to arrange the blocks in a sequence in block-based coding. 15 mins
Engage
Explain the following concept:
Learning Outcome Explanation
Explain block-based coding. Tell the students that block-based coding is a coding language that uses blocks to give instructions, as given on page 47.
● Consider that you are playing with Lego. What will you need to play?
Possible Responses: Blocks, boxes, shapes
Correct Response: Blocks
● How will you make the shape of “number 1” with blocks?
Possible Response: I will join 1 block above the other until the desired shape is created. Build
Cut out one triangle and three rectangles of different sizes using colourful papers.
7 mins
● Present the scenario: Consider these shapes as blocks. Now, build a house using these shapes.
1. Allow some time for the kids to do this activity.
2. Now, similarly ask the students to make a tree using rectangle and oval shape cutouts. Make a sun using oval shape cutout using colourful papers.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that in block-based coding, we join blocks just like Lego.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 2
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 3
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 3

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● solve the given problem.
Keyword
● Problem: A problem is something that we need to solve.
Give some puzzle pieces to the students to solve and ask them how they have solved them.
Discuss the given problem. Group discussion Conclude the concepts
● Give some puzzle pieces to the students to solve, and ask them how they have solved them. Then, relate them to the concept of problem solving.
Note: The teacher can ask the students to bring any puzzle pieces/paper cutouts from home for this activity.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Explanation
Solve the given problem. Explain to the students the problem of ‘Finding Your Friend’s House’ given on page number 47 and give them hints on how to solve it.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 7A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.

Build
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic ‘What are the different ways to solve a problem?’.
Possible Responses: Breaking down a problem into small steps, identifying the pattern, etc.
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that a problem is something that we need to solve.
3 mins
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 1
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 1
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 1

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● solve a given problem.
Keyword
● Problem: A problem is something that we need to solve.
Ask the students the steps to make a sandwich. Discuss the given example. Attempt the given activity Conclude the concepts 5 mins 15 mins 7 mins 3 mins
● Ask the students what steps they follow to make a sandwich.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Explanation
Solve a given problem. Discuss the given example with the students to make a sandwich, as given on page 48.
1. What to do when you can’t find your things?’.
Possible Response: Ask my mom or dad for help, look in all the places where I usually play, wait for some time, and look again later.
● Complete the grid:

Note: The teacher can draw this pattern on the board and ask the students to solve it. Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that a problem is something that we need to solve.
3 mins
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 2
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1 to 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1 to 5

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe what Code.org is.
● describe parts of the Puzzle Code Studio.
Keywords
● Code.org: Code.org is an educational platform to learn coding in a fun and engaging way.
● Play Area: The play area is where the program will run. It is on the left side of the screen.
● Toolbox: The toolbox is the area that holds all the blocks needed to solve the puzzles.
● Workspace: The workspace is the area where we drag the blocks from the toolbox to code.
● Instruction Area: The instruction area holds the instructions to solve a puzzle.
● Jigsaw puzzle: A jigsaw puzzle is like a game where you put pieces together to make a picture.
Ask the students whether they like to solve puzzles.
Explain to the students what Code.org is.
Explain the parts of the Puzzle Code Studio. Group
Conclude the concepts
5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students if they like to solve puzzles. Then, tell them that they can solve coding puzzles on the computer by using Code.org.
Explain the following concepts:
Describe Code.org. Tell the students that we can solve and practice various puzzles using the Code.org platform. Also, tell them that Code.org is an educational platform to learn coding in a fun and engaging way, as given on page 55.
Describe parts of the Puzzle Code Studio. Explain the various parts of the Puzzle Code Studio interface, such as the play area, toolbox, workspace, and instruction area, as given on pages 55 and 56.
Describe jigsaw puzzle. Tell students that a jigsaw puzzle is like a game where you put pieces together to make a picture, as given on page 57.
Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding:
● How would learning about Code.org platform help us?
Correct Response: Learning about Code.org platform will help us to solve puzzles easily.
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic ‘What is the purpose of the workspace?’.
Correct Response: The workspace is the area where we drag the blocks from the toolbox to code.
● Conclude the session by summarising that Code.org is an educational platform to learn coding in a fun and engaging way. Also, mention the different parts of the Puzzle Code Studio, such as play area, toolbox, workspace, and instruction area.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 4
C. Who am I?: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1, 2, and 3
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 1 and 2

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
Ask the students what games they play at home. Discuss the given puzzle problem. Attempt the given activity
Conclude the concepts
● solve the given puzzle. 5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students what games they play at home.
● Build the concept by telling them solving a puzzle is just like a jigsaw puzzle game.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Solve the given puzzles. Tell the students that they need to drag and drop the partial block picture to complete the puzzle picture. Demonstrate the steps to solve the two puzzles, as given on pages 57 to 59.
Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding:
● What will you do to move the puzzle block?
Possible Responses: Drag and drop.
● Where do we need to put the puzzle block?
Possible Responses: On the shaded region.
● Rishi finds difficulty in solving puzzles. Let’s help him to complete his school assignment by solving the puzzle.

Correct Output:

Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that we need to drag and drop the puzzle blocks to complete the puzzle.
● Assign the following question from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 1

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
Ask the students whether they have solved puzzles given in the newspapers, books, etc.
● solve a puzzle. 5
Describe what a puzzle is. Explain how to solve a puzzle. Attempt the given activity Conclude the concepts
● Ask the students whether they have solved puzzles given in the newspapers, books, etc. Then, relate the concept to solving puzzles in Code.org.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Explanation
Solve a puzzle. Explain to the students that to solve a puzzle, we need to observe it first and then place the missing parts by dragging and joining them together, as given on pages 60 to 62.
Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding:
● What is one word for joining pieces together to complete a picture?
Possible Response: Puzzle
● How do you check whether a puzzle is completed?
Possible Responses: When the puzzle is completed, a sound will be played.
● Complete the picture using the picture blocks.

Correct Output:

● Conclude the session by summarising that a puzzle can be solved by observing it and then placing the pieces together to complete the puzzle.
● Assign the following question from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 2

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● solve the given coding challenge.
Ask the students what jigsaw puzzles are.
Discuss the given puzzle problem. Attempt the given activity Conclude the concepts
Warm Up
● Ask the students what jigsaw puzzles are.
● Encourage students to understand the picture given in the coding challenge.
Explain the following concept:
Learning Outcome
5 mins
Explanation
Solve the coding challenge. Demonstrate to the students how to solve the given coding challenge, as given on page 62. Then, ask the students to solve it.
Ask the following question to the students to check their understanding:
● Can we rearrange the blocks while placing them to complete the puzzle?
Possible Responses: Yes/No
Correct Response: Yes, we can rearrange the blocks in a puzzle to complete it.
● Find 8 differences.
Correct Output:
3 mins
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that we need to drag and drop the puzzle blocks to complete the given coding challenge.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1 and 2

Command 2
Sequence 1
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe a command.
● describe various types of command blocks.
Keyword
● Command: Command is the instruction given to a computer to do something.
Instruct the students to touch their eyes, nose, and ears. Play this game and the one who touches correctly will be the winner.
Describe a command.
Describe the various types of command blocks.
Action Plan
Warm Up
● Play a game of instructions where you ask the students to touch their nose, eyes, and ears, and the one who touches correctly will be the winner. Now, relate this concept of giving commands to the students to the commands concept in the computer.
Explain the following concepts:
Describe a command. Tell the students that instructions which we give to a computer to do something are called commands, as given on page 67.
Describe various types of command blocks. Explain the purpose of various types of command blocks, such as east, west, north, and south, as given on page 67.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 9A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Response: Option a
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic ‘Why do we use command blocks?’
Correct Response: We use command blocks to give instructions to the computer.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that instructions given to a computer to do something are known as commands and we have four types of command blocks, such as east, west, north and south.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 1
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 3
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 1

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● solve angry-bird puzzles.
Keywords
● Run button: The Run button allows you to run the code in the workspace.
● Reset button: The Reset button allows you to reset the workspace.
Ask the students if they know what Angry Bird looks like. Discuss the given angry bird puzzle. Attempt the given activity Conclude the concepts
● Ask the students if they know what Angry Bird looks like.
● Now, build the concept by explaining to them the given Angry Birds puzzle.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Explanation
Solve angry-bird puzzles. Describe the activity as given on pages 67 and 68 to the students and demonstrate how to arrange the command blocks to solve the puzzle. Also, explain the purpose of the Run and Reset buttons.
● Ask the following additional questions to check for understanding.
1. The button allows you to run the code in your workspace.
2. button allows you to reset the workspace.
Possible responses: 1. Run 2. Reset
● Solve the following puzzle to make the angry bird move towards the pig.
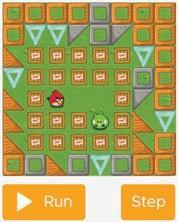
Correct Output:

Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that we use different command blocks to solve the given angry bird puzzle. Also, revise that the Run button is used to run the code and the Reset button is used to reset the workspace, respectively.

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe a sequence.
● describe the types of sequence.
Keywords
● Sequence: When we give more than one command in order, it is called a Sequence.
● Fixed Sequence: In a fixed sequence, there is only one way to do the task.
● Flexible Sequence: In a flexible sequence, there can be more than one way to do the task.
Discuss with the students the process of growing a plant.
Describe a sequence. Describe the types of sequence. Attempt the given activity
Conclude the concepts
Warm Up
● Discuss with the students the process of growing a plant.
● Tell them that to grow a plant, we need to dig the soil, insert a seed, water the seed, make sure to place it in an area that receives sufficient sunlight, seed will sprout slowly, the plant will start to flower, that flower will convert into a fruit and the fruit will grow.
Explain the following concepts:
Describe a sequence.
Describe the types of sequence.
Explanation
Describe the concept of a sequence to the students that when we give more than one command in an order, it is called a sequence. Also, give an example of drawing a hut by following a sequence, as given on page 69.
Discuss the various types of sequence, such as fixed and flexible, with the students. Explain both types by giving examples, as given on page 70.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 9B section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.

● Solve the following puzzle to get bird towards the pig.
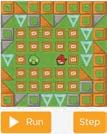
Correct Response:
The code should be look like this:
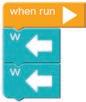
Sum Up
7 mins
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that a set of commands given more than once is called a sequence. Also, we have two types of sequences: fixed and flexible. In a fixed sequence we only have one way to do a task. In a flexible sequence, we have more than one way to do a task.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 2 and 3
C. Who Am I?: Question 1
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1 and 2
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 2 and 3

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
Ask the students about different types of sequences.
Discuss the given examples with the students.
● solve the given examples. 5 mins Warm Up
Attempt the given activity Conclude the concepts
● Ask the students about different types of sequences.
● Now, explain the given examples to them.
Explain the following concept:
Learning Outcome
Explanation
Solve the given examples. Explain the difference between the fixed and flexible sequence with the help of the examples, as given on pages 71 to 73.
● Ask the questions related to the examples to the students.
● Solve the following puzzle to get the bird towards the pig.

Correct Response:
Follow the given code:

Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that we have two types of sequence: fixed and flexible. In fixed sequence, we only have one way to do a task. In flexible sequence, we have more than one way to do a task.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter to attempt in the classroom.
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1 and 2

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● solve the given coding challenge.
Warm Up
Now that the students have understood the concept of fixed and flexible sequences, ask them to solve a few puzzles.
Discuss the given coding challenge with the students and explain how to solve it.
Attempt the given activity
Conclude the concepts
Warm Up
● Now that the students have understood the concept of fixed and flexible sequences, ask them to solve a few puzzles. You can give the puzzles from old magazines or newspapers.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Explanation
Solve the given coding challenge. Discuss the given coding challenge with the students, as given on page 74.
Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding.
1. Which sequence helps us to do the task in one way?
Possible Response: Fixed/Flexible sequence
Correct Response: Fixed Sequence
2. Your mother gives you three commands in an order. Let’s guess the name of it.
Correct Response: Sequence
● Solve the following puzzle to get the bird towards the pig.

Correct Output:
The final code should look like this:

Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that in some situations we can have just one way or multiple ways to solve the given problem.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as to attempt in the classroom.
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1 and 2

Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. machine 2. games 3. mistakes 4. laptop
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
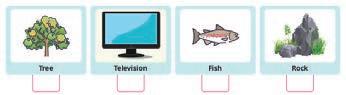
1. b. Television
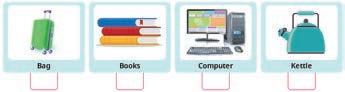
2. c. Computer
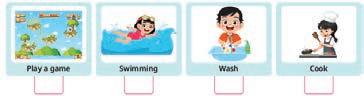
3. a. Play a game
C. Who Am I?
1. Water 2. Washing Machine 3. Computer 4. Tablet
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. F 2. T 3. T 4. F
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. Trees, animals, mountains, rivers, and flowers
2. Machines are human-made things that make our work faster and easier. A computer and a refrigerator are two machines that work on electricity.
3. a. Computers do not make mistakes.
b. The computer never gets tired.
4. A laptop is smaller than a desktop. It can be folded and carried easily.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Microwave
2. Laptop
3. Torch, sewing machine, and clock
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. videos 2. friends 3. input 4. mouse
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. a. Offices

2. a. Mouse

C. Who Am I?
1. Airport 2. Restaurant 3. CPU 4. Monitor
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. F 3. T 4. F
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. We can draw and colour, learn new things, and send emails and messages on a computer.
2. Pen drive and hard disk are two storage devices used in a computer.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. A computer can help Neha to take orders and make bills for food in a restaurant.
2. Pranjal can keep information of patients in a hospital.
3. A printer can help get a card on a computer printed on paper.
4. Divyansh must use a mouse to select a picture of his friend.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. machine 2. electricity 3. shut down 4. Don't 5. CPU

B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. a. Switch the main power button on 2. a. Computer may get damaged
3. b. Clean and dry cloth
C. Who Am I?
1. ON button on the CPU 2. Wires 3. Power icon 4. Keyboard
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. F 2. T 3. F 4. F 5. T
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. To switch the computer on, follow the given steps:
a. Switch on the main power switch.
b. Press the On button on the CPU.
c. Press the Power button on the monitor.
d. Wait till the Windows screen appears.
2. To shut down a computer, follow the given steps:
a. Click Start to open the menu.
b. Then, click on the Power icon.
c. Click on the Shut down option from the second menu.
3. The computer should be cleaned by wiping the computer with a soft and dry cloth.
4. a. Do: Press the keyboard keys gently.
b. Don’t: Don’t touch the computer devices with wet or dirty hands.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Riya must shut down her computer.
2. Sanjay should wipe the computer with a soft and dry cloth.
3. Kalpana and her brother should always keep food away from the computer. So, they must eat food at the dining table.
4. The steps to turn on the computer are:

A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Scroll wheel 2. Two 3. Left 4. List 5. Pointer
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. a. Left mouse button
2. b. Right mouse button


C. Who Am I?
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1.
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. A computer mouse is a pointing device that is used to point at and select things on the computer screen.
2. The Mouse Pointer is the small arrow that moves on the computer screen when you move the mouse.
3. A computer mouse has two buttons.
4. The left button on the mouse opens a file.
5. The mouse has a scroll wheel to help you move up and down on the screen.

F. Apply Your Learning.
1. The middle finger is used to click the right button on the mouse.
2. The palm is kept on the body of the mouse.
3. The scroll wheel is the part of the mouse used for scrolling.
4. The index finger is used to click the left button on the mouse.
5. The right button on the mouse pops up the menu on the screen.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Up 2. Spacebar 3. Keyboard 4. Enter 5. Number
B. Identify the Keys Correctly.
Alphabet keys
Backspace Key Number keys
Spacebar key Enter key Arrow keys
C. Who Am I?
1. Keyboard 2. Backspace Key or Delete Key 3. Enter Key 4. Spacebar Key 5. Cursor
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. T 3. F 4. F
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. We use the keys on the keyboard to type what we want.
2. The arrow keys help us to move the cursor up, down, left or right.
3. The number keys help us type the numbers.
4. The Spacebar key helps us to add a space between the two words.
5. The Delete key is used to erase the letter or the number after the cursor.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Gaurav can use the alphabet keys to type a letter.
2. Sanchit can use the number keys to type his father’s mobile number on the computer.
3. Sara can use the Backspace key or the Delete key to correct her mistake.
4. Gurung can use the Enter key to take the cursor to the next line.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Paint 2. Oval 3. Fill with color 4. Saving
B. Tick () the Correct Option. 1. c. Drawing Area 2. b. File 3. d. Title Bar
C. Who Am I?
1. Drawing Area 2. Circle 3. Left mouse button 4. Save option
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. F 3. T 4. T
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. The Fill with color tool helps us colour our shapes.
2. Saving a file helps us to open our drawing again in Paint.
F. Apply Your Learning. Do it yourself
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Solved 2. Blocks 3. Computer
B. Tick () the Correct Option.








D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. F 3. T
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. A problem is something that we need to solve.
2. Coding is the language that is used to give instructions to a computer.
3. The coding language that uses blocks to give instructions is called Block-based coding.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. The correct path is C. a. No b. Yes
2.



5. Do It Yourself Chapter-8 A Tour to Code.org
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Run 2. Blocks 3. Workspace 4. Instructions
B. Tick () the Correct Option. 1. a.









D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. F 2. F 3. T
E. Answer the Following Questions.

1. The two parts of the Puzzle Code Studio are the play area and the toolbox.
2. The part of the Puzzle Code Studio where programs run is called the play area.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1.

Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Instructions 2. Sequence 3. Fixed
B. Tick () the Correct Option. 1. a.







C. Who Am I?
1. Do It Yourself
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. F 2. T 3. F
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. In coding, the instructions we give to a computer to do something are called commands.
2. When we give more than one command in order, it is called a sequence.
3. The different types of sequences are fixed and flexible.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1.









A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. natural 2. electricity/fuel/human power 3. hospitals 4. right
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. c. Cars
2. a. Refrigerator
3. c. The Windows screen
C. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. F 3. T 4. T
D. Answer the Following Questions.
1. In offices, computers are used to do important work and send messages.
2. Shut down means to turn your computer off.
3. Hard disk is like a box that stores all the data in the computer.
E. Apply Your Learning.
1.

2. Two uses of a mouse are:
i. It helps to point and select.
ii. It helps to play games.
3. Piyush must buy a tablet.
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Typing 2. Visual 3. Toolbox 4. Reset
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. c. Play area
2. b. To drag the blocks and code
3. b. Fill with color tool
4. c. Title Bar
C. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. T 3. F 4. T
D. Answer the Following Questions.
1. Coding is the language used to give instructions to a computer.
2. The four main parts of the Puzzle Code Studio are the Play area, Toolbox, Workspace, and the Instruction area.
3. The Delete key helps us to erase letters or numbers after the cursor.
E. Apply Your Learning. Do It Yourself.
It is a flexible sequence because there is more than one way to complete the task.

Uolo has introduced a comprehensive program, Hexa, for Grades 1 to 8, aimed at empowering young minds with essential knowledge and skills for the digital age.
To support the effective implementation of Hexa in classrooms, this Teacher Manual has been thoughtfully designed. It provides structured lesson plans for each chapter, guiding teachers through both classroom instruction and computer lab activities. Every lesson follows Uolo’s research-based WEBS framework, which simplifies teaching methodologies and enhances lesson delivery, making learning more engaging and impactful for students.
Framework
• Sharp Lesson Planning: Each lesson plan focuses on specific sub-learning outcomes within a chapter and are designed for delivery within the stipulated class or lab time.
• Real-life and Application-based Questions: Additional questions that link Computer Science to real-life contexts and assist teachers to develop learners' conceptual understanding and application skills.
• Support and Detailed Solutions: In-depth solutions for in-class and post-class activities to reinforce learning.
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to bring technology-based learning programs. We believe pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, South East Asia, and the Middle East.
ISBN 978-81-985754-6-3
