





Academic Authors: Jatinder Kaur, Ayushi Jain
Creative Directors: Bhavna Tripathi, Mangal Singh Rana, Satish
Book Production: Rakesh Kumar Singh
Project Lead: Jatinder Kaur
VP, Learning: Abhishek Bhatnagar
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited
First published 2025
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the above-mentioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: Hexa Computer Science Teacher Manual 4
ISBN: 978-81-985754-9-4
Published by Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address:
85, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2017PTC322986
Illustrations and images: www.shutterstock.com, www.stock.adobe.com and www.freepik.com
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, computer science has become an essential field of study, shaping the world around us in countless ways. From the smartphones in our pockets to the vast networks that connect people across the globe, computer science drives innovation and progress in nearly every aspect of modern life. In today’s fast-paced digital world, understanding the basics of computer science is as important as learning to read, write, or solve maths problems.
Recognising this imperative, the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 has strongly recommended the integration of coding skills, computational thinking, critical analysis, and problem-solving abilities into the curriculum.
Inspired by these insights, Uolo has introduced a comprehensive program, Hexa, for grades 1 to 8, to empower young minds with the knowledge and skills they need to thrive in the digital age. From the basics of how computers function to the tools that shape our digital landscape, this series opens the door to a world of endless possibilities.
We believe that learning computer science should be an engaging and accessible experience for all children. This series takes a project-based approach, allowing students to learn by way of concurrently applying acquired knowledge and skills. As they progress through the course, they will build strong foundations in computational thinking, coding basics, and digital literacy. Our program focuses on three key areas:
1. Computer Science Fundamentals: Core concepts are introduced step by step, ensuring a solid grasp of how computers function, and how information is processed and stored.
2. Latest Computer Tools: Various computer tools relevant to today’s world are included, equipping students with the confidence to thrive in the digital age.
3. Introduction to Coding: The series offers an introductory look into coding, preparing students for more advanced learning in the future.
To support teachers in delivering effective and engaging lessons, we offer a thoughtfully designed Teacher Manual to enhance the teaching and learning experience. Rather than prescribing teaching methods, the manual provides examples and demonstrates how and why teachers can apply these examples in their classes.
Each chapter in this manual is structured to provide a comprehensive lesson plan. The chapters are divided into multiple sessions, each following the Warm up, Engage, Build, and Sum up (WEBS) strategy.
• The Warm up phase sets the stage for learning by connecting to prior knowledge and building curiosity.
• The Engage phase captures the students’ attention and motivates them to participate actively.
• In the Build phase, questions from various sections are discussed to build the understanding of the students.
• Finally, the Sum up phase reinforces learning through easy-to-recall activities and questions. Time duration for each section has been suggested based on the requirements of the students. Additionally, an answer key for every chapter is provided to assist teachers in assessing their students’ understanding and guiding their learning effectively.
We hope this Teacher Manual empowers educators to implement the curriculum effectively, support diverse student learning, and create interactive, engaging environments tailored to their students’ needs and interests.
1 How Computers Store Data ������������� 1
Understanding Computers
Computer Memory: Primary Memory
Computer Memory: Secondary Memory 2 Learn about Operating Systems ����� 8
Operating Systems and Windows 10
Desktop Elements and Shortcut Keys
Desktop Settings
3 Working with Files and Folders ����� 15
Introduction to files and folders
Renaming and Selecting Files and Folders
Duplicating and Moving Files and Folders & Shortcut Icons
Deleting and Restoring Files and Folders
Good Practices While Using a Computer 4 Browsing the Internet �������������������� 26
About the Internet and Basic Requirements
Basic Terminologies of the Internet
Introduction to Word Processor
Formatting Documents 1
Formatting Documents 2
Formatting Documents 3
Presentations 1
Presentations 2
Presentations 3
Introduction to Coding Creating a Project and Components of Scratch
Sprites and Backdrops ��������������������
Sprites
Ways to Add a Backdrop
Events and Loops
Events Block
Making a Sprite Say Something
Motion Blocks
Loops, Control, and Sensing Blocks Moving and Making a Sprite Fall

This chapter is divided into the following sessions
Understanding Computers
Computer Memory: Primary Memory
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
Computer Memory: Secondary Memory
● describe ancient devices and modern smart devices, including computers.
● describe the concept of Data, Processing, and Information.
Keywords
● Devices: Things around us that perform specific tasks are called devices.
● Computer: It is an electronic device or a machine that performs various calculations and carries out different tasks for us based on the instructions that we give it.
● Data: It is facts, numbers, or symbols that we collect and enter into the computer.
● Information: It is the knowledge or understanding that we gain when the computer analyses and puts together the data that we entered into it.
● CPU: The CPU is like the brain of the computer. It takes our inputs and processes them.
Ask the students what devices were there in ancient times, for instance, to know the time of the day.
Ask the students what devices are used in modern times and how the present-day devices are different from the older ones.
Explain about the various devices, including computers.
Explain about data, processing, and information.
Think and Tell
Group discussion
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
5 mins Warm Up
● Ask the students what devices were there in ancient times to know the time of the day.
● Tell the students that people used sundials. They used the sun’s shadow to know what time it was.
● Ask the students what devices are used in modern times and how these devices are different from the old ones. Tell them that nowadays smartwatches are being used that not only tell us the time but also allow the use of the internet. Tell them that a computer is also one of these smart devices.
Explain the following concepts:
Describe ancient devices and modern smart devices, including computers.
Describe the concept of Data, Processing, and Information.
15 mins
Tell them that things around us that perform specific tasks are called devices. Explain ancient and smart devices as given on pages 1 and 2.
Tell the students that a computer takes inputs from us in the form of ‘data’, processes them, and finally provides us with output in the form of ‘information’. Then explain the concept of Data, Processing, and Information as given on pages 2 to 4.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 1A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
1. a. Virus
2. a. F
b. T
c. F
d. T
3. Steps
b Processing the input
c Looking at the movement of the mouse on the screen
a Moving the mouse on the table

● Ask the students to give the answer to the question, “Name a few devices around you and say how you use them.” asked in the Think and Tell section, given on page 1.
Possible Responses: I use Television to watch educational shows and cartoons. I use my parents’ smartphone to call my friends, take photos, and access educational apps to make learning fun.
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic, ‘‘Give one example of data and information.” provided in the Discuss section as mentioned on page 3.
Possible Response: Data: (32°C, 50% chances of rain), Information: It’s warm, and it might rain today.
● Ask the students to give the answer to the question, “Can you think of some more examples of input and output in computers?” asked in the Think and Tell section, given on page 4.
Possible Response: Input: Typing on the keyboard and Output: Displaying text on the monitor screen.
3 mins
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that the things around us that perform specific tasks are called devices. Similarly, computers perform various calculations and carry out different tasks based on the instructions that we give them. A computer takes inputs from us in the form of ‘data’, processes them, and finally provides us with the output in the form of ‘information’.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1 and 2
C. Who Am I?: Question 2
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 1 and 5
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe computer memory.
● describe primary memory and its types.
Keywords
● Memory: A computer has memory to store data and information.
● Bytes: Computer memory is measured in units called bytes.
Warm Up Engage Build Sum Up
Ask the students to name the devices that can be used for storage, such as your diary, where you store all the details about your day-to-day activities.
Explain to the students what computer memory is.
Explain to them about the primary memory and its types.
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts Assign homework
5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students to name a few storage devices from their surroundings.
● Tell them that similar to the diary that stores the details of your entire day, a computer has memory to store the data and information. Everything that we do on the computer is stored in its memory.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Describe computer memory. Tell the students that the computer has a memory to store data and information, as given on page 5. Also tell them about the various units of computer memory.

Describe primary memory and its types.
Explain to the students that the primary memory is the computer’s internal memory where it stores data related to currently running programs. Also tell them that the primary memory is of two types—RAM and ROM, as given on pages 6 and 7.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 1B section, Question 2 and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
2. a. RAM
b. ROM
c. ROM
d. RAM
Build
7 mins
● Ask the students to give the answer to the question, “Sometimes, our computers hang, or programs suddenly crash. Is this problem related to RAM or ROM?” asked in the Think and Tell section, given on page 7.
Correct Response: RAM
Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that everything that we do on the computer is stored in its memory, for example, saving a file, storing pictures, and downloading something from the internet. Primary memory is the computer’s internal memory where it stores data related to currently running programs.
● Assign the following from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 3 and 4
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 3 and 4
C. Who Am I?: Question 3
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1 and 4
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 3
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe secondary memory and secondary storage devices.
Keyword
● Cloud storage: It is like a big storage space on the internet where you can keep all your files and access them anytime, anywhere, and from any device as long as you are connected to the internet.
Warm Up Engage Build Sum Up
Ask students: Since our mind’s memory is limited, how do you think we store information to ensure it is not lost? Can you relate this to how computers manage their memory?
Explain to the students about the secondary memory and the various secondary storage devices.
Group discussion
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Warm Up
● Ask students: Since our mind’s memory is limited, how do you think we store information to ensure it is not lost? Can you relate this to how computers manage their memory?
● Tell students that we store information in a diary to retain things. The diary is an example of secondary memory in computers.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Describe secondary memory and secondary storage devices.
Explanation
Explain to the students about the secondary memory and secondary storage devices, like Hard Disk Drive (HDD), Pen Drive, Memory Card, etc., as given on pages 7 to 9.

● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 1B section, Questions 1 and 3 and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
1. a. CD: Secondary Memory Device
b. HDD: Secondary Memory Device
c. DVD: Secondary Memory Device
d. ROM: Primary Memory
e. Pen Drive: Secondary Memory Device
f. RAM: Primary Memory
3. Cloud Storage HDD Pen Drive DVD CD
Note: These are general trends and the actual storage capacity may vary from model to model and with advancements in technology.
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic ‘How to increase the memory of your computer’.
Correct Response: The memory of your computer can be increased using secondary storage devices.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that the Secondary memory, also known as auxiliary memory, is the computer’s external storage beyond the primary memory. It is used to store data and programs that are not immediately needed by the computer’s processor. Some examples of secondary storage devices are external hard disks, pen drives, and SD cards.
● Assign the following from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1 and 2
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1 and 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 2 and 3
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 2, 3, and 4
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1 and 2
This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Operating Systems and Windows 10
2. Desktop Elements and Shortcut Keys
3. Desktop Settings
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe an operating system and its features.
● describe about the Windows 10 operating system.
Keywords
● Operating system: An Operating System is a software that helps us to communicate with the computer and tell it what to do.
● Software: It is a set of instructions that tells a computer what to do.
● Booting: When you press the power button to turn on your computer, the computer starts getting the system ready for you to use it. This process is called booting.
Ask the students what things they can do on a computer.
Ask the students if they know what makes a computer run smoothly and do multiple things.
Explain to the students about the operating system and its features.
Also tell them about the popular operating system— Windows 10.
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts
Assign homework

Warm Up
● Ask students what tasks they can do on a computer.
● Tell the students that they can do a lot of things on computers—play music, watch videos, play games, etc. And then tell them that the operating system makes the computer run smoothly.
15 mins
Explain the following concepts:
Describe an operating system and its features.
Describe about the Windows 10 operating system.
Explain to the students that an operating system is a software that helps us communicate with the computer and tell it what to do. Also, explain its features, as given on pages 13 and 14.
Introduce the students to the Windows 10 operating system and tell them the steps to start a computer with this operating system. Also, brief them about the taskbar, start button, icons and wallpaper, as given on pages 14 and 15.
● Read aloud the questions provided in Do It Yourself 2A. Encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
1. d. All of the above
3
2. a. F b. T c. T
3. Match the Columns.
Column A
Column B
Desktop Manages computer software
Booting Process of starting the computer
Taskbar Area where you see icons and wallpapers
Build
7 mins
● Ask the students to give the answer to the question ‘’Which icons do you think we should have on our desktop?’’ asked in the Think and Tell section, as given on page 15.
Possible Responses: Recycle bin, Google Chrome
● Conclude the session by summarising that an operating system helps us to communicate with the computer and tell it what to do. An operating system has features such as easy-to-use interface, file management, multitasking, etc. Booting is the process that starts getting the system ready for you to use it when you turn on the computer. The Taskbar is the bar in the bottom of the window.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1, 2, and 3
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 2 and 4
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1, 2, and 3
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 1
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 1 , 2, and 3
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 2

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● discuss the different elements of the Windows 10 desktop.
● apply few shortcut keys for Windows 10.
Ask the students the names of different elements they studied in the previous session.
Explain the students about the different elements of the desktop. and the Windows 10 shortcut keys.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
homework
● Ask the students the names of different elements they studied in the previous session.
● Now, build the concept by discussing the different elements of the Windows 10 desktop.
Explain the following concepts:
Discuss the different elements of the Windows 10 desktop.
Apply few shortcut keys for Windows 10.
Explain to the students about the taskbar and its components. Describe the Aero Peek feature of Windows 10. Also, tell them the steps to change the taskbar location, as given on pages 16 and 17.
Tell the students that the windows key is a special key at the bottom-left of the keyboard. Also, tell them about a few shortcut keys and their functions, as given on page 18.
● Read aloud the questions provided in Do It Yourself 2B section. Encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.

Build
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic “Is the functionality of the desktop show/hide button and Aero Peek feature the same?'' provided in the Discuss section, as mentioned on page 16.
Possible Response: Yes, both the desktop show/hide button and Aero Peek feature allow you to view the desktop, but Aero Peek also lets you temporarily preview the desktop without minimizing open windows.
Correct Response: Do It Yourself 2B Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising different elements of a desktop such as taskbar and its components, aero peek, changing taskbar location. Also tell them that the windows key is used in combination with other keys to make the shortcut keys.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 4 and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1 and 3
C. Who Am I? Question 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 3 and 4
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 4 and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 3

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● set the theme colour and theme font of the desktop.
● set date and time.
Ask the students if they know that they can change the theme colour of the desktop.
Explain to the students how to set the theme colour and theme font of the desktop. Also, tell them how to set the date and time.
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts
● Ask the students if they know that they can change the theme colour of the desktop.
● Then, build the concept by telling them how to customise the colours on their computer.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning
Explanation
Set the theme colour and theme font of the desktop. Tell the students the steps to customise the colours on their computers. Also tell them the steps to adjust fonts on their computers, as given on pages 19 to 21.
Set date and time. Explain to the students the steps to set the date and time, as given on page 21.
● Ask the following questions from the students to check for understanding.
1. How can you set the date and time on your computer? a. Go to the Control Panel and select “Date and Time”.
b. Right-click on the taskbar and choose “Date and Time Settings”.
c. Use the shortcut key “Ctrl + D”.
d. Open the Start menu and click on “Time and Date”.
2. Write T for True and F for False.
a. The theme setting colour can be changed.
b. The theme font style can be changed.
Correct Responses:
1. d. Open the Start menu and click on “Time and Date”.
2. a. T b. T
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic “How to customise the colours on your computer”.
Possible response:
Click the Start button and select the Settings menu The Windows Settings opens. Choose the Personalization option from the menu Select Colors option from the sidebar Choose a colour of your choice from the Windows colors palette The changes will take effect right away.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that we can apply various settings such as theme colour, font, date and time, on the computer desktop, etc.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 2
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1 and 4

This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Introduction to Files and Folders
2. Renaming and Selecting Files and Folders
3. Duplicating and Moving Files and Folders & Shortcut Icons
4. Deleting and Restoring Files and Folders
5. Good Practices While Using a Computer
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● work with files and folders.
● create a file, folder, and subfolder on the desktop.
Keywords
● File: A file is a digital space used to store different types of information on a computer. It acts like a container for items, like images, videos, texts, etc.
● Folder: A folder is a container that stores files. Folders help organise files, making them easier to find.
Ask the students how they keep their toys or books organised and why do they think it is important to have a designated place for everything.
Describe that just like we organise our physical belongings, we also organise our digital information on a computer using files and folders. Also, explain the steps to create files, folders, and subfolders to the students.
Group discussion
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students that how they keep their toys or books organised and why do they think it is important to have a designated place for everything.
● Relate the concept of organising the items on the computer to files and folders.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
15 mins
Explanation
Work with files and folders. Explain the concept of files and folders to students. Describe how all the information is stored in files on a computer system. A file is a digital space used to store different types of information on a computer and a folder is a container that stores files and other folders, as given on pages 27 and 28.
Create a file, folder, and subfolder on the desktop.
Explain the steps to create a Word file, folder, and sub-folder to the students as given on pages 28 and 29.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 3A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in the book.
Correct Responses:
The steps to create a folder are:
a. Right click on the desktop.
b. Position the cursor over the New option.
c. Click on the Folder option.
d. Give it a name. Build
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic ”When we are at school, we take notes in our notebooks. Can we compare a computer file with a notebook?” provided in the Discuss section as mentioned on page 27.
Possible Responses: Yes, we can compare a computer file with a notebook. Just like we write and store information in a notebook at school, we can create and save information in a computer file. Both notebooks and computer files help us keep our thoughts, ideas, and important information organised and accessible.

● Conclude the session by summarising that files are digital containers that store different kinds of information on a computer, and folders help us organise these files. We learnt how to create a Microsoft Word file and folders or subfolders on the desktop to manage information effectively on a computer.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1 and 3
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1, 2, 3, and 4
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1 and 2
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1 and 2
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 1
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 4
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● rename files and folders.
● select files and folders.
Keyword
Ask the students if they label the boxes containing their important things.
Now, relate them to the concept of renaming the files and folders according to their preferences.
Explain to the students how to rename files and folders and how to select them.
● Renaming: Renaming a folder or a file means changing the name of the digital files and folders. 5 mins
Action Plan
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Warm Up
● Ask the students if they label the boxes containing their important things.
● Now, relate them to the concept of renaming the files and folders according to their preferences.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
15 mins
Explanation
Rename files and folders. Explain to the students that the new files and folders are assigned the default names once they are created. However, they can be renamed later, according to our preferences. Describe the steps to do so as given on pages 29 and 30.

Select files and folders. Explain that to do any operation on a file or folder, we first need to select it. Discuss that there are various methods to select single or multiple files and folders, as given on pages 31 and 32.
● Read aloud the questions provided in Do It Yourself 3B section Questions 1, 2, and 3. Encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in the book.
Correct response
1. Left 2. Ctrl 3. Shift
● Ask the students to give the answer to the question “Why do you think it is important to give correct names to folders?” asked in the Think and Tell section given on page 30.
Possible Response: Giving correct names to folders is important for efficient organisation and easy access to files.
● Conclude the session by summarising that we can rename the files and folders in our computer. We need to select the files before performing any operations on them.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 4
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● duplicate files and folders.
● move files and folders.
● describe how to create shortcut icons on the desktop.
Keywords
● Duplicate: To duplicate is to make an exact copy of a file or folder.
● Move: To move is to transfer a file or folder to a different location.
● Shortcut icons: Shortcut icons are quick-access symbols on the desktop for frequently used files or folders.
Ask the students if they ever copied the same assignment in their school.
Explain how to create a duplicate file and how to move a file or folder to a different location. Also, describe how to create shortcut icons on the desktop.
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Ask the students if they ever copied the same assignment in their school.
● Then, build the concept by telling them how to duplicate a file in the computer.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Duplicate files and folders. Explain to the students that we can create a duplicate file or a folder by using the Copy and Paste options as given on pages 32 and 33. Also, describe the steps to do so.

Move files and folders. After that, explain the concept of moving a file or folder to a different location on the computer along with the steps as given on page 34.
Create shortcut icons on desktops.
Explain to the students that the shortcut icon helps us quickly open a file or folder, as given on page 34. Also, describe the steps to do so as given on page 35.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 3B section Questions 4 and 5. Encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in the book.
Correct Responses:
4. Copy
5. Cut
7 mins
● Ask the students to give the answer to the question “How is moving files and folders different from duplicating them?” asked in the Think and Tell section given on page 34.
Possible Response: Moving files and folders relocates them, while duplicating creates copies of them.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarizing that we can also create duplicate files using the Copy and Paste options and move the files using the Cut and Paste options. At last, revise the steps of creating the shortcut icons on the desktop.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 5
C. Who Am I?: Question 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 3 and 4
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 2 and 3
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 4
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● deleting files and folders.
● restoring files and folders.
Keywords
● Delete: Deleting a folder or file means removing it from our computer.
● Restoring: Restoring a folder or file means getting it back to the previous location from the recycle bin.
Ask the students in order to keep their home organised and clean, have they keep throwing away things that are not in use anymore. Explain how to delete a file and folder. Also, tell them how to restore it.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Ask the students in order to keep their home organised and clean, do they keep throwing away things that are not in use anymore?
● Then, build the concept by telling them how to delete a file or folder from a computer.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
15 mins
Explanation
Deleting files and folders. Explain to the students that deleting a folder or file means removing it from our computer, as given on page 36. Also, describe the steps to do so.

Restoring files and folders. Explain to the students that you can restore the deleted folder or file. Restoring means to bring something back along with the steps as given on page 36.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 3C section. Encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in the book.
Correct Responses:
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic “What is a recycle bin?”
Possible Response: The Recycle Bin is a special folder on a computer where deleted files and folders are temporarily stored. It allows you to recover files that were deleted by mistake.
● Conclude the session by summarizing that deleting a folder or file means removing it from our computer and restoring means to bring something back.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 2
C. Who Am I?: Question 3
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 2
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● follow good practices while using a computer.
Ask the students whether they follow the teacher’s instructions to move in a line or to keep quiet in the class. Tell them that just as they practice good manners in daily life, we also have a few good practices when using a computer.
Discuss the various good practices with the students that they should follow while using the computer.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Warm Up
● Ask the students whether they follow the teacher’s instructions to move in a line or to keep quiet in the class.
● Tell them that just as they practice good manners in daily life, we also have a few good practices when using a computer.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcome
Follow good practices while using a computer.
15 mins
Explanation
Explain to the students that they should follow a few good practices when using a computer, such as naming and storing the files and folders properly, organising the files in labelled folders, being respectful of others’ files, etc., as given on page 37.

Ask additional questions to the students to check for understanding.
1. Give any two good practices that we should follow while using a computer.
Possible response: Organise the files in labelled folders. This will help you locate a file quickly.
2. Be respectful of others’ files. Do not delete or change the files that belong to someone else without their permission.
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among students based on the topic provided below:
Discuss why it is important to name and store files properly.
Possible Responses: It helps to keep the computer organised, especially when many people share one computer.
● Conclude the session by summarising that students should follow a few good practices when using a computer, such as naming and storing the files and folders properly, organising the files in labelled folders, being respectful of others’ files, etc.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1 and 3
This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. About the Internet and Basic Requirements
2. Basic Terminologies of the Internet
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● define internet.
● identify the basic requirements for an internet connection.
Keywords
● Internet: The internet is a network of networks that connects computers and devices from all over the world.
● Network: A network is a group of computers connected to each other.
Ask the students what makes it possible to video call a friend who may be in a different part of the world. Explain the term ‘internet’ to the students. Also, discuss the basic requirements for an internet connection.
Think and Tell Group discussion
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework

5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students what makes it possible to video call a friend who may be in a different part of the world.
● Then relate the concept by telling them that internet helps them do so.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
15 mins
Explanation
Define internet. Explain to the students that the internet is a network of networks that connects computers and devices from all over the world. Also, get them familiar with the term network, as given on page 40.
Identify the basic requirements for an internet connection.
Tell the students that we need a computer and an internet connection to start exploring the internet. Tell them to set up an internet connection, we need a modem, ISP, and communication media as given on pages 40 and 41.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 4A and encourage students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their notebook.
Correct Responses:
● Ask the students to answer the question, “Can you think of more examples of Analog and Digital signals?” asked in the Think and Tell section on page 41.
Possible Responses: Analog signals: Human voice transmitted through airwaves. Digital signals: Text message sent over a cellular network.
● Conduct a group discussion in the class based on the topic “Find out which type of internet connection your house or school has.” provided in the Discuss section on page 41.
Possible Response: Cable networks are used in homes. A cable from a local central office (CO) runs to our homes or schools and provides internet.
3 mins
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that the internet is like a web that connects computers and phones all over the world, letting us send messages, pictures, and even see each other on video calls. It started many years ago with just a few computers and has grown so much that we can now shop online, learn new things, and make friends in faraway places. To connect to the web, our computers use a special box called modem and an ISP. The fastest connection is through fibre optic cables as they carry information in the form of light.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1 and 2
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 1
C. Who Am I?: Questions 4 and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 1 and 2
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1 and 2

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● define the basic terminologies of internet.
● Describe about Google Chrome, search engines, URL, and Net Surfing.
Tell the students that whenever they pick a new hobby, they need to learn some basic terms about it. Similarly, before using the internet, they need to know some basic terms about it.
Discuss the basic terminologies of the internet such as Web page, Website, WWW, Web browser, Search Engine, URL, and Net Surfing. Discuss Google chrome and the steps to use Chrome and its components.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Tell the students that whenever they pick a new hobby, they need to learn some basic terms about it. Similarly, before using the internet, they need to know some basic terms about it.
● Build the concept to introduce and explain to them the basic terminologies of internet.
Explain the following concepts:
Define the basic terminologies of internet.
Describe the basic terminologies of the internet, such as webpages, websites, WWW, etc., to students, as given on pages 42 and 43. Describe about Google Chrome, search engines, URL, and Net Surfing.
Explain to the students that Google Chrome is a web browser made by Google. It is one of the most popular browsers in the world. Explain the steps to open Chrome. Also, describe about search engines, URL, and net surfing to students, as explained on pages 43 to 45.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 4B and encourage the students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their notebook.




c Web World Wide
Correct Responses:
Match the column:
1. b. World Wide Web
2. a World Wild Web
Column A



Build











7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class on the topic ‘Net Surfing’.
Possible Responses: Net surfing is used to visit websites, watch videos, listen to music, and shopping. We require an internet connection and web browser for it.
3 mins
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising that digital documents, called webpages, when grouped together, form a website. We use programs called web browsers to explore websites and find information through search engines such as Google Chrome, all by typing in unique addresses called URLs. Net surfing involves using a computer or mobile device with an internet connection and a web browser to visit websites, watch videos, listen to music, and discover new things online.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 3, 4, and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 2, 3, and 4
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1, 2, and 3
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 3 and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 3 and 4

This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Introduction to Word Processor 2. Formatting Documents 1 3. Formatting Documents 2 4. Formatting Documents 3
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe what a word processor is.
● create a document.
● identify the components of a Google document.
● add text in a Google document.
● format text.
Keywords
● Word processor: A word processor is a software used to type and edit text.
● Google Docs: It is a free online word processor that is easy to use. It allows you to work together with your friends.
● Formatting: Formatting refers to the process of changing the appearance and layout of a written document or text to make it more visually appealing, organised, and easier to read and understand.
Warm Up
Ask the students how they would write a paragraph on the topic ‘Hockey’ on a computer.
Engage
Explain to the students what a word processor is. Then, guide them through the steps to create a Google document. Explain the different components of a Google document and show them how to add and format text in Google Docs.
Build Sum Up
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students how they would write a paragraph on the topic ‘Hockey’ on a computer.
● Tell the students that a word processor is a software which is used to type and edit text. Microsoft Word and Google Docs are the two of the most popular ones.
Explain the following concepts:
Describe what a word processor is.
15 mins
Tell the students that a word processor is a software that is used to type and edit text. Also, explain the features of Google Docs, as given on page 49.
Create a document. Demonstrate the steps to create a Google doc, as given on page 49.
Identify the components of a Google document.
Tell the students about the different components of the Google document window, such as the menu bar, toolbar, working area, etc., as given on page 50.
Add text. Demonstrate to the students how to add text in a Google document, as given on page 50.
Format text.
Tell the students what formatting text means and demonstrate the steps to format text, as given on pages 51 and 52.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 5A section, Questions 1 and 2. Encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct them to write the answers in their book.
Correct Response:
1. Google Docs
2. Bold
Build
7 mins
● Ask the students to answer the question, “Would you ever make the title of your paragraph bold? Why or why not?” given in the Think and Tell section on page 52.
Possible Responses: Yes/No
Correct Response: Yes, because the title of the paragraph should look thicker and darker than the rest of the text.

● Conclude the session by stating that a word processor is a software which is used to type and edit a text. The two most popular ones are Microsoft Word and Google Docs. There are different components of the Google document window, such as the menu bar, toolbar, working area, etc. Formatting text refers to the process of changing the appearance and layout of a written document or piece of text to make it more visually appealing, organised, and easier to read and understand. Also, summarise the steps to create a Google document and how to add and format text.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1 and 4
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 1
C. Who Am I?: Question 1
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 3, 4, and 5
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 1 and 4
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● use the Paint format tool.
● use superscript and subscript formatting styles.
Keywords
● Paint format: This tool helps us copy the formatting from one piece of text and apply it to another text.
● Superscript: It is a formatting style where the text or number is made smaller and raised above the regular text line.
● Subscript: It is a formatting style where the text or number is made smaller and lowered below the regular text line.
Warm Up Engage Build Sum Up
Ask the students if they want to apply the same formatting to all the texts in the document. Should they repeat the steps one by one all over again?
Explain to the students how to apply the Paint format, superscript, and subscript features.
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Warm Up
● Ask the students if they want to apply the same formatting to all the texts in the document. Should they repeat the steps one by one all over again?
● Tell them that they can use the Paint Format tool. This tool will help to format in a quicker way.
15 mins
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Use the Paint format tool. Tell the students that the Paint Format tool helps us copy the formatting from one piece of text and apply it to another text. Demonstrate the steps to use the Paint Format tool, as given on pages 52 and 53.

Use superscript and subscript formatting styles. Tell the students that applying a superscript makes the text or number smaller and raised above the regular text line, while applying a subscript makes it smaller and lowered below the regular text line. Demonstrate the steps to apply these two features, as given on pages 53 and 54.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 5A section, Questions 3 and 4. Encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct them to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
3. Paint format
4. Superscript, Subscript
Build
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class on the topic, ‘How can superscript and subscript enhance the readability of scientific or mathematical documents?’
Correct Response: They make formulas, equations, and references clear and professional, helping the reader easily distinguish elements like powers and indices.
Sum Up
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that the Paint Format tool helps us copy the formatting from one piece of text and apply it to another text. Applying a superscript makes the text or number smaller and raised above the regular text line, and applying a subscript makes it smaller and lowered below the regular text line.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 2 and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 3
C. Who Am I?: Question 2
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● add a header and a footer to a document.
● insert a page break in a document.
● Insert a line break in a document.
Keywords
● Header: The text that appears at the top of every page in a document.
● Footer: The text that appears at the bottom of every page in a document.
● Page break: It is an instruction to the computer that tells it where to start a new page, when writing or printing.
● Line break: It is an instruction to start a new line.
Ask the students if they have noticed the page number on every page in all the books.
Explain the use and the steps to apply the header and footer, page break, and line break.
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students if they have noticed the page number on every page in all the books.
● Now, tell the students that this is possible because of a feature called footer in word processors.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Explanation
Add a header and footer to a document. Tell the students that the header is the text that appears at the top of every page, and the footer is the text that appears at the bottom of every page in a document. Also demonstrate to them the steps to add a header and footer to a document, as given on page 55.

Insert a page break in a document.
Insert a line break in a document.
Demonstrate the steps to insert a page break, as given on page 55.
Demonstrate the steps to insert a line break, as given on page 56.
● Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding.
1. Differentiate between a header and a footer.
Correct Response: The header is the text that appears at the top of every page in a document, whereas the footer is the text that appears at the bottom of every page in a document.
2. What is a page break?
Correct Response: A page break is an instruction to the computer that tells it where to start a new page, when writing or printing.
3. Define line break.
Correct Response: The line break is an instruction to start a new line.
● Ask the students to answer the question “What information can you include in headers and footers?” given in the Think and Tell section on page 55.
Possible Responses: The header can include the company logo, title of the document, author name, etc., while the footer can include the page number, notes, etc.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that the header is the text that appears at the top, and the footer is the text that appears at the bottom of every page in a document. Also, tell them the steps to use the header, footer, page break, and line break in Google Docs.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 3
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 2, 4, and 5
C. Who Am I?: Question 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1 and 2
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 3
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1, 2, and 3
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● insert a column in a document.
● set the page orientation.
Keyword
● Page Orientation: It refers to the direction in which a document is displayed.
Ask the students if they have ever noticed how a newspaper is set up. Explain the steps to insert a column and set the page orientation in a document.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts Assign homework
Warm Up
● Ask the students if they have ever noticed how a newspaper is set up.
● Tell them that newspapers use a column format. We can use the column format in Google Docs as well.
15 mins
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Insert a column in a document. Tell the students the benefits of using a column format in a document. Demonstrate to them the steps to use the column format in Google Docs, as given on page 56.
Set the page orientation. Tell the students that the page orientation refers to the direction in which a document is displayed. Demonstrate to them the steps to set the page orientation, as given on page 57.

● Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding.
1. What refers to the direction in which a document is displayed?
Correct Response: Page orientation
2. Name the two types of page orientation.
Correct Response: Portrait, landscape
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students on the topic “Benefits of using a column format”.
Correct Response: Easy reading, organised look, space saving, etc.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that newspapers use a column format and page orientation refers to the direction in which a document is displayed.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
C. Who Am I?: Question 3
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 2
This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Presentations 1
2. Presentations 2
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● define and identify the uses of a presentation.
● create a presentation.
3. Presentations 3
● identify the components of the Google Slides window.
● provide a name and add a title to a presentation.
Keywords
● Presentation: It is a tool to create, showcase and share information in an interactive, interesting, and visually appealing way.
● Slide workspace: It is the main area where you can add and arrange content like text, pictures, and videos on a slide.
● Slides panel: It is a section where you can see small versions of all your slides, helping you to navigate through your presentation easily.
● Speaker notes: It is a space to write notes for each slide that can help the presenter remember what to say during the presentation.
Ask the students how they will share the information in a more presentable and interesting way. Introduce them to what presentations are and the uses of presentations. Introduce Google Slides to make the presentations and explain its components. Introduce how to name a presentation and add title to a presentation.
Think and Tell Conclude the concepts
Assign homework

● Ask the students how they will share the information in a more presentable and interesting way.
● Build the concept that a presentation is a tool to share information in a more presentable and interesting way.
Explain the following concepts:
Define and identify the uses of a presentation.
Explain that a presentation is a tool to create, showcase and share information in an interactive, interesting, and visually appealing way. Discuss with them that presentations are used to share information, add visuals, stay organised, visualise and present. Presentations are used at various places like education, training, workshops, etc. as given on page 60.
Create a presentation. Tell them Google Slides is an online presentation tool that lets you create and share exciting presentations as given on page 61.
Identify the components of the Google Slides window.
Provide a name and add a title to a presentation.
Explain the components of Google Slides windows to the students as given on pages 61 and 62. Also, get them familiar with using Google Slides.
Explain that before adding more things to the presentation, they should give a name to the presentation. After giving a name, add the title to the presentation as given on page 62.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 6A section Questions 1, 2, and 3 and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their notebook.
Correct Responses: 1. d 2. a 3. b.
● Ask the students to answer the question “Where else can we use presentations?” given in the Think and Tell section on page 60.
Possible Responses: marketing, seminars, hospitals, etc.
● Conclude the session by summarising that a presentation is a tool to create, showcase and share information in an interactive, interesting, and visually appealing way. Presentations are used to share information, add visuals, stay organised, visualise and present. Presentations are used at various places like education, training, workshops, etc. Google Slides is an online presentation tool that lets
you create and share exciting presentations. Google Slides window has various components like Rename box, Menu bar, Toolbar, Slide workspace, Speaker notes, etc. Everything we do gets saved automatically, and we can identify a presentation by giving a name and adding a title to it.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1, 3, and 4
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1 and 2
C. Who Am I?: Question 1
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1 and 2

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● add and change the position of the text box after adding text in it.
● add new slides.
● work with shapes on a slide.
● work with images in a slide.
Keyword
● Text box: A space on the slide where you can add text.
Ask the students to imagine preparing a presentation on renewable energy. Do you think incorporating visual aids could enhance the impact of their presentation and make the concepts more accessible?
Explain the text box to add text and get them familiar with changing the position of the text box. Introduce adding new slides to an existing presentation.
Introduce working with shapes in a slide and also, get them familiar with working with images.
Group discussion Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
Warm Up
Ask the students to imagine preparing a presentation on renewable energy. Do you think incorporating visual aids could enhance the impact of their presentation and make the concepts more accessible?
Build the concept that Google Slides allows us to add visuals to our presentations which makes the presentation more attractive and informative.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning
Add and change the position of the text box after adding text to it.
Explanation
Demonstrate to the students how to add a text box and move the position of the text box after adding text to it as given on page 63.
Add new slides.
Demonstrate to the students how to add new slides as given on page 64.
Work with shapes on a slide. Demonstrate to the students how to insert, move, resize and colour shapes on a slide as given on pages 65 and 66.
Work with images in a slide. Demonstrate to the students how to add and edit image in a presentation as given on pages 66 to 68.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 6A section Question 4 and Do It Yourself 6B sections Questions 1, 2, and 3. Encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their notebook. Do It Yourself 6A
Correct Response: 4. a Do It Yourself 6B
Correct Responses: 1. Insert 2. Resizing 3. crop
Build
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among students based on the topic ‘How would you decide which shapes to use for each planet, and what colours would you choose to make a presentation on Solar System?’
Possible Responses: For the sun, we should use a big yellow circle because the sun is really big and bright. For Earth, we can use a smaller circle but colour it blue and green to show the water and land. For Saturn, we should also use a circle but add rings around it. Mars can be a red circle because it’s called the Red Planet. Jupiter is the biggest planet, so we should make its circle bigger than the others, except for the sun. Venus is similar to Earth in size, so we can use a circle of the same size as Earth. For Mercury, we need a small grey circle because it’s the smallest planet and Uranus and Neptune can be light blue and dark blue circles because they’re known as ice giants and have a lot of water and ice.
3 mins
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising how to work with text boxes, slides, shapes, and images in a presentation. It explains how to add text, move text boxes and shapes by clicking and dragging with the mouse, add new slides and add images. It also covers resizing shapes and images by clicking and dragging the blue squares, and cropping images using the Crop tool.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 2
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 3 and 4
C. Who Am I?: Questions 2, 3, and 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 3
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 1, 3, and 4
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1, 3, and 4

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● create a copy of a slide.
● delete a slide.
● showcase a presentation.
● close and open a presentation.
Ask the students what a photocopy machine does. Introduce how to duplicate a slide. Explain the steps to delete a slide. Also, get them familiar with presenting slides and steps to close and open an existing presentation. Group discussion Conclude the concepts Assign homework
Ask the students what a photocopy machine does.
Build the concept that like the photocopy machine Google Slides allows us to duplicate a slide.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes Explanation
Create a copy of a slide. Demonstrate to the students how to create a duplicate slide as given on page 68.
Delete a slide.
Demonstrate the steps of deleting a slide if it’s not needed anymore in the presentation as given on page 69.
Showcase a presentation. Demonstrate them how to showcase a presentation as given on page 69.
Close and Open a presentation.
Explain to the students how to close and open a presentation as given on pages 69 and 70.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 6B section Questions 4 and 5 and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their notebook.
Correct Responses: 4. Duplicate 5. Deleted
7 mins
● Conduct a group discussion in the class among the students based on the topic “Will you be able to retrieve the presentation, if you accidentally deleted your presentation?”
Possible Response: Deleted presentations go to a “Trash” or “Recycle Bin” where they stay for a while before they’re deleted permanently. Yes, a deleted presentation can be restored.
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising how to make a copy of a slide, delete a slide that we don’t need, show the presentation to others. Also, describe them how to close and open an existing presentation.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 4
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 2
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 2

This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Introduction to Coding
2. Creating a Project and Components of Scratch
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● explain what coding is.
● describe block-based coding.
● explain about Scratch 3.0.
Keywords
● Coding: Coding is a way of giving instructions to tell a computer what to do.
● Block-based coding: It is a computer language where we use colourful coding blocks to make computers do a task.
● Scratch 3.0: Scratch 3.0 is a free and simple platform where we use colourful blocks to create our own games, stories, and art.
Have you ever created a fish using an origami sheet by following a sequence of instructions?
Explain to them what coding is; tell them about block-based coding; and introduce them to Scratch 3.0.
Attempt the given activity
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
5 mins
Warm Up
● Have you ever created a fish using an origami sheet by following a sequence of instructions?
● Now, introduce the concept of coding to the students by relating it to the instructions they followed to create the fish.
15 mins
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Explain what coding is. Tell the students that coding is a way of giving instructions to tell a computer what to do, as given on page 73.
Describe block-based coding. Tell the students that block-based coding is is a computer language that uses colourful coding blocks to make computers do a task, as given on page 74.
Explain about Scratch 3.0. Introduce students to Scratch 3.0. Tell them it is a free and simple platform that lets you create your own games, stories, and art, as given on page 74.
Ask the following questions to the students to check their understanding:
● Can you give an example of block-based coding?
Possible response: Scratch, Code.org
● Do you think Scratch is a paid platform?
Possible response: No, it is free to use.
Build
● Solve the maze game.
7 mins











● Conclude the session by summarising that coding is a way of giving instructions to tell a computer what to do. Block-based coding, such as Scratch 3.0, employs colourful coding blocks to create games and perform tasks. It’s a free and simple platform that allows individuals to create their own games, stories, and art.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 1
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 1 and 2
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 1
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● create a project in Scratch.
● identify and define the components of the Scratch window.
Keywords
● Sprite: A sprite can be a character or an object in a Scratch project.
● Script: A script is a set of blocks that are placed on top of each other to make a sprite do something.
Ask the students to define the term Scratch. Explain to the students how to create a project in Scratch and the various components of the Scratch window. Attempt the given activity Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students to define the term Scratch.
● Encourage them to create a project in Scratch.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Create a project in Scratch. Demonstrate to the students how to create a project in Scratch, as given on pages 74 and 75.

Identify and define the components of the Scratch window.
Introduce the students to the various components of the Scratch window, such as the Menu bar, Tabs, Blocks panel, Blocks palette, Coding area, Backdrop, etc., as given on pages 75 and 76.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 7A section and encourage the students to solve the questions. Instruct the students to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
a. Sprite
b. Sprites pane
c. Blocks panel
d. Coding area
e. Blocks palette
Build
7 mins
● Unscramble the words below. All the words are related to Scratch components. Write the correct word in the blank space.
ETRISP
BSTSA
SESUMTCO
Correct Response:
ETRISP SPRITE
BSTSA TABS
SESUMTCO COSTUMES
TPIRSC GATES
TPIRSC SCRIPT GATES STAGE
● Conclude the session by summarising how to create a project in Scratch. The Scratch editor holds all the components needed to create and run a Scratch project. Some of these components are Menu bar, Tabs, Blocks panel, Blocks palette, Coding area, Backdrop, etc. Revise these components with the students.
● Assign the following from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 2, 3, 4, and 5
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5
C. Who Am I?: Question 1
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 3, 4, and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 2, 3, 4, and 5
This chapter is divided into the following sessions
1. Sprites
2. Ways to Add a Backdrop
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● explain what a sprite is.
● add sprites from the sprites library.
● delete a sprite.
Keywords
● Sprite: A character or an object on the stage.
● Costume: It is the appearance of a sprite.
● describe the ways to add a sprite.
● choose a sprite.
● rename a sprite.
● Sprites library: A collection of ready-to-use sprite images.
Ask the students if they have ever worn a costume while participating in a theme event.
Explain to the students what a sprite is; tell them about the costumes and sprites library; show them how to delete a sprite; describe them the ways to add a sprite; tell them how can they choose a sprite and how to rename the sprite’s name.
Attempt the given activity
Conclude the concepts Assign homework

5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students if they have ever worn a costume while participating in a theme event.
● Now, introduce the concept by explaining that a costume in Scratch is a different appearance or look of a sprite, which can be changed to create animations or movements.
Explain the following concepts:
Explain what a sprite is.
Add sprites from the sprites library.
8 mins
Tell the students that a sprite is a character or an object on the stage in Scratch, as given on page 81.
Explain to students that they can add sprites from the sprites library of scratch, as given on pages 81 and 82.
Delete a sprite. Demonstrate to the students the steps to delete a sprite, as given on page 82.
Describe the ways to add a sprite.
Discuss the different ways to add a sprite as given on page 83.
Choose a sprite. Demonstrate to the students the steps to choose a sprite for the project as given on pages 83 and 84.
Rename a sprite. Demonstrate to them the steps to rename the sprites for the project as given on pages 84 and 85.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 2A section Question 1 and encourage students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
1. a.
Build
● Let’s add a sprite from the Scratch’s Sprite library.
Correct Response:
Follow the steps given below:
1. Click on the Delete icon to delete the current sprite.
2. Click on the Choose a Sprite button.
3. Select Choose a Sprite option from the displayed list.
4. The Sprite library opens. Scroll and select the sprite of your choice.
5. The selected sprite appears on the stage.
14 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that sprites are characters that can move, talk, and do things on the stage in a project. Also, explain to the students the steps to add a sprite from the sprites library and delete a sprite. Tell them about different ways to add a sprite, how to choose a sprite, and how to rename it on the stage.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1, 2, and 3
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1, 2, 3 and 5
C. Who Am I?: Questions 2, 3, and 4
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1, 2, 3 and 5
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 1, 3, and 4
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 4

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● describe the ways to add a backdrop.
● choose a backdrop.
● paint a backdrop.
Ask the students what the meaning of “background” is.
Explain to the students different ways to add a backdrop; demonstrate to them how to choose and paint a backdrop. Attempt the given activity Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Ask the students what the meaning of “background” is.
● Now, introduce the concept by explaining that in Scratch, the background is called a backdrop, which sets the scene for a project.
15 mins
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Describe the ways to add a backdrop. Explain to the students that there are four ways to add a backdrop, as given on page 85.
Choose a backdrop. Demonstrate the steps to the students on how to choose a backdrop, as given on pages 85 and 86.
Paint a backdrop. Demonstrate the steps to the students on how to paint a backdrop, as given on pages 87 to 89.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 2A section Question 2 and encourage students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their book.
Correct Responses:
2.

● Create a project and insert the Forest backdrop from the Scratch’s library.
Correct Response:
1. Click on the Choose a Backdrop button in the bottom right corner of the interface.
2. Select the Choose a Backdrop
3. The Scratch library of backdrops opens.
4. Select the Forest
5. The backdrop you have selected appears on the stage.
Sum Up
7 mins
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising the ways to add a backdrop in Scratch. Also, discuss the steps on how to choose and paint a backdrop.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 4 and 5
B. Tick the Correct Options: Question 4
C. Who Am I?: Questions 1 and 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 4
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 2 and 5
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1, 2, and 3

This chapter is divided into the following sessions
Events Block 2. Making a Sprite Say Something
Motion Blocks
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● explain what an event and action is.
● explain what Events blocks do.
Keywords
● Event: They tell us when an action will happen.
● Action: An action happens when an event occurs.
Loops, Control, and Sensing Blocks
Moving and Making a Sprite Fall
Ask the students if they have ever received any invitations. Explain to them what an event and action is. Also, tell them about various Events blocks and their description. Attempt the given activity Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students if they have ever received any invitations.
● Now, build the concept by telling them receiving the invitation is an event, and going to the event is an action.
15 mins
Explain the following concepts:
Explain what an event and action are. Tell the students that an event tells us when an action will happen, as given on page 94.
Explain what Events blocks do. Tell the students that Events blocks tell the computer when to run a script. Also, tell them about some of the Events blocks and their description, as given on pages 94 and 95.
● Ask the following additional questions from the students to check their understanding.
1. Give a real-life example of events and action.
Possible response: Event: Being Hungry
Action: Having Food
2. What is the colour of the Events block?
Possible response: Yellow
Build
● Lets make the ball sprite appears at a random position each time the button is pressed.
Correct Response:
1. Select the Ball sprite in the Sprites List.
2. Go to the Events block category in the Blocks panel.
3. Drag the when green flag clicked block to the Coding Area.
4. Go to the Motion block category.
5. Drag and attach the go to random position block to the when green flag clicked block.
7 mins
6. Click the Go (Green flag) button multiple times to test if the ball sprite appears at a random position each time the button is pressed.

● Conclude the session by summarising that an event tells us when an action will happen. An action happens when an event occurs. The Events blocks tell the computer when to run a script. Also, describe different Events blocks used in Scratch.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Question 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Questions 1 and 5
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 3
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● explain what Looks blocks do.
● make a sprite say something.
Ask the students if they remember the colour of the Looks block.
Explain to the students what Looks blocks do. Also, demonstrate the steps to make a sprite say something.
Attempt the given activity
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students if they remember the colour of the Looks block.
● Now, build the concept by telling them what Looks blocks do.
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explain what Looks blocks do.
Make a sprite say something.
Explanation
Explain to the students that these blocks are used to control how a sprite looks, as given on page 95.
Demonstrate to the students how to make a sprite say something, as given on pages 95 and 96.

Ask the following additional questions from the students to check their understanding.
● Which block is used to make the sprite talk?
Possible response: Say
● Which button is used to check if the sprite says the specified message?
Possible response: Go button
● Create a script to display “Health is Wealth”.
Correct Response:
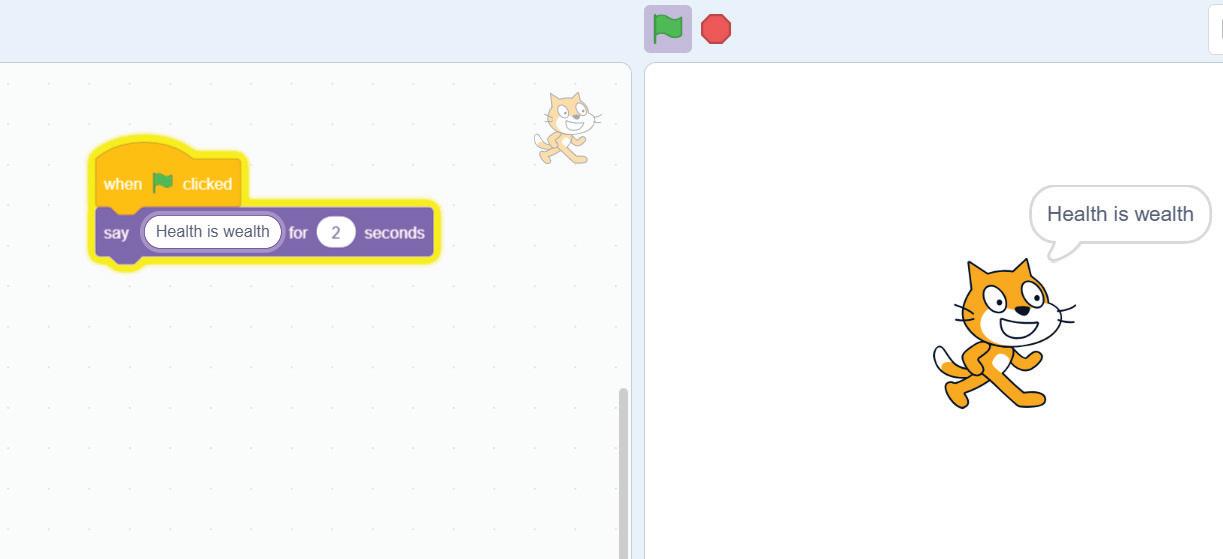
● Conclude the session by summarising that the Looks blocks are used to control how a sprite looks. Their colour is purple. The Say block makes the sprite talk. The Say block is found in the Looks category of blocks. Also, revise the steps to make a sprite say something.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 5
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 2
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 3
At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● explain what Motion blocks do.
● move the sprite to the specified position.
Ask the students which blocks are used to make a sprite move.
Explain to the students what Motion blocks are. Explain to them about different Motion blocks. Demonstrate to them the steps to move a sprite to a specified position. Attempt the given activity
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
5 mins
Warm Up
● Ask the students which blocks are used to make a sprite move.
● Now, build the concept by telling them what motion blocks do.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Explain what Motion blocks do.
Move a sprite to a specified position.
15 mins
Tell the students that Motion blocks control the movement of the sprites on the stage. Also, tell them that a sprite’s X position is its location on the X (horizontal) axis of the stage, and the Y position is where the sprite is on the Y (vertical) axis of the stage. Tell them the uses of some of the Motion blocks, as given on pages 96 and 97.
Demonstrate to the students the steps to move a sprite to a specified position using Motion blocks, as given on page 97.

● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 9A section and encourage students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their book.
1. Correct Responses:
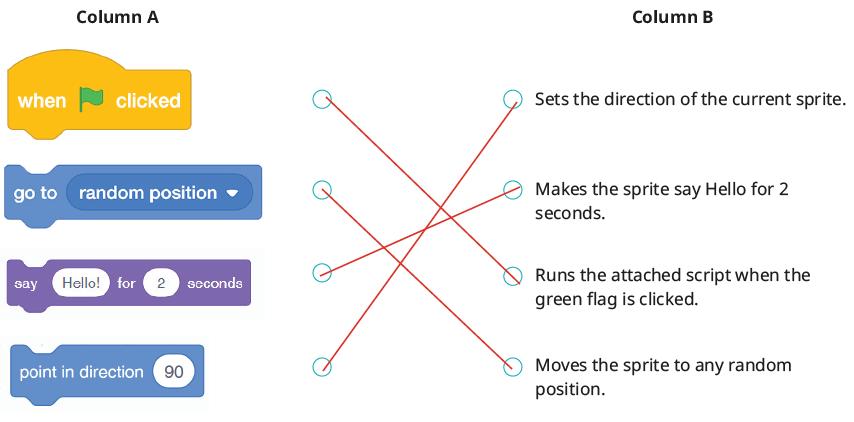
2. a. Events Blocks
b. Looks Blocks
c. Motion Blocks
Build
● Let’s make the Abby sprite move 50 steps forward.
Correct Response:
7 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that the Motion blocks control the movement of the sprite on the stage. Revise the various Motion blocks and the steps to move a sprite to a specified position.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 1 and 4
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 3
C. Who Am I?: Questions 2 and 3
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 4
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 2
F. Apply Your Learning: Question 4

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● explain what a loop is.
● explain what Control blocks do.
● describe Sensing blocks.
Keyword
● Loop: A loop means doing something over and over again.
Ask the students if they have ever been given a task that they needed to repeat a certain number of times. Explain to the students what a loop is; tell them about various Control blocks and Sensing blocks. Attempt the given activity Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Ask the students if they have ever been given a task that they needed to repeat a certain number of times.
● Now, build the concept by explaining that loops are used to repeat a set of instructions multiple times, making tasks easier and more efficient.
Engage
Explain the following concepts:
Learning Outcomes
Explanation
Explain what a loop is. Tell the students that a loop means doing something over and over again, as given on page 99.
Explain what Control blocks do.
Describe Sensing blocks.
Tell the students that the Control blocks are used to control the flow of scripts based on some criteria. Tell them the uses of some of the Control blocks, as given on page 99.
Explain to students that Sensing blocks are the blocks that are used to detect when two sprites touch each other. They also detect the colours on stage, keypress, mouse click, etc., as given on pages 99 and 100.
Ask the following additional questions from the students to check their understanding.
● Which block is used to pause the script for specified seconds.
Possible Response: wait () seconds
● Which block activates the blocks below it when a sprite touches the specified colour.
Possible Response: touching color
Build
7 mins
● Unscramble the following words related to block coding in Scratch. Write the correct word in the blank.
Jumbled Words:
OTLNRCO NGSENIS
Correct Response:
OTLNRCO CONTROL NGSENIS SENSING
ROEFERV FOREVER OPLO LOOP
Sum Up
ROEFERV OPLO
3 mins
● Conclude the session by summarising that loop means doing something over and over again. The Control blocks are used to control the flow of scripts based on a criterion and these blocks appear in orange colour. Sensing blocks are used to detect when two characters touch each other. Their colour is light blue.
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
A. Fill in the Blanks: Questions 2 and 3
B. Tick the Correct Option: Question 4
C. Who Am I?: Question 1
D. Write T for True and F for False: Question 3
E. Answer the Following Questions: Questions 1 and 5

At the end of the session, the students will be able to:
● move a sprite.
● make a sprite fall.
Ask the students to continue with the project. Demonstrate to the students how to write a script to move a sprite and make a sprite fall.
Attempt the given activity
Conclude the concepts
Assign homework
● Ask the students to continue with the project.
Explain the following concepts: Learning
Move a sprite. Demonstrate to the students how to move a sprite, as given on pages 100 and 101.
Make a sprite fall. Demonstrate to the students how to make a sprite fall, as given on pages 101 and 102.
● Read aloud the questions provided in the Do It Yourself 9B section and encourage students to solve them. Instruct them to write the answers in their book.
Correct Response: 1. a.
● Create a script to make the sprite appears at a random position and falls forever.
Correct Response:
1. Select the sprite in the Sprites List.
2. Drag and drop the when green flag clicked block from the Events category in the Scripts Area.
3. Drag and drop the go to x: () y: () block from the Motion category in the Scripts Area.
4. Change the value of x to 9 and y to 155. Join it below the when green flag clicked block.
5. Drag and join the forever block to the go to to x: () y: () block.
6. Go to the Motion block category.
Drag and join the change y by block inside the forever block.
Change the value of y by -10.
Go to the Control block category.
7. Drag and join the wait () seconds block under the change y by -10 block inside the forever block.
8. Change the seconds to 0.2.
9. Click the Go button to test if the sprite appears at a random position and falls forever.
Sum Up
● Conclude the session by summarising the steps to move a sprite and make a sprite fall.
3 mins
● Assign the following questions from the Chapter Checkup given at the end of the chapter as homework.
B. Tick the Correct Option: Questions 1 and 2
E. Answer the Following Questions: Question 4
F. Apply Your Learning: Questions 1 and 2

Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Data 2. information 3. 1024 4. RAM 5. Primary, Secondary
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. a. Hard Drive 2. b. Cloud Storage 3. a. Byte 4. b. Two 5. b. The user clicks on the Print command.
C. Who Am I?
1. Memory Card 2. Data 3. RAM 4. Cloud Storage
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. F 2. F 3. T 4. T
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. Yes, a computer is an electronic device or machine that performs various calculations and carries out different tasks for us based on the instructions that we give it.
2. There are two types of computer memories—Primary and Secondary.
Primary Memory is the computer’s internal memory where it stores data related to currently running programs. It is the built-in memory of the computer. It is always accessible to the CPU.
Secondary memory is the computer’s external storage beyond the primary memory. It is used to store data and programs that are not in use by the computer’s processor.
3. Secondary memory, also called auxiliary memory, is the computer’s external storage beyond the primary memory. It is used to store data and programs that are not in use by the computer’s processor. Some examples are hard disk drive (HDD), pen drive, memory card, etc.
4. Cloud Storage is a digital space where you can store your files and get them whenever you want, using the internet.
Some advantages are as follow:
● Cloud Storage can provide large storage capacity. Often, we get free Cloud Storage of up to a few GBs
● It is like a big storage space on the internet where you can keep all your files and access them from any device, anywhere, and anytime , as long as you are connected to the internet.
5. Data:
● Data is facts, numbers, or symbols that we collect and enter into the computer.
● Data takes up less space.
Information:
● Information is the knowledge or understanding that we gain when the computer analyses and puts together the data that we entered in it.
● Information may require more storage due to added context and structure.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Cloud Storage
2. She should keep in mind the capacity of the RAM and hard disk or SSD.
3. No, Rahul will not find his document exactly as he left it when he turns his computer on again after the power cut. When a computer unexpectedly shuts down, such as during a power cut, any unsaved work or changes made since the last save will be lost.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Operating system 2. booting 3. desktop 4. aero peek 5. notification
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. d. Windows Key + D 2. a. Tracks Memory Usage 3. b. Search Bar 4. a. Icons
C. Who Am I?
1. Operating System 2. Desktop 3. Icon 4. Taskbar
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. F 2. F 3. T 4. T
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. An Operating System is a software that helps us to communicate with the computer and tell it what to do.
2. The two features of the Windows 10 operating system are:
● Search Button: The Search button is a handy tool next to the Start button. It allows you to search for files, programs, settings, and even search the internet.
● Aero Peek: Aero Peek is a feature in Windows that lets you see your desktop without actually minimising any of your open windows. To use Aero Peek, you just need to hover your mouse over open applications in the taskbar.
3. When we press the power button to turn on a computer, the computer starts getting the system ready for use. This process is called booting.
4. The Search button is a handy tool next to the Start button. It allows you to search for files, programs, settings, and even search the internet.
5. Aero Peek is a feature in Windows that lets you see your desktop without actually minimising any of your open windows. To use Aero Peek, you just need to hover your mouse over open applications in the taskbar.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Anika can customise the colour and font settings of her Windows 10 interface, by following the given steps:
i. Click the Start button and select the Settings option.
ii. Choose the Personalization option from the menu.
iii. Select the Colors option from the sidebar and choose a colour of your choice.
iv. Now, select the Fonts option from the sidebar and choose the font style and size.
v. Preview the font as you make the changes.
2. The operating system allows multitasking, enabling Shrishti to open the painting application and the music player at the same time. She can switch between these apps or use them side by side.
3. Urmi can pin shortcuts on the dock area of the taskbar to quickly open her favourite apps. This way, she can access them directly with a single click.
4. John should change the time zone on his computer to India Standard Time (IST) to match the local time. He can do this from the Date and Time settings.
5. John should change the date and time settings on his computer by following the given steps:
i. Open Settings from the Start button.
ii Select the Time & Language option.
iii. Select the Date & Time option.
iv. Toggle the switch to turn on the automatic time settings.

Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. containers 2. Recycle Bin 3. information 4. Ctrl 5. Cut
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. a. Opens it 2. b. Group similar files together 3. a. Digital containers of information
4. a. folder inside another folder
C. Who Am I?
1. Folder 2. File 3. Recycle Bin 4. Cut and Paste
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. F 3. T 4. F
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1 A file is a digital space used to store different types of information on a computer. It acts like a container for items like images, videos, texts, and so on. A folder is a container that stores and organises files and other folders.
2. Moving a File
Moving a file means removing it from its original position and pasting it to another location.
When we want to move a file on a computer, we can use a special command called Cut and Paste.
Duplicating a File
Duplicating a file means making an exact copy of a file and pasting the copied file into a different location.
When we want to duplicate a file on a computer, we can use a special command called Copy and Paste.
3. Shortcut icon helps us quickly open a file or folder. Shortcut icons are usually kept on the desktop to open the most frequently used items.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Avni should not explore the folder without Nishant’s permission because one must be respectful of others’ files. One must not explore the files that belong to someone else without their permission.
2. Raj can get the deleted picture back by restoring the file using the following steps:
i. Opening the Recycle Bin on his computer.
ii. Right-clicking on the file he wants to restore.
iii. Selecting the Restore option from the pop-up menu.
3. No, it is not a wise thing to do because folders are used to organise files and make them easier to find. Tanya should therefore, store the maths homework in the ‘Maths’ folder only.
4. Satish must follow the given steps to create a new folder:
i. Right-click on an empty space on the desktop. A pop-up menu will appear.
ii. Select the New option.
iii. Click on the Folder option.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. computers 2. fibre optic 3. websites 4. information 5. Uniform Resource Locator
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. d. All of the above
2. a. A program that lets you see websites on the internet
3. a. Browsing the internet to visit various websites
4. a. To access websites on the internet
C. Who Am I?
1. URL 2. Search Engines 3. Web browser 4. Modem 5. DSL
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. T 3. T 4. F 5. T
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. The internet is a network of networks that connects computers and devices from all over the world. It allows people to collect and share information, and communicate with each other.
2. Just as we can do only two things with the switch on the switchboard—turn it on or turn it off, similarly, a digital signal either comes in or does not come in.
Just as how a regulator on the switchboard changes the speed at which the fan spins—we can have the fan spin at the fastest speed, reduce it to a slower speed and finally switch it off. That is how analog signal is.
3. A webpage is a digital document on the internet. It can have text, images, videos, and other content.
4. Search engines are used to find information on the internet. Some examples of search engines are Google, Bing, etc.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Riya can use the email service on the internet to wish her friend on his/her birthday. She would need a modem, an ISP and a communication media to connect to and use the internet.
2. DSL
3. Yes, I can help Rohan by telling him that:
a. A webpage is a single document on the internet that can have text, images, videos, and other content whereas, a website is a collection of multiple webpages that are all related to each other.
4. Some popular search engines that Lovey can use are:
a. Google b. Yahoo c. Bing
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. plus (+) 2. subscript 3. top 4. bold 5. paint format
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. b. Working area
2. b. The text at the bottom of every page
3. a. Select the text and click on Superscript in the Format menu
4. a. Line break
5. c. Insert menu
C. Who Am I?
1. Google Docs 2. Paint Format 3. Page Orientation 4. Header
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. F 2. F 3. T 4. F 5. T
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. One of the features of Google Docs is that you get to see all the changes that your friends make online.
2. Page orientation refers to the direction in which a document is displayed.
Steps to change the page orientation:
a. Click on File, and then select Page setup.
b. In the Page setup dialog box, in the Orientation section, select the Portrait or Landscape option.
c. Click on OK.

3. Steps to insert a page break:
a. Click where you want the page break to appear.
b. Click on the Insert menu and select Break.
c. Select the Page break. A page break will be inserted at the current cursor location within the document.
4. Formatting text refers to the process of changing the appearance and layout of a written document or piece of text. This makes it more visually appealing, organised, and easier to read and understand.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Aman can add his name and roll number in the Header so that it appears on every page of the document.
2. Simran can use the Page Break feature.
3. Rahul can use a line break to separate his poem into different stanzas.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. presentation 2. move 3. Toolbar 4. automatically
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. b. Sharing information with others
2. d. Paint
3. a. By clicking on the + button on the toolbar
4. a. Insert
C. Who Am I?
1. Google Slides 2. Crop tool 3. Resize 4. Fill color tool
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. F 2. T 3. F 4. T
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. Click on the Insert tab in the menu bar → Image menu → Select “Upload from computer” → Select the image you want to add to the slide.
2. Steps to duplicate a slide:
● Select the slide you want to duplicate from the Slides Panel.
● Right-click on the slide, and then select the Duplicate slide option.
3. Click on Insert tab → Text box → Move the mouse cursor on the screen where you want to add the text box, then press the left button on the mouse.
4. The method to insert a shape in Google Slides is:
● Click on the Insert tab in the menu bar.
● Select the Shape option from the drop-down menu. Then, select the Shapes option.
● Click on the shape you want. It will appear on your slide.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. Shikha can add an image to her slide with text by following these steps: Click on the Insert tab → Image → select “Upload from computer” option. A selection window opens. She can then select the image to put on the slide. To display text, Shikha should click on Insert tab → Text box → Move the mouse cursor on the part of the image where she wants to add the text box, then press the left button on the mouse and type text.
2. Rahul can add shapes to his slides by clicking on Insert → selecting Shape → selecting any of the options in Shapes.
3. Resizing is changing the size of image from small to large and vice versa, whereas Cropping means to remove those parts of the image that we do not want to show.
4. Jyoti can add colour to the shapes on her Google Slide in the following way:
● Select the part of the shape that you want to colour.
● Click on the Fill color tool on the toolbar and select the colour of your choice.
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Coding 2. Blocks Palette 3. Stage 4. Sprites Pane 5. Stop
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. d. All of these 2. a. Make changes to the sound 3. a. Coding Area 4. b. run the script
5. d. All of these
C. Who Am I?
Sprites Pane
Holds nine categories of blocks
Backdrop Pane Shows backdrops and sprites in action
Blocks Panel Shows the details of sprites
Blocks Palette Adds backgrounds
Stage Holds all blocks of each block category
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. F 2. T 3. F 4. T 5. T
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. Block-based coding is a computer language where we use colourful coding blocks to make computers do a task.
2. Scratch 3.0 is a free and simple platform where we use colourful blocks to create our own games, stories, and art.
3. The Code tab has different code blocks and the Coding Area, where we can drag and join the blocks to make the sprite move and do things.
4. The Add Extensions button provides additional blocks that can be integrated into the Scratch editor’s block palette, expanding its functionality.
5. The green flag is the Go button. You can click on it to run the script. The red button is the Stop button. You can click on it to stop the script from running.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. She can start with block-based coding like Scratch 3.0. It is a free and simple platform where we use colourful blocks to create our own games, stories, and art.
2. Sprite
3. Add Extensions button
4. Change costumes
5. Backdrops Pane

Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Sprite 2. Sprites Library 3. Costume 4. Upload Backdrop 5. four
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. c. Upload Sprite
2. a. Fill
3. b. Size
4. c.

5. c. Add a sprite
C. Who Am I?
1. Backdrop
2. Delete
3. Sprite text box
4. Surprise
5. Upload Backdrop
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. T 3. F 4. T 5. F
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. In Scratch, the sprite is a character that can act. Ways to add a sprite to a project are:
Choose a Sprite
Paint
Surprise
Upload Sprite
2. The Backdrop Pane is used to add, upload, edit, or delete backdrops in our project.
3. Steps to delete a sprite are:
Select the thumbnail of the sprite you want to delete from the Sprite List.
Delete icon will appear.
Click the delete icon to delete the sprite.
4. Follow the given steps to rename a sprite:
Click on the sprite you want to rename in the Sprites Pane.
Click on the Sprite text box and delete the default name.
Type in the new name for your sprite.
Press Enter or click outside the text box.
The new name will be reflected in the Sprites Pane.
5. There are four ways to add a backdrop.
Choose a Backdrop – To choose a backdrop from the Scratch Backdrops Pane.
Paint – To create a backdrop using Paint Editor.
Surprise – To add a random backdrop.
Upload Backdrop – To upload a backdrop from the computer.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1. a. Delete b. Backdrop Pane
2. 1. Upload Backdrop
2. Paint
3. Choose a Backdrop
3. Paint
4. Upload Sprite
Chapter-9 Events and Loops
Chapter Checkup
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. go to random position
2. loop
3. repeat
4. blue
5. event
B. Tick () the Correct Option.

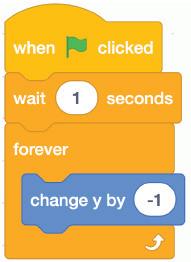


C. Who Am I?

D. Write T for True and F for False. 1. T 2. T 3. F 4. T 5. T
E. Answer the Following Questions.
1. In Scratch, the repeat blocks help us to repeat the actions of a sprite for a specified number of times.

2. a. “change x by 100” will move the sprite forward by 100 steps.
b. “change y by -100” will move the sprite downwards by 100 steps.
3. In Scratch, Events blocks tell the computer when to run a script.
4. The sprite will move backwards by 10 steps on pressing the left arrow key.
5. Repeat Block: A loop that repeats for the specified number of times.
Forever Block: Runs the given set of blocks forever until the Stop button is pressed.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1.
2. The sprite will move upwards by 2 steps forever until the Stop button is pressed.
3.
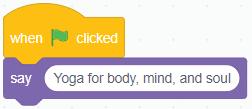
4. The Penguin sprites are moving along the x-axis because they are going right.
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Devices 2. Windows 3. Subfolder 4. Web pages
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. c. 1 GB 2. a. DSL 3. a. Deleting
C. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. T 3. F 4. F
D. Answer the Following Questions.
1. Cloud storage is a digital space where you can store your files and get them whenever you want, using the internet.
2. An operating system is a software that helps us to communicate with the computer and tell it what to do.
3. Restoring a folder or file means getting it back from the Recycle Bin and moving to the previous location.
4. Search engines help you find information on the internet. The internet has billions of websites. So you can find almost anything instantly. Example: - Google, Bing, Yahoo
E. Apply Your Learning.
1. Move the mouse pointer to the taskbar and right-click on it.
Choose the Taskbar settings option from the pop-up menu.
The Settings window opens up for the taskbar features. Scroll down to the option ‘Taskbar location on screen’.
Choose Right from the dropdown menu.
The taskbar will move to the right side of the screen.
2. Right-click on an empty space on the desktop. A pop-up menu will appear.
Place the cursor over the New option.
Click on the Folder option.
A new folder will be created with a default name—New folder.
Type a name for the folder (e.g., "Personal Documents") and press Enter.
To create a folder quickly, press the Ctrl+Shift+N keys together.
3. A web browser is a program that lets you see websites on the internet. Whereas, a website is a collection of web pages that are all related to each other.
A. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Go button 2. Surprise 3. Action 4. Italics
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1. b. Duplicating 2. a. Coding area 3. c. Motion 4. b. Costume
C. Write T for True and F for False.
1. T 2. F 3. T
D. Answer the Following Questions.
1. The Sprites Pane is below the stage. It shows all the details of sprites, like their name, location, and size. You can use it to add, upload, edit, or delete sprites.
2. The Control blocks are used to control the flow of scripts based on some criteria.
3. Formatting text refers to the process of changing the appearance and layout of a written document or piece of text. This makes it more visually appealing, organised, and easier to read and understand.
4. Click on Rename box. Type the new name for your file. Press the Enter key and the file will be automatically saved.
E. Apply Your Learning.
1. When (green flag) clicked Say (Health is wealth) for 2 seconds
2. Eat an apple
3. Atishay should use the subscript formatting option to make the "2" appear below the the regular text line, as in CO2

Uolo has introduced a comprehensive program, Hexa, for Grades 1 to 8, aimed at empowering young minds with essential knowledge and skills for the digital age.
To support the effective implementation of Hexa in classrooms, this Teacher Manual has been thoughtfully designed. It provides structured lesson plans for each chapter, guiding teachers through both classroom instruction and computer lab activities. Every lesson follows Uolo’s research-based WEBS framework, which simplifies teaching methodologies and enhances lesson delivery, making learning more engaging and impactful for students.
• Sharp Lesson Planning: Each lesson plan focuses on specific sub-learning outcomes within a chapter and are designed for delivery within the stipulated class or lab time.
• Real-life and Application-based Questions: Additional questions that link Computer Science to real-life contexts and assist teachers to develop learners' conceptual understanding and application skills.
• Support and Detailed Solutions: In-depth solutions for in-class and post-class activities to reinforce learning.
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to bring technology-based learning programs. We believe pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, South East Asia, and the Middle East.
ISBN 978-81-985754-9-4
