Revolutionizing Organ Transplantation From Matching to Printing
SHRIYA SHARMA, MBBS, Division of Advanced Heart Failure and Transplant, Mayo Clinic
ROHAN GOSWAMI, MD, Director of Heart Transplant Innovation and Research, Mayo Clinic

Sponsors:






SHRIYA SHARMA, MBBS, Division of Advanced Heart Failure and Transplant, Mayo Clinic
ROHAN GOSWAMI, MD, Director of Heart Transplant Innovation and Research, Mayo Clinic

Sponsors:





In this edition of our magazine, we explore the ground-breaking frontier in medical technology that is set to redefine the horizons of healthcare and bioengineering: 3D bio printing. This cutting-edge technology, capable of fabricating patient-specific organs with unprecedented precision, represents a significant leap forward from the traditional challenges of organ transplantation.
3D bio printing serves as a beacon of hope amidst the pressing challenges of modern medicine. Leveraging advanced bio inks composed of biopolymers and stem cells, this technology allows for the creation of complex organ structures tailored specifically to individual patients. This breakthrough significantly reduces reliance on donor organs and opens unprecedented opportunities for personalized medicine. The precision of 3D printing enables the production of organs that perfectly match the patient’s tissue characteristics, thereby minimizing the risk of rejection and improving transplantation outcomes.
As we delve deeper into this issue, we uncover the vast potential of 3D bio printing in revolutionizing the field of organ transplantation. From reducing wait times and eliminating organ shortages to offering more predictable and successful outcomes, the implications of integrating 3D bioprinting into healthcare are profound. Moreover, this technology fosters advancements in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, paving the way for innovations that extend beyond transplantation to therapeutic applications and drug testing.
However, the road to integrating 3D bioprinting into clinical practice is not devoid of hurdles. Technical, ethical, and regulatory challenges need to be addressed to fully realize the potential of this technology. Issues such as cell sourcing, long-term viability of printed organs, and the development of standardized regulatory frameworks are among the critical areas requiring focused attention and concerted effort.
As we present this edition, filled with expert insights, case studies, and in-depth analyses, we invite our readers—healthcare professionals, policymakers, and technology innovators—to explore the remarkable capabilities and future prospects of 3D bioprinting. This issue not only aims to illuminate but also to inspire action towards embracing and advancing this technology to meet the urgent needs of patients worldwide.
Turn the page and explore how 3D bioprinting is expanding the horizons of what medical science can achieve, taking us into a future where the possibilities of medicine reach dimensions we once only imagined.
Thank you for joining us on this captivating exploration into the future of medicine!
N D Vijaya Lakshmi Editor08 Leadership in Healthcare Innovation: Aligning Education Curricula to Address Adaptive Challenges
Dr Dimitrios Kalogeropoulos, Chief Executive, Global Health Digital Innovation Foundation
16 Surgical Simulation and VR training in Cardiothoracic Surgery
Anitha Chandrasekhar, Clinical Lead- Lung Bioengineering and Organ Procurement, Northwestern Medicine
24 Rare Disease Diagnostics
James Doulgeris, Chairman, Population Health, Advisory Board, RSDSA
34 Adapting To Change: How Advanced Technology Can Elevate Healthcare Outcomes
Preetha Vasanji, President – Emerging Markets, Doceree
39 Innovative Medical Devices in Cardiology: Shaping the Future of Medicine
Thomas Bartel, MD, PhD, Interventional Cardiologist, flexdoc GmbH
46 Digitally Empowered Collaborative Care: Revolutionizing Healthcare Delivery in India
Col (Dr) Surendra Ramamurthy, Healthcare Technology & Digital Health Advisor, Indian Armed Forces Veteran
52 Advancing Healthcare The Case for AI in Care Coordination
Dr DJ Hamblin-Brown, CEO,

Shriya Sharma
MBBS, Division of Advanced Heart Failure and Transplant, Mayo Clinic
Rohan Goswami MD, Director of Heart Transplant Innovation and Research, Mayo Clinic
57 Healthcare in the New Era: Healthy Life, Disease Prevention, and Precision Medicine
Constantine A. Stratakis, Director, Human Genetics & Precision Medicine, FORTH, Greece
64 Digital Health and AI Integration in Healthcare
Dipu Patel, Vice Chair for Innovation and Professor, University of Pittsburgh’s DPAS program
72 Unveiling Patient Outcomes in Minimally Invasive Interventions
Nikolaos Patelis, Vascular & Endovascular surgeon. Head of Department of Minimally Invasive Vascular Surgery. Co-founder of MED-Pie group


Andrey Andreevich Kapitonov
CEO, Oxygen Technologies Group, UK














Aung Pyae Kyaw
Executive Director, Asia Royal Hospital, Myanmar
Eiman Shafa
Medical Director, Spine Surgery Abbott Northwestern Hospital, USA
David Anthony Pearce
Director, Business Alliance EMEA, Asensus Surgical, Germany
Gabe Rijpma
CEO, Aceso Health, New Zealand
Guglielmo Brayda
CEO, Inframedica Sarl, Luxembourg
Hassan Mostafa Mohammed
Chairman & Chief Executive Officer, ReyadaPro, Saudi Arabia
Likaa Najuib
Medical Marketing Operational Officer, Alfacure Oncology Center, Egypt
Paola Antonini
Chief Scientific Officer, Meditrial Global CRO, Italy
Pinheiro Neto Joao
Chief Executive Officer, Meu Doutor, Angola
Piyanun Yenjit
Managing Director, APUK Co.,Ltd, Bangkok
Predrag Ristic
CEO, Pharmillennium Consulting L.L.C., Serbia
Simon Ferdinand Waslander
Director of Collaboration, CureDAO, Aruba
Thitisak Kitthaweesin
Chief of Phramongkutklao Center of Academic and International Relations Administration, Thailand
Vicknesh Krishnan
Associate Medical Director, Fresenius Medical Care Malaysia Sdn. Bhd., Malaysia
EDITOR
Vijaya Lakshmi N D
EDITORIAL TEAM
Sarah Richards
Debi Jones
Harry Callum
Supraja B R
ART DIRECTOR
M Abdul Hannan
PRODUCT MANAGER
Jeff Kenney
SENIOR PRODUCT ASSOCIATES
Sussane Vincent
John Milton
Peter Thomas
PRODUCT ASSOCIATE
Ethan Wade
Jacob Higgins
CIRCULATION TEAM
Sam Smith
SUBSCRIPTIONS IN-CHARGE
Vijay Kumar Gaddam
HEAD-OPERATIONS
Sivala VNR


www.europeanhhm.com






• Use the webinar as a platform to launch new products and services
• Grow your audience with increased reach, Impact and user-friendliness
• Rise above geographical boundaries
• Generate new business
• Gain the strong web presence differentiating yourself from competitors
Highly accountable marketing campaigns. Every dollar counts. Digitally powered marketing campaigns may be cheaper than you thought...
Email: advertise@europeanhhm.com
Web:-www.europeanhhm.com
• Connect and engage with your target audience
• Give more exposure to industry specific people
• Increase your brand profile and share your capabilities with leading industry professionals
Healthcare confronts unparalleled challenges, necessitating innovative solutions such as upstream, collaborative, and adaptive innovation to alleviate the strain on acute care facilities. Grassroots community engagement and digital health autonomy hold immense potential for enhancing efficiencies and supporting healthcare professionals grappling with unprecedented complexity and stress. However, realizing these objectives demands a cultural shift toward adaptive leadership and collaboration. Effective leadership is paramount for driving open patient-centred innovation and ensuring timely advancements are effectively translated into tangible patient care improvements. Establishing a new educational paradigm focused on adaptive leadership in healthcare innovation is advocated to drive progress and bolster industry sustainability.
Dr Dimitrios Kalogeropoulos Chief Executive, Global Health Digital Innovation FoundationThe COVID-19 pandemic has brought to light the vulnerabilities of global healthcare systems, shedding light on deep-seated disparities and overlooked populations. Addressing these gaps requires urgent action, with robust digital solutions, including Artificial Intelligence (AI), emerging as promising avenues. However,
effectively leveraging such technologies necessitates a fundamental reassessment of leadership culture, emphasizing inclusivity and trust to foster full stakeholder participation and coordinated public health services. Realising the full potential of digital solutions demands a culture of open innovation, digital collaboration, and adaptive leadership. Leaders must skilfully foster cooperation to ensure that technological advancements translate into tangible improvements in patient care, outcomes, and system efficiency.

Establishing academic units dedicated to Leadership in Healthcare Innovation is imperative, to prioritise data-coupled collaborative innovation, accelerate medical progress, and fortify critical healthcare sectors such as biotechnology and clinical trials. Central to this approach is empowering Learning Health Systems (LHS) with precision medicine knowledge mobilisation, facilitating value co-creation, and driving the adoption of digital health technologies and telehealth for civic engagement. By involving patients in healthcare approaches and enhancing disease
understanding, transparency is maximised, optimising decision-making and resource allocation while advancing health equity. This transition towards “just-in-time” adaptive LHS holds the promise of ushering healthcare into a circular economy, where resources are used efficiently, and rendering sustainable healthcare systems achievable.
The primary objective of this new educational paradigm is to cultivate a cohort of healthcare leaders equipped with the skills needed to foster collaborative innovation across the industry. Through interdisciplinary
education, research, and stakeholder engagement, these units instil a culture of innovation, enabling leaders to navigate the complexities of modern healthcare systems adeptly. This initiative aims to drive positive change in innovation ecosystems and propel healthcare advancement for all.
In the dynamic landscape of healthcare innovation, discussions surrounding generalpurpose AI and Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly shaping policy agendas. As regulatory efforts intensify, public leaders must emphasize their potential to revolutionize translational research and foster agile LHS. Acknowledging both their benefits and risks is crucial, ensuring evidence transparency and addressing concerns regarding digital responsibility and patient autonomy.
Aligned with the 73rd World Health Assembly Resolution on Digital Health (2018), our efforts to strengthen digital ecosystems in global health aim to address unmet needs and equitable access to health care. The World Health Organization (WHO) prioritizes leadership, public health impact, and the promotion of global public goods, emphasizing resilience. However, persisting silos and fragmentation hinder progress. In navigating the adaptive challenges involved, collaborative leadership must prioritize broad industry and patient engagement to ensure successful adoption and integration
of innovative technologies. By fostering cooperation and transparency, stakeholders can navigate the complexities of the evolving healthcare landscape and drive positive transformations benefiting patients and healthcare systems alike.
Responding to the challenge, global health leaders are realigning their strategies and policies to prioritize collaboration. The United Nations, the WHO, and the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development have published relevant approaches to bridge the growing innovation divide, accelerate progress on the Sustainable Development Goals, and address the challenge of responsible AI adoption.
Regulatory optimization is vital to foster digital cooperation and transform the medical technology industry. Initiatives like the EU AI Act highlight the importance of regulatory sandbox facilitation for safe innovation acceleration. This approach holds immense potential for industry value sharing and promoting cooperation and synergies while upholding evidence quality and mitigating environmental impacts associated with current evidence practices. Additionally, it supports regulatory bodies in understanding adaptive regulatory requirements- such as those set forth by LLMs and continual learning, accelerates responsible adoption of innovative solutions in the pre-marketing phase, and encourages industry-wide collaboration, minimizing regulatory burdens on small to medium enterprises and start-ups.
Harnessing the power of evidence has long been a goal of AI, aiming to bridge innovation divides and create an expanded evidence ecosystem accessible to all patients and caregivers. However, health governance in this digital age often lags, struggling to keep pace with the accelerating risks and complexities created by technology. It is crucial that coherent information is available and translational mechanisms are retooled to respond to existing and future health challenges and emergencies adequately. Recent initiatives that refocus health innovation governance further upstream underscore the commitment to bridge data gaps and asymmetries across health systems and communities. Enabling data-coupled innovation is key to upstream change and equitable outcomes, empowering historically marginalized populations with digital health autonomy.
Yet, despite strides in standardizing information sharing in the healthcare industry, the digital divide continues to grow, as underscored by continuing care fragmentation and information asymmetries. Efforts to address this must move beyond technocratic innovation to embrace collaborative governance models that include environmental and societal considerations in design, as outlined in the quintuple helix innovation model. The clinical trials industry, as the gatekeeper to social innovation in healthcare, faces significant
challenges in efficiency and inclusivity. There is a pressing need to evolve towards a more inclusive and agile industry, advancing patient safety and addressing the translation chasm from innovation to market.

The goal of collaborative leadership is to empower a new culture of adaptive LHS that evolve alongside technological advancements. By prioritizing collaborative evidence generation and inclusivity, stakeholders can create shared value, drive systemic change, and advance towards achieving our goals for health equity. The proposed culture of collaborative leadership presents a paradigm shift in healthcare and innovation governance, fostering ecosystems that encourage participation and shared value creation. By harnessing the power
of technology, data, and collective intelligence, it shapes a future where healthcare innovation serves society and the environment, leaving no one behind. Key objectives include breaking down data silos, promoting cross-cutting collaboration to support the quintuple aim of healthcare improvement, scaling innovation, embedding equity and inclusion in evidence ecosystems, establishing a robust governance framework, and expanding patient data portability standards and regulatory approaches. An adaptive collaboration model is emphasized to accommodate evolving challenges and foster ongoing dialogue among stakeholders.
As we venture further into the realm of integrating AI into our social innovation endeavours aimed at revolutionizing healthcare delivery, it's crucial to stay grounded in the multidisciplinary approach that has brought us this far. Revisiting health informatics with a focus on necessary agility at the intersection of intervention design, clinical practice, and innovation management, empowers designers and leaders to enhance patient-centred care with evidence-based approaches. A key aspect is integrating data analysis practices more closely with intervention design as complementary components and enhancing participation. This approach not only facilitates the ecological synthesis of data into decision-supporting information and knowledge but also addresses the complexities of adopting a systems approach
to patient-centric knowledge development. This requires iterative cycles of inductive and deductive reasoning and experimentation. This iterative process has paved the way for the modern coupling of data-driven, AI-powered, and telehealth-delivered healthcare solutions. This convergence holds the potential for significant innovation acceleration, driven by embedded scientific inquiry. Moreover, amidst the ongoing hype surrounding AI, it's essential to maintain a focus on tangible targets and outcomes and their systematic pursuit. Responsible and meaningful uses of AI are paramount in harnessing the transformative opportunities it presents, benefiting patients inclusively and across diverse populations.
The objectives of new multidisciplinary education curricula must align with the need to address adaptive challenges in global health systems by fostering collaborative leadership capabilities. Overall, the aim is to equip future healthcare leaders with the skills, knowledge, and values needed to navigate complex healthcare environments and drive positive change in global health systems. Key objectives include:
• Develop a dynamic curriculum integrating leadership theories, innovation management principles, healthcare policy analysis, informatics and digital health technologies.
• Offer courses on adaptive and collaborative
Advocating for a new educational approach centered on adaptive leadership in healthcare innovation, aiming to propel progress and enhance industry sustainability.
leadership, design thinking, communitybased participatory research, and ethical implications of social innovation in care models, including AI adoption.
• Conduct cutting-edge research on collaborative innovation models, patient navigation, community engagement strategies, and the impact of digital health technologies on healthcare delivery.
• Encourage research addressing health equity, population health management, AI integration in clinical practice, and regulatory interventions.
• Cultivate adaptable collaboration networks among medical schools, healthcare providers, professional associations, and regulatory bodies to align educational goals with healthcare outcomes.
• Strengthen connections between academic curricula and clinical practice for real-world applicability.
• Address data-related risks and robust regulatory oversight.
• Promote innovative pre-marketing solutions and standards for responsible technology use that minimise regulatory burdens on SMEs/ startups.
• Support collaborative ecosystems for interconnected AI and other digital applications and ensure regulatory sandboxes operate with reliable evidence.
• Forge strategic alliances with healthcare providers, technology firms, government agencies, and community organizations to co-create educational programs and research initiatives.
• Develop mentorship programs and incubation support for healthcare startups and social enterprises.
• Offer mentorship, coaching, and networking opportunities for students and alumni dedicated to driving healthcare innovation.
• Harness healthcare informatics to advance patient-centred care and evidence-based approaches.
• Integrate data analysis practices with adaptive intervention designs to synthesize
decision-supporting information and accelerate innovation driven by scientific inquiry.
• Guide the industry with a focus on tangible outcomes and responsible technology use for inclusive patient benefits.
By achieving these objectives, the education curricula aim to bridge the gap between current fragmented healthcare services and the envisioned shift towards patient-centric and community-focused care models. Key outcomes include:
• Develop a cohort of healthcare leaders adept at nurturing collaborative innovation industry-wide, navigating adaptive challenges, and driving systemic change to enhance patient outcomes across diverse healthcare environments.
• Cultivate a culture of continual learning, experimentation, and adaptation among healthcare professionals to accelerate the adoption of innovative practices and technologies, including AI.
• Facilitate the collaborative creation of scalable solutions that target the underlying causes of healthcare challenges, promote health equity, and bolster the resilience of healthcare systems.
• Advance systems thinking in evidence-based policies, practices, and regulations to ensure the ethical and responsible utilization of innovation in healthcare, contributing to sustainable progress in the field.
The establishment of academic units dedicated to collaborative leadership in healthcare innovation is a proactive response to the evolving needs of healthcare systems globally. By providing leaders with the necessary knowledge, skills, and networks to drive collaborative innovation, we can expedite progress toward a more equitable, efficient, and patient-centred healthcare ecosystem. Through interdisciplinary collaboration, community engagement, and transformative leadership, we can shape a future where healthcare innovation flourishes, ensuring that every individual receives the quality care they deserve.

Dr Dimitrios Kalogeropoulos is Chief Executive at the Global Health Digital Innovation Foundation, UK, and Health Executive in Residence at the UCL Global Business School for Health and mentor in leading accelerator programmes. He has a twenty-year track record consulting with multilateral organizations and philanthropies to advance global health with collaborative and digitally inclusive innovation.





The intensifying complexity of surgical procedures, the pursuit of better outcomes, greater emphasis on patient safety, and the ever-increasing audit of surgical practice and associated complications have diminished the quality of hands-on surgical training in cardiothoracic surgery. Advancements in computing have enabled the creation of high-quality Virtual Reality (VR) simulations and anatomy visualization tools. VR technology has already proven effective in industries such as aviation, construction, and the military. VR technology is now revolutionizing healthcare and healthcare education by providing an immersive learning experience through VR-based simulation scenarios. This enables healthcare professionals to gain practical knowledge and skills in a safe and controlled environment, leading to better patient outcomes.
Anitha Chandrasekhar Clinical Lead- Lung Bioengineering and Organ Procurement, Northwestern MedicineFor more than 2,500 years, surgical simulators have been a crucial tool in the field of medicine.
One of the earliest recorded instances of surgical
simulation dates back to around 600 B.C. in India when leaf and clay models were used to visualize nasal reconstruction with a forehead flap. Subsequently, wooden bench-top models, live animals and human cadavers were all utilized for surgical simulator training, to devise pioneering procedures and ensure that patient safety was never compromised. Their continued use today is a testament to their effectiveness and the advantages they bring to both medical professionals and patients alike.
In the 1980s, the field of medical simulation witnessed a significant breakthrough with the introduction of computerized patient simulators (manikins) into anesthesia training programs. This development revolutionized the way medical students and practitioners learn and practice their skills, paving the way for more effective and efficient training methodologies. The original manikins employed cutting-edge technology, including microprocessor chips and advanced computer software, to flawlessly imitate vital signs and respond to interventions and emergencies with utmost accuracy and precision. Since then, remarkably realistic computer images have been developed utilizing wireless technologies with high-fidelity human similitude to enable training for a wide range of surgical procedures.
The introduction of VR simulation in the 1990s revolutionized the field of surgical simulation. VR offers immersive, stereoscopic, 3D views of an environment through a headmounted or console-mounted display. VR simulations are state-of-the-art computer-
based systems that provide an unparalleled opportunity for surgical trainees to practice surgical techniques. By utilizing advanced tools to manipulate a series of highly realistic computerized images, trainees can perform complex surgeries in a virtual environment, allowing them to hone their skills with absolute precision and confidence. VR simulators have evolved and today they combine physical surgical tools with digital technology by incorporating the latest advancements in both medical equipment and computerized imaging. The next unequivocally impressive advancement in surgical simulation is the creation of simulation programs for the robot-assisted surgical system that instructs inexperienced surgeons on the techniques necessary for performing robot-assisted surgery.
Simulation can greatly benefit Cardiothoracic (CT) surgery training due to the high risks and broad range of techniques involved including open, minimally invasive, and endovascular procedures. CT surgery is uniquely suited for virtual reality due to its dynamic anatomy, focus on decreasing invasiveness and commitment to innovation. With a rise in cardiovascular and thoracic disease burden, the number of CT surgeons is expected to decrease by 50% in the next 10 years, leading to a high demand for well-trained and efficient CT surgeons. Simulation can increase learning opportunities, reduce costs, decrease OR time, and help in
the seamless integration of new technologies into patient care.
Newly structured curricula are being created that focus on incorporating simulations into the daily training of residents. This dedicated approach aims to improve the quality of training by providing practical experience in a controlled setting. Hybrid simulators represent a valuable tool for improving surgical skills and ultimately enhancing patient outcomes.
Current surgical simulators fall into various categories of innovations, with significant heterogeneity in their quality and methodology. One involves the use of cutting-edge technologies such as rapid prototyping and patient-specific virtual reality. Surgeons
can achieve the highest level of realism by practicing on models that precisely represent their patient’s case. Another involves increasing access to expert surgeons through telesurgery, which can be especially beneficial in remote or underserved areas. Through the Virtual interactive presence and augmented reality (VIPAR) system, the visual field of a surgeon in one location is projected to another surgeon elsewhere through simulation, allowing realtime guidance by a more experienced surgeon. By utilizing augmented reality technology, the VIPAR system enables low-latency audiovisual collaboration over the Internet. Therefore, participants located in different places can join forces to recognize anatomical structures, guide surgical maneuvers, and brainstorm comprehensive surgical approaches.

A Cardiopulmonary bypass simulator system has been devised to train a team of surgeons, anesthesiologists, perfusionists, and OR nurses together in an OR with a heart-lung machine, heater/cooler system, patient monitor, anesthetic machine, and an artificial patient alternative. This system can be connected to a monitor to display vital parameters, blood gas analysis, and coagulation parameters based on a pre-set model prepared by an instructor. This learning method was found to be better than classroom or clinical-based teaching.
The Virtual Reality Extracorporeal Circulation simulator or VRECC sim is a unique system that helps to build up competency and experience with rare events/ machinery malfunctions, without necessitating a physical simulator or jeopardizing patient safety.
A beating heart simulator system consisting of a porcine heart with right and left ventricular chambers filled with balloons, connected to a computer-assisted pneumatic system allows the balloon inflation to simulate the heart contraction. With artificial blood supplying the entire system, the heart is positioned in a well in the anterior chest wall of an adult Manikin mimicking standard median sternotomy.
In practice, the 3D VR visualization of coronary and thoracic anatomy can help produce a surgical plan for graft locations, as well as optimize port placement in minimally
invasive coronary artery bypass surgery for internal mammary artery harvesting, and minithoracotomy positioning.
Valvular repair
Valvular surgeries have been significantly enhanced by VR technology. Surgeons can now visualize different types of valvular lesions with greater clarity, which in turn has increased their confidence in determining the optimal surgical approach. VR shows valvular & annular pathology more clearly than echocardiography. This has ultimately led to better outcomes for patients undergoing these procedures.
cardiac surgery
VR has a compelling application in visualizing intracardiac malformation during congenital cardiac surgery. A study reported the use of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging to show a 3DVR image of a child with multiple VSDs to both a cardiac surgery team and a cardiac intervention team, and both succeeded in closing these defects via a hybrid approach after VR deemed that the largest VSD the approach for the largest VSD via the tricuspid valve was impossible. VR 3D anatomical visualization of Major Aortopulmonary collateral arteries (MAPCAs) is a valuable tool that can confirm findings not detected by angiography. For Double outlet right ventricle (DORV) cases, VR has helped in improved visualization of the location, a better understanding of the relation to other structures, and the severity of obstruction.
Using VR technology, trainees can get familiar with various real-life pathological models and complex cases derived from imaging data of actual patients, which would be highly challenging to replicate using animal tissue.
VR assists with positioning the inflow cannula for left ventricular assist devices and reduces imaging artifacts associated with implanted devices.
The Virtual Reality system for VATS lobectomy consists of a computer screen projecting an OR view of a patient in the left lateral decubitus position, transitioning to an internal view of the lung, hilum, and mediastinum on thoracoscope placement into an artificial chest wall. A haptic feedback device controls the movement of virtual instruments to mimic the physical constraints of VATS.
Using 3D VR visualization, VR-guided segmentectomies and lobectomies have been shown to produce great results.
VR Simulation training improves accuracy, confidence, and timing during procedures. Significant takeaways include better clinical
knowledge, increased confidence in handling adverse events like air embolisms, and improved teamwork and collaboration with the surgical team. A study reported that medical students were able to achieve coronary anastomotic accuracy and scores like those of experienced surgical trainees.
The ultimate goal of simulation-based training in cardiothoracic surgery is to enhance patient outcomes and service delivery. VR technology is playing an increasingly crucial role in the field of presurgical planning. The ability to create interactive and realistic 3D models of complex anatomical structures is revolutionizing the way surgeons plan and prepare for procedures. With VR, surgeons can explore the intricacies of a patient's unique anatomy in a virtual environment, enabling them to identify potential challenges and develop appropriate strategies to mitigate surgical risk. Moreover, VR offers a more intuitive and immersive experience than traditional 2D images or physical models, allowing surgeons to gain a better understanding of the spatial relationships between anatomical structures. This technology is particularly valuable in cases where the anatomy is complex or aberrant, making it more challenging to visualize using conventional methods. VR planning is making a significant impact on daily clinical practice, particularly in the fields of congenital cardiac surgery and sub-lobar lung resections.

Surgeons have claimed that VR planning is the most significant advancement since the introduction of CT scans in the 1970s.
Over the past decade, the financial obstacles to the implementation of VR and augmented reality (AR) in a surgical environment have decreased as more affordable technology with considerably more robust processing capability has become available and the advantages of using VR for enhancing patient safety, surgical education, and quality assessment have become apparent. The costs associated with implementing VR and AR technology in surgical settings are becoming more affordable due to the use and adaptation of commercially available hardware that is
non-specific in its use. Recently developed VR headsets provide high-quality visuals and realistic surgeon-hand interactions, thus making these technologies more accessible for healthcare providers.
VR can replace costly cadaveric and animal tissue models in surgical teaching while offering a wider range of anatomical variations. Moreover, VR enables learners to repeat the learning experience, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of the curricula while also leading to long-term cost savings. VR has proven to be an effective and valuable alternative to traditional operating room learning sessions, especially in the context of robotic surgery. This is particularly significant as robotic surgery can be quite expensive to use and implement.
The major advantages of VR in surgical education include patient safety, the opportunity to make mistakes, global health outreach, remote learning, improved longitudinal training, and evaluation of trainee competencies.
Because simulation tools seem to score high in their potential to mimic reality and their possibility to present a varying set of cases and differing levels of difficulty, there is no doubt in clinical usefulness. Apart from visual simulation advantages, the development of instrumental simulation tools having haptic feedback also seems to add great value to the potential of surgical training simulators in cardiothoracic surgery. All these various benefits of VR surgical training simulators are suitable for use by surgical residents during their training stage, for less experienced surgeons attempting to master surgical techniques, and for experienced surgeons learning new surgical procedures. VR can not only improve technical skills but also surgical team dynamics. This could involve simulating surgical emergencies, modifying operative planning, or refining communication skills among team members. The implementation of a multiuser platform where trainees can collaborate in a virtual environment could expand the potential of VR beyond technique acquisition.
The global implementation of VR for training purposes is still hindered by a lack of some important features. Despite
Extended reality (XR) combines physical and virtual 3D interfaces using wearables and remote controllers for humanmachine interaction.
improvements in this technology over the last few years, some users may still experience discomfort, such as dizziness, headaches, or motion sickness. Users may also become disoriented by extensively manipulating, scaling, and rotating VR patient models in a fully virtual world. Moreover, the lack of tactile feedback remains a challenge for learners who must use controllers instead of real surgical instruments. Other disadvantages of VR in surgical education include financial barriers, decreased human interactions, access to internet connectivity, and possible potentiation of educational inequity.
Extended reality (XR) combines physical and virtual 3D interfaces using wearables and remote controllers for human-machine interaction. This includes the sub-techniques of VR, AR, and mixed reality (MR). All these interfaces allow users to view or interact
with computer-generated 3D interfaces in a physical and virtual world, either in VR or hybrid (MR and AR) environments. With the instantaneous development of new XR devices, their potential for use in healthcare is unavoidable. It is believed that emerging digital techniques will extensively impact healthcare, particularly in surgical fields where narrow and clear visualization is mandatory.
The swift progress in XR technology presents a promising opportunity to address various obstacles in the surgical field through the development of cutting-edge hardware and software solutions. Further, the advancement of digital systems specified to cardiothoracic surgery will allow more accurate and detailed studies to validate this still unexplored, promising field
VR presents a multifaceted opportunity to improve various aspects of clinical education, training, and patient care. It can significantly enhance surgical skill acquisition and confidence among medical professionals by offering a flexible and immersive learning modality. It addresses the critical issue of medical errors by allowing trainees to practice in a safe and controlled environment before transitioning to real-life cases. Although initial implementation costs may be high, the slashing prices of VR technology and the long-term cost-effectiveness point to a promising future. Given these advantages, it is apparent that VR
is an invaluable addition to medical education complementing hands-on clinical training. As medical institutions and professionals continue to explore and adapt to this revolutionary technology, VR can transform the field, improving patient safety, surgical outcomes, and healthcare access globally.
 AUTHOR BIO
AUTHOR BIO
Dr. Anitha Chandrasekhar is a Cardiothoracic surgical professional with over two decades of involvement in cardiac surgeries including the entire spectrum of congenital, coronary, valvular, aortic, heart and lung transplantation, and ventricular assist device implantation procedures. She has presented scientific papers extensively in national and international surgical conferences and published many articles in indexed journals. She has held leadership positions in various associations and carved a unique pathway in the cardiac surgical domain. As a passionate ‘Surgical Scientist’, she serves as Clinical Lead- Lung Bioengineering and Organ Procurement at Northwestern Medicine, Chicago, IL, USA.
 James Doulgeris Chairman, Population Health, Advisory Board, RSDSA
James Doulgeris Chairman, Population Health, Advisory Board, RSDSA
Rare diseases cost society an estimated one trillion Euros in Europe and one trillion US dollars in the USA. With over 10,000 rare diseases, there is no practical way to educate doctors on how to identify, diagnose, and treat them. Until now. This article outlines the solution including the pathway to more effective treatments and potential cures.
Among the rare diseases representing about 90% of presently diagnosed rare disease victims, those rare diseases are likely less rare than they are rarely diagnosed. This leaves their undiagnosed victims to suffer needlessly while their disease festers, gathering comorbidities and demanding more and more expensive care.
There is a solution now available that healthcare systems, insurers, legislators and regulators lag behind in recognising. They must work together to solve a problem costing society an estimated two trillion dollars in each of Europe and the United States.
To date, training well over a million clinicians to identify even hundreds out of thousands of rare medical conditions has been simply impossible, which is why, despite the best efforts of so many nonprofit champions of those diseases, has failed.
I know. As the chair of the Advocacy Committee of one of the most notorious, Complex Regional Pain Syndrome, or CRPS, also known as RSD, the subject of the hit Netflix documentary “Take Care of Maya,” even this one disease with a solution at hand has been an uphill battle. And not for lack of trying. I am uniquely motivated because I am a patient.
CRPS is recognised as the most painful chronic disease known to medicine, scoring a 42 out of 50 on the McGill University Pain Scale. It is disabling with a suicidal ideation of 75% and high comorbidity of medication resistant depression and PTSD, all according to peer reviewed studies. Its most effective drug, ketamine, again highlighted in numerous peer reviewed studies, is controversial and not approved for use by regulatory authorities. It is, paradoxically, viewed as a drug of abuse despite its record as an opiate sparing drug.
CRPS is just one example of over 10,000 recognised rare diseases in 2024. The vast
majority are so rare they have populations of one or two. In the world. Five years ago, there were seven thousand.
The economics are shocking, just shy of one trillion US Dollars in 2019 according to a major US study. More on that in a moment because the technology to diagnose the bulk of them, the most destructive to people and society, a silent mass disabler and killer, is available, but healthcare, from payers to providers, are surprisingly disinterested.
The total number of distinct diseases is less relevant than their collective impact.
A 2019 study funded by the EveryLife Foundation for Rare Diseases and conducted by the Lewin Group found that the economic burden in the United States of just 379 of the 10,000 rare diseases with the most patients (a rare disease is defined as occurring in less than one in about 1,700 people) was just shy of one trillion US dollars annually. Europe being larger than the US in population is likely to meet or exceed the US 2019 number. Today, considering the impact of the pandemic, inflation and other economic changes, both Europe and the US are likely to have easily topped the one trillion US dollar and Euro mark in 2023 and continue to be rising.
Furthermore, just these rare diseases were estimated to consume about fourteen percent of all US healthcare spending. These outsized costs should make the most common and costly rare diseases a top priority for early detection, diagnosis, and proper treatment when they
are most effectively managed, yet there are no economic incentives to do so. In the US, government grants are met with little to no interest by legislators and relevant agencies. Public payers actively resist. Regulators are inflexible, introducing chaos into rare disease healthcare communities with off-label drugs that impoverish patients and invite profiteering. Money for research, effective medications, and cures is non-existent because the large investment required for approval cannot be recovered with so few customers at the back end. Rare, or orphan diseases as they are also known, draw little attention and less financial support from private sources.
Despite the public/private disinterest, there is a relatively inexpensive and readily available solution: Employing AI based sub-routines in existing analytic programs to identify rare disease candidates using symptoms and test results common to those diseases. Identifying rare disease candidates is relatively simple as the following five step program shows'. Using healthcare data lakes matched to a patient’s physician through their electronic medical record (EMR) system using unique patient numbers:
1. Establishing clinical identifiers in test, imaging, and natural language to identify potential candidates,
2. Matching the candidate patient with their physician and uploading the proper diagnostic protocol to their physician’s electronic medical record system,
3. Alerting a central database to download
the latest diagnostic protocols to walk the clinician through the proper diagnostic steps, and,
4. If the patient is positive, downloading treatment protocols from the same database, then, finally,
5. Connecting the physician to the relevant nonprofit support group to assist in finding proper specialist support.
Sound complicated? Not really. At scale, a small data center dedicated to the task can “fish” the multiple existing data lakes yielding extraordinary results. What is a healthcare data lake?
A healthcare data lake is a centralized storage center for vast amounts of structured and unstructured data from disparate sources within the healthcare industry. These include electronic health records from physician’s offices (EHRs), medical imaging reports and images, laboratory and other test results, patientgenerated data, clinical trials data, wearable device data, genomic data, billing records, and other historical data on thousands or millions of patients.
Here's an explanation of key aspects and benefits of a data lake in healthcare:
1. Centralized Storage: A data lake provides a centralized location for storing diverse datasets without needing to pre-structure or format them. This allows for easy access to a wide variety of data types without the need for extensive data transformation.
2. Scalability: Data lakes are designed to scale horizontally, meaning they can handle
Rare diseases cause immense suffering and missed treatment opportunities. Using AI analytics is crucial to alleviate pain and find effective solutions.
increasing volumes of data seamlessly, an important factor since health data pours into them at a ferocious rate. This scalability is essential in healthcare, where data volumes are growing rapidly due to advancements in medical technology, increased adoption of electronic health records, and the proliferation of healthcare-related wearable devices feeding data into EHRs.
3.Flexibility: Unlike traditional data warehouses, which require data to be formatted and structured before storage, data lakes accept raw, unprocessed data in its original form, parsed by unique patient identifying numbers. This flexibility allows healthcare organizations to store data from disparate sources without worrying about data format or schema changes while allowing it to remain tied to individual patients.
4.Analytics and Insights: Data lakes enable healthcare organizations, insurers, and analysts to perform advanced analytics and obtain insights from their data limited only by their needs and imagination. By integrating data from
various sources, including clinical, operational, and financial data, healthcare providers can gain a comprehensive understanding of patient populations, treatment outcomes, operational efficiency, and, in the case of classifying individual disease candidates and grouping disease clusters to quickly identify outbreaks like COVID quickly and geocentrically.
5.Data Governance and Security: Despite the massive mixing of tens or hundreds of millions of individual data points, robust data governance and security measures are built into data lakes ensuring patient privacy. Data lakes allow organizations to implement granular access controls, encryption, and auditing capabilities to ensure data privacy and regulatory compliance such as HIPAA laws in the United States.
6.Machine Learning and AI: Data lakes serve as a foundation for implementing machine learning and artificial intelligence algorithms. By leveraging the vast amounts of data stored in data lakes, which can be connected to create data oceans, analysts, researchers and scientists can develop predictive models for disease diagnosis, treatment optimization, patient monitoring, and personalized medicine. These capabilities are critical to develop effective treatments and even cures for rare diseases, most which center around personalized medicine strategies.
7.Interoperability: Interoperability is a significant challenge in healthcare, as data is often siloed across different systems and institutions. Data lakes facilitate interoperability
Rare diseases come at a high cost, measured in human suffering and missed treatment chances. AI analytics are vital to reduce pain and find effective solutions.
by serving as a central data repository where data from various sources can be integrated and accessed seamlessly.
More realistically, even a small nonprofit support group can yield big results on a modest budget with an analytics partner.
Let us pick an excellent candidate, Complex Regional Pain Syndrome, or CRPS, which I have personally worked on a program for from beginning to implementation. CRPS impacts fewer than one of every 2,000 people. A condition that a physician may recognize once or twice in their entire career.
CRPS has an internationally established protocol for diagnosis. While incurable and worsening over time, if diagnosed early, it has a history of being put into remission for years and potentially a lifetime.
Rare diseases like CRPS are rarely diagnosed because physicians are trained to “look for horses when they hear hoofbeats,” otherwise, like Occam’s Razor, the simplest solution is the most likely.
Using indicators and a sub-routine in a powerful analytics program like those available through Optum, Innovaccer, EPIC and many others sifting through data lakes, CRPS candidates can be identified, matched with their primary care physicians, and partnered with downloaded diagnosis and treatment protocols with relative ease.
For example, matching four or five of the following CRPS/RSD Indicators can reliably indicate a candidate:
1. A major or minor trauma or surgery that heals but the pain does not go away and gets worse over time.
2. Pain from the injury spreads to another area or limb.
3. Abnormal hair, nail or skin growth including discoloration and abnormal digit growth such as a toe or finger or multiple toes or fingers.
4. Unexplained edema and/or venial insufficiency.
5. Body temperature instability and temperature differential between one limb to another in excess of 1 degree C.
6. Parkinsonian type tremors or myoclonic spasms.
7. Weakness and/or dystonia in the affected limb.
8. Extreme fatigue.
9. Algesia or hyperalgesia or loss of sensation. Since CRPS frequently strikes children aged 9 to 14 years old, when remission can be achieved through the use of steroid therapy protocols sparing a lifelong disabling disease,
they can be separately be identified using common symptoms including:
1. Severe, Prolonged Limb Pain: This is often described as burning, shooting, or stabbing in nature, or may feel like a "pins and needles" sensation.
2. Allodynia: Pain caused by stimuli that are usually not painful, such as light touch.
3. Hyperalgesia: An increased sensitivity to painful stimuli.
4. Swelling and Changes in Skin Color: Affected limbs may exhibit swelling and changes in skin color, including dry, mottled skin.
5. Functional Impairment: The pain can induce functional impairment, making it difficult for the child to use the affected limb normally.
6. Deep Limb Pain: The pain is often felt deep inside the limbs with a burning, stinging, or tearing sensation.
This is true for many of the most common rare diseases (ironic as it may seem, less than 400 rare diseases represent the vast majority of rare disease patients), virtually all of which have common indicators that can be used to identify candidates using the same method.
Given the massive cost to healthcare systems and society that can be mitigated with a relatively de minimis investment, public/private partnerships with nonprofit rare disease support organizations and academic institutions that have the necessary information to begin these programs and public institutions that have the infrastructure and resources to carry out their implementation must be a pressing priority.
Furthermore, with these mechanisms in place, identifying candidates to participate in studies leading to safe and effective treatments and even cures solve the most difficult element in carrying out those studies with the greatest efficiency and timing.
What is learned here can be shared and implemented throughout the world.
Technology has finally caught up with a great and compelling need. It is time for legislators, government leaders and health officials to act because when they do, a silent epidemic of needless human suffering and impoverishment can be addressed and vanquished.

is a medically retired healthcare executive with over 35 years’ experience in CEO roles in hospitals, accountable care and medical device companies. He is a tireless advocate in the rare disease community chairing the Advocacy Committee for RSDSA and a leader in important initiatives including using AI analytics to identify, diagnose and treat rare disease, bring medically necessary medications on label and prospective cures. He is an active business, science and medical writer and award-winning author.
3D bioprinting revolutionizes tissue engineering by fabricating patientspecific organs using stem cells and biomaterials. Despite challenges like cell sourcing and long-term storage, its precision in creating complex structures offers promise for personalized medicine. Regulatory and ethical considerations are important for its integration into healthcare, potentially transforming organ transplantation and patient care.
Shriya SharmaMBBS, Division of Advanced Heart Failure and Transplant, Mayo Clinic
Rohan GoswamiMD, Director of Heart Transplant Innovation and Research, Mayo Clinic
Transplantation of human cells, tissues, and organs plays an important role in saving lives and restoring essential functions where no comparable alternatives exist. The process involves matching organs based on various characteristics such as blood type, organ size, urgency, and geographical
proximity. The United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) manages the national organ transplant waiting list, ensuring fair distribution of organs from deceased donors.
Currently, approximately half a million patients in the United States await organ transplants, with mortality rates rising due to organ scarcity. Deceased or living donors can potentially donate 25 different organs or tissues, including the kidney, liver, pancreas, lungs, and heart. However, finding a perfect organ match remains challenging, with patients facing an average wait time of 3-5 years, or even longer in certain regions.

Despite significant achievements in transplantation, such as over 800,000 transplants performed in the US since 1988, disparities exist between countries in access to transplantation and the quality of donation and transplantation practices. Ethical concerns, including the shortage of organs leading to potential trafficking, remain significant challenges.
To address the organ shortage crisis, regenerative medicine has seen remarkable advancements, particularly in 3D bioprinting. This technology utilizes bioinks containing biopolymers and stem cells to create 3D-printed organs or tissues. These bioengineered
structures offer potential solutions for organ transplantation or drug testing, with patientspecific treatments becoming feasible through cell differentiation.
3D bioprinting is an innovative technique that employs biopolymers and stem cells, commonly referred to as bioinks, as materials for constructing three-dimensional (3D) structures resembling actual organs. These bioinks are loaded into a 3D printer, which then deposits them layer by layer to fabricate a 3D organ. These printed organs can be utilized for organ
transplants or drug testing purposes, either in vivo or in vitro. Initially, the 3D structure of the tissue or organ is modeled using computer software, followed by the printing of bioinks to create the desired structures. Bioinks typically comprise cultured cells combined with biopolymer hydrogels, such as gelatin or alginate, which provide structural support and protect the living cells during the printing process. Researchers must first determine the specific organ they aim to artificially replicate to create bioinks, then harvest stem cells from the patient. These stem cells, lacking specialized functions, are then induced to differentiate into specific cell types, enabling researchers to develop organ-specific and patient-specific treatments on a larger scale. 3D bioprinting is an industrial manufacturing technology enabling rapid and mass production of components by utilizing computer-aided design (CAD) files to guide the printing process.
3D bioprinting is revolutionizing tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, creating personalized organs for transplantation. Ongoing research and innovation are unlocking its full clinical potential.
3D bioprinting holds significant potential to revolutionize organ transplantation by addressing global organ shortages and improving tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. The technology allows precise control over the deposition of biological components, including biomaterials, stem cells, and biomolecules, in predetermined designs. It offers a solution to the growing need for testing novel tissue fabrication methods and creating advanced disease models. By enabling layer-by-layer deposition of various biomaterials, stem cells, and biomolecules, 3D bioprinting allows for the creation of complex tissue and organ structures with controlled spatial distribution. One of the primary advantages of 3D bioprinting is its ability to fabricate patient-specific organs and tissues, transforming the field of bioengineering and biomedical research. The technique involves directly printing living cells and biomaterials layer by layer according to a CAD model of the desired structure. This enables precise positioning and architectural control of 3D products, including shaping, pore geometry, and interconnectivity, to mimic real human tissue and organs. With its capability for precise cell positioning and patterning, 3D bioprinting has become a powerful tool in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine for fabricating complex, multiscale structures with high reproducibility and repeatability.
Despite its potential, there are several challenges associated with translating 3D bioprinting into clinical applications. One major challenge is sourcing cells for bioprinting, especially patient-derived cells, which require time-consuming processes such as cell expansion and achieving a critical mass of cells for printing tissues of the required scale. Additionally, long-term studies in large animal models are necessary to validate the efficacy and safety of bioprinted constructs before clinical translation. Another challenge is the compatibility of bioprinted tissues for long-term storage and transportation, as well as addressing ethical, legal, and social considerations surrounding the use of bioprinted tissues and organs. Regulatory aspects of bioprinting and commercialization also need to be carefully addressed to ensure the safety and efficacy of bioprinted products.
3D bioprinting represents a groundbreaking advancement in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, offering the potential to create patient-specific organs and tissues for transplantation. While challenges remain, ongoing research and technological innovations hold promise for overcoming these obstacles and realizing the full potential of bioprinting in clinical practice. The integration of 3D bioprinting into
mainstream healthcare could revolutionize organ transplantation and medicine, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
References are available at www.europeanhhm.com

Dr. Sharma, originally from Kathmandu, Nepal, is a Nepalese Army Institute of Health Sciences - College of Medicine graduate. She is currently a Research Fellow in the Division of Advanced Heart Failure and Transplant at the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Florida. She is interested in staying current with the latest developments and contributing to the advancement of medicine with her clinical research in heart failure, artificial intelligence, and transplant medicine. Her aspirations are directed toward a future practicing cardiology, and she eagerly anticipates commencing her Residency training in internal medicine this year.

Dr. Goswami is a Transplant Cardiologist practicing at Mayo Clinic in Florida. He is a graduate of the American University of the Caribbean School of Medicine and completed his internal medicine residency at Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons – Stamford Hospital, a cardiology fellowship at The University of Tennessee Memphis, and a Transplant Fellowship in 2017 at Mayo Clinic in Florida. He has a keen interest in clinically focused artificial intelligence research to improve outcomes in patients with advanced heart failure.
With a host of digital innovations, ranging from AI and telemedicine to wearable technologies and beyond, coming into play, healthcare is set to ride on a new era. This means opening the door to a promise much more comprehensive. Healthcare will be more efficient and accurate, and, at the same time, there will be a way more personalized and patient-centric approach.
 Preetha Vasanji President – Emerging Markets, Doceree
Preetha Vasanji President – Emerging Markets, Doceree
At a time when technology influences almost every aspect of our lives, healthcare is at a critical crossroads. The digital transformation in healthcare is not only a paradigm shift but a revolution— something that purports to change the very meaning by how care is delivered, accessed,
and experienced. Against this background, the industry struggles with pressures of rising costs to inefficiencies and inequities in access and quality of care. Key drivers, including IoT and AI technology, hold great potential to improve the efficiency of operations, predict patient infirmity, and outcomes for patients.
They should rather come with a beacon of hope, radiating rays of shining light in ways that can solve these challenges, yet adopting them is accompanied by a complex array of implications for patients, providers, and the system at large.
As we enter the digital age, it will indeed dawn on us more and more that the traditional paradigms of healthcare delivery are changing in a revolutionary manner. Digital health represents everything from telehealth services and AI-powered diagnostics to IoT-backed wearable health devices and mobile health apps that reshape the very character of the healthcare ecosystem into an agile, responsive, and patient-centric orientation. This transformation focuses not just on the improvement of efficiency and effectiveness of the health care services, but also involves individual empowerment towards taking a basically proactive role in managing their health.
However, the road to realizing the full promise of digital health is not without several real, yet unsolved, challenges along the way, just some of which are noted above and include substantial cultural, regulatory, and technological shifts. It will mean today's healthcare leaders and innovators must also ensure this sector steers forthrightly into the future where the very fabric of the delivery of health interfaces in an unobtrusive way with digital innovation and, from doing so, gains better outputs and, hence, opens doors for a healthier, connected world.
Digital transformation in the sector would imply a huge shift in the way medical services are offered and accessed, with the core being based on the adoption of electronic health records (EHRs). EHRs have really laid the groundwork for a more coordinated, effective, and qualitydriven health care system by ensuring that patient information is accurately kept and accessed with protection in different health care settings.
This foundational shift has set the stage for a suite of digital innovations that are remaking the healthcare landscape. In accordance with recent technology, telemedicine has been noted to be the most indispensable tool in the ongoing of care to patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is also gearing up to disrupt the very core of diagnostics and treatment planning, offering improved, earlier diagnoses and tailor-made treatment tactics with pinpoint targeting of outcomes for the patient. Furthermore, Internet of Things (IoT) in medical devices enable intelligent interactions within healthcare environments, elevating patient care and operational efficiency.
Tech-based solutions are not only growing in the landscape of emerging technologies within healthcare, but might revolutionize the global ecosystem, with capabilities that at times seem science fiction. The technologies that top the list are Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the
Internet of Things (IoT). These are making a revolutionary impact is diagnostic and predictive analytic tools, in patient care management, and effective messaging to HCPs, with enormous data processing and analytical abilities, with great speed and accuracy.
For example, consider there is a new drug for a specific condition in a patient suffering from Diabetes (or any other disease). The pharmaceutical manufacturer has already spent years and huge amounts of investment in testing and manufacturing of the drug that is more effective than the existing drugs. To make HCPs prescribe the drug, ideally and traditionally a representative personally meets with HCPs and tells them about the drug benefits. Imagine this happening, with information reaching thousands of HCPs in a matter of a second, with just a click, that too at the time that the HCP is providing care to the patient. That is the power of AI.
Effective use of AI in healthcare marketing is also enabling clinical trials, affordability and drug adherence in ways that the industry had never imagined.
With healthcare stepping into the realms of digital transformation, it will have to surmount several challenges, and risks will have to be taken up on a gargantuan scale. The only key for such gigantic prospects in new technologies can be complex within the corners of data privacy, cyber security, and ethical angles. Sensitive patient information, amidst ever-growing cyber threats, would need both immense security protocols and a culture of incessant vigilance. This potential bias in AI-driven tools means there should be testing and validation, with an aim toward rigorous checks so that those varied populations of patients can be assured they are receiving an equitable and accurate outcome. The importance of these lies in the fact that the digital divide can, in turn, exacerbate health disparities through unequal access to digital technologies.
The healthcare digital revolution isn't just about technology; it's about progress that aims to enhance life quality for all.
This creates further emphasis on the needs to raise the level of digital literacy and access felt by members of underserved communities. These challenges should be addressed through collaborative interventions of stakeholders in the health ecosystem, ranging from policymakers to technology providers, healthcare professionals, and to the patients themselves, as the final beneficiary. Collaborative frameworks that

would enhance digital health innovation, while at the same time safeguarding patients' safety, data integrity, and fairness, are going to be key to finally seeing digital health realize its full potential.
Digital health is on the verge of a new future with deeper innovations and shifts. Genomics is increasingly entwining with digital technologies, which could set off an explosion in medicine— one that would be highly individualized to the person's genetic makeup and promises to further improve the chances for better outcomes with treatment or possibly even prevent some treatments in the first place.
Artificial intelligence (AI) would further mature, sharpening its acuity in predicting diseases, optimizing treatment plans, and, most profoundly, even helping by being
more precise than human beings in complex surgery. The further development and spread of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) would open the way for much more expanded and detailed monitoring of health and would tend to change health models from the reactive one to proactive or even predictive ones.
In addition, the digital platforms have the capability to improve the access and provision of health services by geographical breaking points and make quality health care available to the population that has been long underserved. This is where, as the company navigates in this future, collaboration should be taken by tech innovators, healthcare providers, and policymakers to grapple with the ethical, regulatory, and security challenges and learn to bear the social and financial costs that are essential to make the digital revolution work for all elements of society equitably.
To conclude, these are proof that digital transformation in health care presents a great opportunity to improve health outcomes, patient care, and efficiency of health delivery. With a host of digital innovations, ranging from AI and telemedicine to wearable technologies and beyond, coming into play, healthcare is set to ride on a new era. This means opening the door to a promise much more comprehensive. Healthcare will be more efficient and accurate, and, at the same time, there will be a way more personalized and patient-centric approach. Nevertheless, it is going to take hard work and cooperation among multidisciplinary efforts to swim through the treacherous waters of data privacy, cyber, and digital divide to ensure that

Preetha Vasanji is a distinguished member of the senior management team at Doceree, where she serves as President – Emerging Markets. With an extensive career spanning over two decades in the Healthcare Communications and Marketing sector, Preetha brings a wealth of experience and expertise to her role. Throughout her illustrious career, Preetha has had the privilege of collaborating with numerous multinational and domestic organizations, enriching her professional journey with diverse perspectives and insights
the benefits from digital health are redound to all. Our response as leaders in the health industry, legislators, and technology innovators will be the ways through which we resolve to tackle these challenges facing health in determining how the future landscape of health should look like. Encouragement of innovation, ethical consideration, and inclusivity, where the environment hosts these aspects, can bring about unlocking full potential for the technologies in digital health towards a healthier connected world. The digital revolution in healthcare means more than technology; it represents progress, which may or may not come, and hopefully one day improves life quality for people and society.

A lot of new medical devices to be deployed via percutaneous and other minimal invasive approaches have been introduced during the last two decades. Most important reasons for this ongoing development are complex cardiac conditions as well as increasing age and comorbidities of patients we are confronted with in cardiology.
Thomas Bartel MD, PhD, Interventional Cardiologist, Flexdoc GmbHImplantable cardiac devices have been part of routine therapy in cardiology for decades. Classic devices have formed a basis for the development of innovative ones. Cardiac pacemakers (PMs) and implantable cardiac defibrillators (ICDs), which are electronic devices usually placed into the chest wall just below the collarbone, and heart valves to be deployed by open chest surgery and later by minimally invasive cardiac surgery (MICS) are such classics.

Main indication for PM insertion is to help regulate slow heart rate occurring due to diseases of the electrical conduction system. As a substitute, PMs provide the heart with missing electrical impulses conveyed by electric leads to the right atrium (RA), right ventricle (RV) or both right-sided heart cavities. Percutaneous implantation of an entirely intracardiac leadless PM represents the lates development in this field. No surgery is needed for that kind of PM implantation, which is rather deployed via an endovascular approach from the right femoral vein. However, functionality of leadless PMs is limited to ventricular stimulation. That is why leadless PMs are just suitable for a minority of patients.
In individuals suffering from heart failure due to cardiomyopathies or other extended damage of the heart muscle, timing of electrical stimulation and subsequent response of pumping heart chambers (ventricles) may be altered what often results in asynchrony between left and right ventricular performance and may further worsen heart failure symptoms. Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) has been shown to improve heart failure symptoms in a certain proportion of such patients. Therefore, special PMs with CRT capability are used in patients with asynchrony if positive response is likely.
ICDs are another kind of PM-like devices providing with overdrive pacing or delivering electric shocks if needed. ICD implantation
is indicated for primary prevention of sudden death due to ventricular fibrillation or tachycardia (VF/VT) in patients deemed to be on high risk due to poor heart function (severe heart failure) or for secondary prevention if individuals have already survived an event of VF/VT, e.g. after successful resuscitation. PM functionality is inherent to ICDs in order to start pacing once a shock has been delivered. That can also include CRT capability because both, ICD implantation and CRT, may be indicated in the same patient population.
Surgical heart valves belong to the first therapeutic cardiac devices and have been implanted since the sixties. All four cardiac valves can be replaced by open chest or minimal invasive cardiac surgery. Therefore, native heart valves need to be excised to implant artificial ones as a surrogate, durability of which may be limited depending on type and material of those prostheses. An important distinction is made between mechanical and biological ones. The latter are made from cow, pig or human heart tissue. Current mechanical prostheses are characterized by mostly life-long durability but require permanent anticoagulation what entails bleeding risks. Ten to twenty years after implantation, biological valves often have to be replaced again once prosthesis degeneration is progressing. However, they just require short-term anticoagulation followed by long-term therapy with aspirin
or another antiplatelet therapy. That is why they are predominantly recommended to be implanted in patients beyond the age of sixty years.
In nonsurgical valve replacement, native valves are left in the human body and artificial ones are implanted inside the native valve pushing the latter aside. Consequently, although still in common use, the term nonsurgical or transcatheter “valve replacement” is actually not correct and might be superseded by “valve implantation”.
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) also known as transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) was the first percutaneous approach for valve therapy when prevalence of calcific aortic stenosis (AS) increased with progressing life-expectancy, since AS is a disease of advanced age. Consequently, an increasing percentage of candidates for surgical aortic valve replacement were deemed on high risk so that TAVI became a therapeutic alternative of utmost importance. Transfemoral access represents the approach of choice and other ones as are transapical, transjugular and transaortic access techniques are just considered surrogates in case the valve prosthesis, which is always a biological one, cannot be advanced through the femoral artery for anatomic reasons, e.g. artery occlusive disease.
A major cardiology advance: innovative devices via minimally invasive methods, addressing complex conditions in an aging population.
Prostheses for TAVI differ according to two deployment techniques as are self-expandable and balloon-expandable ones. The latter are mounted on a balloon and are deployed by inflating the same in a way comparable to coronary stent implantation. Balloon expansion pushes calcific native valve tissue aside which also works as an anker for the TAVI prosthesis. There is no need for sutures what is another difference to surgical valve replacement requiring the prosthesis to be sewed in. In contrast, self-expending prostheses are released from the shaft of a catheter. In some cases, pre-dilatation of the stenotic valve is needed before placing a self-expandible prosthesis. Overall, TAVI has been shown to be safe and feasible. According to recent trials, the use of TAVI extends the scope of high and even intermediate risk surgical candidates and is at the least equivalent to surgical aortic valve replacement. TAVI can also be done after previous biological valve replacement be it
surgically or percutaneously. This kind of implantation is called valve-in-valve (ViV) TAVI.
Transcatheter mitral valve implantation or replacement (TMVR) is much less common compared to TAVI. That mitral stenosis (MS) is very rare in industrialized countries and declining in emerging regions is just one reason for that. Balloon-expandable prosthesis designed for TAVI can be implanted into heavily calcified MS or degenerated biological valve prostheses (ViV procedure) restoring physiological diastolic filling of the left ventricle (LV). Those procedures must be planned carefully, since there is always a risk of LV outflow tract obstruction. However, large majority of patients with mitral valve disease shows regurgitation, which finally causes congestion and subsequent left-to-right heart failure. TAVI prostheses, which need calcified environment, cannot be used for therapy of mitral regurgitation (MR). Among numerous percutaneous devices just one implant to be deployed through a transapical approach (no classic percutaneous access) could gain acceptance. That is why, TMVR does not loom large. Instead, surgical and percutaneous mitral valve repair are considered therapeutic approaches of choice.
As severe tricuspid regurgitation (TR) has
been largely undertreated in the past due to questionable surgical results, the first percutaneous tricuspid valve replacement (TTVR) system has been recently approved. However, this therapy is still preserved for lifethreatening conditions as is severe and highly symptomatic TR. At present and in near future, majority of patients will undergo percutaneous tricuspid valve repair using similar techniques as proven successfully for treatment of MR. For those who received surgical valve replacement in the past, percutaneous ViV implantation remains an option as described above.
Percutaneous pulmonary valve implantation (PPVI) has been in use for more than two decades to treat patients with pulmonary stenosis, RV hypertension due to dysfunction of the outflow tract after surgical repair of congenital heart disease or, as another ViV procedure, for carriers of surgical valve prostheses.
Procedures summarized under this term are characterized by targeted changes of valve anatomy in order to mitigate regurgitation and restore valvular function. These techniques are just applicable to non-calcific mitral and tricuspid valves.
Valve clipping has been in use for about fifteen years. Valve leaflets are permanently clipped together what is also known as ‘edge-to-edge repair’, although it does not represent any real
repair of the valve. However, ‘clipping’ enables leaflets to better adapt and consequently the valve to close more sufficiently during systole. Therefore, one or more clips are deployed via the inferior vena cava from the left atrium (requires previous septal puncture) to the mitral valve or directly from the right atrium to the tricuspid valve using sophisticated catheterbased delivery systems. The technique can be employed in valve prolapse and in cases of functional regurgitation but is prohibited in valve degeneration due to endocarditis. It is inefficient in cases of leaflet perforation or paravalvular regurgitation.
TR and MR are often considered ‘functional’ as a result of annulus dilatation. In these scenarios, percutaneous annuloplasty is an option if a surgical one is too risky. However, these procedures are extremely challenging and are provided just by a few teams worldwide. Devices induce shrinkage of valve annulus from inside the RA or the left atrium (LA). For mitral annuloplasty, devices can be implanted into the coronary sinus for achieving shrinkage from outside the mitral annulus. Percutaneous annuloplasty can also be combined with clipping techniques what may improve sustainability of the result (figure 1).
This set of implants has had a kind of pioneering
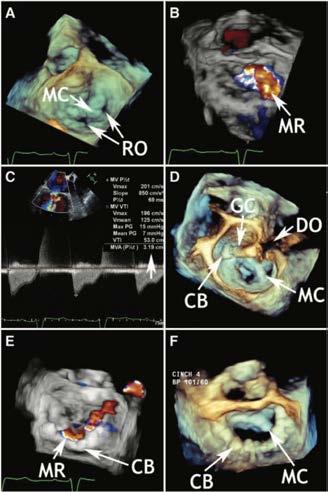
1: Percutaneous annuloplasty after mitral valve clip implantation shown by echocardiography. CB, Cardioband device for annulus shrinkage; DO, drop out caused by the guiding catheter (artifact); GC, guiding catheter in the left atrium; MC, MitraClip-device in place; MR, mitral regurgitation years after clipping of the mitral valve; RO, regurgitant orifices. Reference: Bartel et al. Percutaneous mitral annuloplasty complements clip implantation in functional mitral regurgitation. European Heart Journal 2019;40:2584
role and initiated the era of catheter-based, permanent deployment of devices. Closure of patent foramen ovale (PFO), atrial septal defect (ASD) and patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) are straightforward procedures performed via a transfemoral venous approach. Most commonly, closure devices consisting of nitinol are released
from a tube catheter previously introduced into the opening. Devices each consist of a left-sided and a right-sided counter occluder (figure 2). The left-sided one is released first and closes the opening from the arterial side. The right-sided one is released in a second step and is then pushed against the opening from the venous side. Within six months, devices become permanently ingrown preventing the
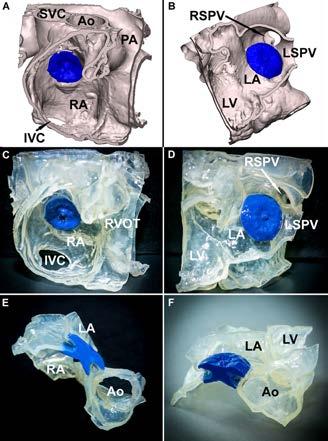
Figure 2: Medical three-dimensional printing after ASD device closure (blue: implanted closure device). Ao, aorta; IVC, inferior vena cava; LA, left atrium; LSVP, left superior pulmonary vein; LV, left ventricle; RA, right atrium; RSVP, right superior pulmonary vein; RVOT, right ventricular outflow tract. Reference: Bartel T, et al. Three-dimensional printing for quality management in device closure of interatrial communications. European Heart Journal – Cardiovascular Imaging 2016;17:1-8.
patient from shunting and paradoxical (venous to arterial) embolism. PFO device closure is explicitly done for secondary prevention of strokes and other arterial embolism. ASD device closure may be indicated if left-toright shunting causes significant recirculation of blood through the pulmonary vascular tree leading to pulmonary hypertension, right heart overload and finally to impairment of pulmonary function. Stroke prevention has been accepted as another indication. In contrast, PDA device closure is just indicated for interruption of aortopulmonary shunting and therefore, implementation of physiological cardiopulmonary hemodynamics.
Left atrial appendage (LAA) device closure is to prevent patients from clot formation inside the LA, which is considered cardiac source of embolism. It is recommended for those individuals suffering from chronic atrial fibrillation (AF) who are no candidates for long-term anticoagulation because of increased bleeding risks, e.g. those with severe bleeding events in history or concomitant diseases, which entail increased likelihood of bleeding. Deployment of dedicated occluder devices is very similar to device closure of interatrial communications or PDA but requires transseptal puncture as mentioned above for clipping of the mitral valve. In LAA closure, devices work as ‘place holders’ to shut the LAA out of circulation. Percutaneous LAA device closure
has gained worldwide acceptance for stroke prevention as an effective alternative to longterm anticoagulation in AF.
There are devices for mechanical circulatory support providing long-term or short-term but no permanent assistance to patients with acute or chronic heart failure to keep their heart pumping enough blood, e.g. LV assist devices (LVADs). Such devices are temporarily implanted in order to ‘bridge’ patients to heart transplantation, to gain time for effective drug treatment or to optimally prepare for heart surgery. Intra-aortic balloon pump or intraventricular heart pump are other temporary devices just left inside the human body for a few days to recover from acute left or right heart failure. They are also increasingly in use to support circulation during risky percutaneous procedures, e.g. coronary intervention of the left main stem if LV function is already impaired. Such kind of temporary assistance is prone to improve safety of these procedures.
Implantation of cardiac devices usually entails high costs. Particularly, percutaneous procedures for device implantation require highly trained and specialized personnel and sophisticated devices are comparatively expansive. In those healthcare systems, settlement is based on diagnoses related groups (DRGs), such procedures are remunerative for health care providers, what finally may end up in some
oversupply. In contrast, high costs may prevent patients from receiving adequate therapy in budget-based healthcare systems so that certain undersupply may be a consequence if budgeting is insufficient.
In summary, medical devices are thought to restore or at least improve cardiac functionality. Vast majority of implants just requires minimal invasive or completely percutaneous procedures but no open-heart surgery anymore. With aging of the population, implantable cardiac devices are increasingly in common use.
 AUTHOR BIO
AUTHOR BIO
Dr. Thomas Bartel is an interventional cardiologist with about 35 years of professional experience. He finished Charité Medical School in Berlin in 1987. He worked at different academic institutions in Germany, the United States, Austria and the United Arab Emirates. In that regard, he was confronted with a broad spectrum of healthcare conditions and systems.

In India, digital transformation is reshaping healthcare delivery through collaborative care models. Integrated health ecosystems leverage technology to streamline workflows, enhance patient engagement, and drive better outcomes. Through telemedicine, data analytics, and patient empowerment tools, hospitals are revolutionizing healthcare, making it more and analyses the potential impact of these initiatives on the future of healthcare delivery.
Col (Dr) Surendra Ramamurthy Healthcare Technology & Digital Health Advisor, Indian Armed Forces VeteranIndia's healthcare system faces myriad challenges, including limited access to healthcare services, escalating costs, and
disparities in healthcare delivery. Traditional healthcare models are often fragmented, leading to inefficiencies, care gaps, and suboptimal patient outcomes. Additionally, the burden of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer is escalating, necessitating a shift towards preventive and proactive care approaches.
Digital technologies present a transformative solution to address these challenges by enabling hospitals to embrace a collaborative care model. By leveraging data-driven insights, telemedicine, remote monitoring, and patient engagement tools, hospitals can deliver holistic, patient-centered care. Integrating digital technologies into healthcare operations streamlines workflows, enhances care coordination, and empowers patients to actively manage their health.
India's healthcare system grapples with several pressing issues
Limited Access: A significant portion of the population, especially those residing in rural areas, lack access to essential healthcare services. Distance, transportation limitations, and a shortage of qualified healthcare professionals further exacerbate this problem.
Escalating Costs: The cost of healthcare in India is rising steadily, often outpacing inflation. This financial burden can deter individuals from seeking necessary medical attention, leading to delayed diagnoses and poorer health outcomes.
Fragmented Care Delivery: Traditional healthcare models often operate in silos, with limited communication and coordination between different healthcare providers involved in a patient's care. This fragmentation can lead to duplication of services, medication errors, and suboptimal care.
Shifting Disease Burden: The rise of NCDs necessitates a proactive approach to healthcare. Traditional models, heavily focused on acute care, are ill-equipped to address the growing need for preventive care, chronic disease management, and long-term patient engagement.
Digital technologies offer a transformative solution to these challenges.
By leveraging telemedicine, remote monitoring, data analytics, and patient engagement tools, hospitals can create a collaborative care model that delivers
Improved Accessibility: Telemedicine expands healthcare services beyond traditional settings, allowing patients in remote areas to connect with specialists virtually. This reduces travel time and costs, improving access to quality care.
Enhanced Affordability: Technologydriven solutions can streamline workflows, minimize administrative overhead, and optimize resource allocation. This can potentially lead to cost reductions, making healthcare more affordable for patients.
Integrated health ecosystems facilitate seamless communication and collaboration between healthcare providers. This reduces care fragmentation, minimizes errors, and ensures continuity of care.
Data analytics empowers healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans based on individual patient data and risk factors. Remote monitoring tools allow for early detection of potential issues and enable proactive interventions.
tools educate patients about preventive care, promote medication adherence, and support self-management of chronic conditions. This fosters patient engagement and ownership of their health journey.

EHR systems serve as the foundation of a digital healthcare ecosystem, allowing hospitals to digitize patient records, streamline documentation processes, and facilitate interoperability among healthcare providers. Centralizing patient information in electronic format enhances care coordination, reduces errors, and improves clinical decision-making.
Telemedicine platforms and remote monitoring solutions extend healthcare services beyond traditional settings, particularly in rural and underserved areas. Virtual consultations enable remote access to healthcare services, reducing the need for in-person visits and lowering travel-related expenses. Remote monitoring technologies, including wearable devices and IoT sensors, enable real-time tracking of vital signs, facilitating early intervention and proactive management of chronic conditions.
Data analytics and predictive modelling harness big data and machine learning algorithms to derive actionable insights from vast healthcare datasets. Analysing clinical data, demographics, and outcomes enables hospitals to identify high-risk patients, predict disease progression, and optimize treatment plans. Predictive analytics helps anticipate healthcare trends,
allocate resources efficiently, and personalize interventions, leading to improved outcomes and cost savings.
Patient engagement platforms empower individuals to participate actively in their healthcare journey and make informed decisions. Mobile apps, patient portals, and health tracking tools educate patients about preventive care, facilitate medication adherence, and support self-management of chronic conditions. Fostering patient empowerment enhances satisfaction, adherence, and reduces hospital readmissions.
Collaborative Care Coordination Platforms: Collaborative care coordination platforms facilitate communication and collaboration among healthcare providers across specialties and settings. These platforms enable care teams
to share patient information, collaborate on care plans, and track progress in real-time. Promoting care coordination enhances continuity, safety, and resource utilization.
The Indian government plays a pivotal role in catalysing the transformation of healthcare delivery through digitally empowered collaborative care. Through policy formulation, the government establishes strategic frameworks such as the National Health Policy and the National Digital Health Mission (NDHM), which set the direction for integrating digital technologies into the healthcare ecosystem while ensuring interoperability and data privacy. By allocating funds and providing incentives through initiatives like the Digital India program and the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan, the government encourages investment in digital healthcare infrastructure, startups, and innovation. The government invests in building digital infrastructure, such as broadband connectivity and telecommunication networks, to facilitate the seamless exchange of health information and telemedicine services, particularly in rural and remote areas. Capacity building and training programs ensure that healthcare professionals are equipped with the skills and knowledge to leverage digital health technologies effectively, with initiatives like the Health ID program under the National Digital Health Mission providing digital
health literacy and training. Regulatory bodies like the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) and the National Health Authority (NHA) oversee the approval and regulation of digital health products and services, ensuring safety, efficacy, and interoperability. Public-private partnerships (PPPs) foster collaboration between the public and private sectors, driving innovation and implementation of scalable healthcare solutions. Through grants, funding, and initiatives like the Digital India Healthcare Startup Challenge, the government promotes research, entrepreneurship, and innovation in digital health, creating a conducive ecosystem for healthcare transformation. Overall, the Indian government's multifaceted approach to promoting digitally empowered collaborative care lays the foundation for a modern, efficient, and patient-centric healthcare system that benefits all citizens.
Apollo Hospitals:
Apollo Hospitals, one of the largest healthcare providers in India, has implemented a comprehensive digital health ecosystem to deliver collaborative care to its patients. Through its Apollo 24/7 telemedicine platform, patients can access virtual consultations with specialists, schedule appointments, and manage their health records online. The hospital also utilizes remote monitoring technologies to track patients' vital signs and provide timely
interventions for chronic conditions such as diabetes and hypertension. By leveraging data analytics and predictive modelling, Apollo Hospitals identifies high-risk patients and tailors personalized care plans to improve clinical outcomes.
Manipal Hospitals:
Manipal Hospitals has embraced digital transformation to enhance care coordination and patient engagement across its network of hospitals and clinics. The hospital leverages collaborative care coordination platforms to facilitate communication among multidisciplinary care teams, ensuring seamless transitions of care for patients. Through its patient engagement tools, Manipal Hospitals empowers patients to actively participate in their healthcare journey, leading to improved treatment adherence and better health outcomes.
In conclusion, the future of healthcare in India is intricately tied to the adoption of a technology-driven integrated health ecosystem. This ecosystem, anchored by collaborative care, patient engagement, and data-driven decision-making, holds immense potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery across the country. By harnessing the power of digital technologies such as Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems, telemedicine platforms, data analytics tools, patient engagement solutions, and collaborative care platforms, hospitals can usher in a new era of healthcare that is more accessible, affordable, and effective.
However, realizing this vision requires concerted efforts from various stakeholders. Firstly, there is a need for policymakers to create an enabling environment that supports the widespread adoption and integration of digital health technologies. This includes developing regulatory frameworks that ensure interoperability, data security, and patient privacy while fostering innovation and investment in healthcare technology.
Secondly, healthcare providers must embrace digital transformation and actively incorporate technology into their practice. This entails investing in training and upskilling healthcare professionals to effectively utilize digital tools and platforms. It also involves fostering a culture of collaboration and innovation within healthcare organizations to drive continuous improvement and adaptation to evolving technologies.
Thirdly, technology vendors play a crucial role in developing and delivering innovative digital health solutions that address the unique needs and challenges of the Indian healthcare system. This requires a deep understanding of the local context, close collaboration with healthcare providers and policymakers, and a commitment to delivering solutions that are user-friendly, scalable, and cost-effective.
Lastly, patients are key stakeholders in the healthcare ecosystem and must be actively engaged in their own care. Patient education, empowerment, and involvement in decisionmaking processes are essential for achieving
better health outcomes and ensuring the success of digital health initiatives.
In summary, the future of healthcare in India lies in the convergence of technology, collaboration, and patient-centric care. By working together towards a shared vision of a digitally empowered healthcare system, India can overcome its healthcare challenges and pave the way for a healthier and more prosperous future for all.
References are available at www.europeanhhm.com
 AUTHOR BIO
AUTHOR BIO
Col (Dr) Surendra Ramamurthy, M.B.B.S, M.D, D.N.B, F.I.C.S. is an esteemed Indian Armed Forces Veteran, boasts a distinguished career spanning over four decades in healthcare, medical education, and digital health. His roles as a consultant gynaecologist, associate professor, and healthcare technology leader reflect his commitment to advancing healthcare and leveraging technology for patient benefit.
In healthcare, AI has the potential to transcend its initial focus on diagnosis, extending to care coordination. This article advocates for a shift towards proactive, collaborative platforms. It examines the limitations of EMRs and shared care records and proposes systems focused on future care needs, integrated with AI.
 Dr DJ Hamblin-Brown CEO, CAREFUL
Dr DJ Hamblin-Brown CEO, CAREFUL
Healthcare systems everywhere are suffering from shortages of clinicians. Productivity is under strain from fragmented pathways and inefficiencies built into the way that such systems are designed. New uses of AI in healthcare are being devised and discovered. For a long time, the main thrust was the ability to support more rapid and more accurate diagnoses, especially within imaging specialities.
This article argues that AI's true power lies not just in diagnosis, but in revolutionising the most difficult aspect of healthcare – the coordination of multidisciplinary teams spread across multiple institutions.
We argue that merging data silos is not the answer. We need instead to create seamless pathways of data, supported by AI, to empower
collaboration and support a holistic and helpful view of each patient’s journey. This requires real-time communication and the ability of care teams to answer crucial questions and ensure that patients receive the right care at the right time.
Principally, the use of AI in this scenario, we believe, is in focusing practitioners on the ‘next best action’ for a patient and distributing those actions to the most appropriate person. This is not possible either within current silos or even by merging silos into data lakes or common care records. Instead, what is required is a whole new category of patient record – one that abandons the metaphor that has dominated EPR manufacture until now, the ‘digitisation of the patient’s folder of notes’, and instead embraces the metaphor of whiteboards and patient lists, where cohorts of patients are managed together, across multiple teams and – most importantly - where AI

can learn from one patient and inform the care of another.
Our view is that we must use new learning models to generate the ‘future view of care’ and allow practitioners, patients and their families to select from among the choices that are then presented, providing a learning loop within the AI models.
This approach will abandon the exclusive focus on looking backward and recording the care that has been provided in the past and instead use machine learning to drive care decisions and focus on what the patient worries about most: their future.
The following are case studies drawn from the author’s own clinical experience:
Case 1: A five-year-old child suffers an unexpected asthma-like attack while playing outside during summer. The child is brought to the emergency department and a few days later to their general practitioner. The child presents at the ED several times, often at night, and is followed up by the GP on another occasion. There is little improvement in symptoms, despite maximal asthma therapy. The parents visit a private paediatrician who orders extensive blood tests and a chest x-ray. The x-ray is reported by a third party as showing some partial lung collapse. An otherwise reassuring letter is sent to the GP asking that the report is followed up, but this is missed. The child deteriorates over some weeks and is eventually admitted as an inpatient with fever and malaise. A plastic foreign body is eventually retrieved on bronchoscopy and the child makes a full recovery.
Case 2: An elderly man who lives alone suffers an unwitnessed fall at home suffering a clinically insignificant head injury. He is treated at a local emergency department, where he waits for 24 hours before being mobilised and discharged to a rehab hospital in the community. There, he is found to have atrial fibrillation and is placed on warfarin. He makes a good recovery and returns home but soon afterward suffers an acute gastrointestinal bleed, which requires further emergency treatment.
In both of these cases, there was no visibility of the workflow of the teams in different institutions. Once the patient has been removed to the next place of care, the actions that are required to complete the cycle of care become disjointed. In the first of these, a chest x-ray needed to be reported and acted upon. In the second, the INR needed to be regularly checked.
The challenges presented by fragmented healthcare systems are well understood. Siloed care, where information is restricted to individual institutions, creates barriers to effective communication and collaboration among care teams. As patients transition between different care settings, crucial information often gets lost, leading to disjointed care pathways and suboptimal outcomes.
Cases such as the two above are often used as reasons for joining up the care records of individual institutions in order that the ‘buff folder of notes’ from one hospital or care setting is visible to the other. This creates ‘common care records’ from which ‘data lakes’ can be created.
There are significant disadvantages to this approach. The largest barrier is that these big silos of healthcare data need to by joined together technically and made to work together. As the UK’s National Programme for IT (later known as ‘Connecting for Health’) found after many billions of wasted taxpayer money, doing this is immensely complicated and prohibitively expensive.
The other problem is that there is always, somewhere, a boundary that will not be included in the ‘greater record’. For instance, in the UK, Manchester has brought in a common care record that allows emergency services, GPs and hospitals to see each other’s records. But there will inevitably be patients who are not covered by this. They
AI in healthcare must move beyond digitizing patient records to creating collaborative platforms that empower care teams and patients alike.
may be living on the outskirts of the Greater Manchester area, or they may select to be treated outside the NHS or they may migrate into or out of the area from other parts of the UK or the world.
In our view, addressing these challenges requires a fundamental shift away from traditional metaphor of the ‘digitised folder’ as the electronic medical record, towards a more collaborative metaphor based – for want of a better image – on the whiteboard found in wards and other healthcare departments. These whiteboards are often future-focused and action-oriented; they can be seen, adapted and accessed by many individuals from
many teams. Rather than merely serving as repositories of past medical data, whiteboards facilitate real-time communication and decision-making within and between care teams.
The most powerful whiteboard would be one that could be seen by teams across the entire range of a patient’s care journey, in all settings. To re-emphasise, this does not need to be a complete sharing of the medical record from each of these settings. Just enough to make the coordination of care a reality.
It is our view that the thrust of the next generation of healthcare digitisation must create platforms such as these, which provide users with small, highly relevant amounts of distilled information that allows for rapid decision-making and which provide a view of a cohort of patients, rather than individualised, deep silos of information about individuals.
It is here that the transformative potential of AI can then be made possible.
By harnessing the power of machinelearning algorithms, AI can analyse the information of such patient lists, in real time, identifying patterns and predicting future needs and, in particular, future actions: the ‘next best action’. This predictive capability will then enable care teams to intervene rapidly and precisely address specific patient needs bearing ‘in mind’ the context of the team and the cohort of patients for which the team is responsible.
To give an example, a machine-learning algorithm could analyse the discharge summaries and short-text-based clinical summaries, comparing this data to historical summaries of similar patients managed by that team. From this analysis, can come a list of the most likely next best actions for that patient. These actions can be verified by human users in order to provide further learning feedback for the model.
Once these actions are agreed, they can be assigned to the relevant clinicians, who can then receive automated alerts, prompting them to ensure that these actions are carried out. The AI can assist in care planning by recommending personalised treatment pathways based on best practices and patientspecific factors.
The benefits of AI-powered care coordination extend beyond increased efficiency. As implied by the case studies, the enhanced communication and collaboration will lead to a reduction in medical errors and improved patient outcomes. By streamlining workflows and automating the allocation of actions, AI will allow clinicians to focus more on direct patient care, ultimately enhancing the overall quality of healthcare delivery.
Perhaps most importantly, this AI-supported care coordination can be used to empower
the patient, by giving the patient an active role in managing their health. Through realtime access to their own care plan and to the multidisciplinary team looking after them, they can make more informed decisions about their care, leading to greater engagement and satisfaction.
While the promise of AI in care coordination is immense, it is not without its challenges. Concerns around data security, privacy and algorithmic bias must be addressed to ensure the responsible development and implementation of AI systems in healthcare. Robust data security measures and transparent governance frameworks are essential to safeguard patient information and mitigate the risk of unauthorised access or misuse. Furthermore, efforts to mitigate algorithmic bias and ensure the fairness and equity of AI-driven recommendations are imperative to build trust among patients and healthcare providers.
As healthcare begins to adopt AI – and the care coordination platforms just outlined become a reality – collaboration and cooperation among stakeholders will become a real possibility. However, to make this a reality, provider organisations, clinicians, developers and policymakers – and in particular healthcare system designers – will need to work together
to design and implement these future-focused, action-orientated platforms that prioritise collaboration. By breaking down silos and embracing AI as a catalyst for innovation, we can create a healthcare ecosystem that is truly transformative. We need to seize this opportunity to harness the full potential of AI in revolutionising care coordination and improving the lives of patients around the world.
 AUTHOR BIO
AUTHOR BIO
Dr DJ Hamblin-Brown, a qualified doctor and emergency medicine specialist from London has extensive experience in healthcare leadership and management. He previously held senior positions at United Family Healthcare and Aspen Healthcare before founding CAREFUL, a platform focused on improving clinical care coordination.

In the era of genomics entering medicine, societies have huge opportunities to revolutionize healthcare but also face great challenges. Through a series of answers to important questions, Professor Constantine Stratakis presents ways that healthcare is changing and discusses the challenges, such as those of access, affordability, and ethical use of new technologies.
Constantine A Stratakis Director, Human Genetics & Precision Medicine, FORTH, Greece1. Can you share your insights on how advancements in genomic and sequencing technology have revolutionized healthcare in the past decade, particularly in terms of diagnosis, treatment, and patient outcomes?
The completion of the human genome project (HGP) sparked the new era of Genomic Medicine. The identification of single-nucletoide polymorpshims (SNP) and the discoveries of genome-wide association stusies (GWAS) have since revolutionized diagnosis and prediction by providing information of many genes that are linked to the development of diseases, predispositions, and even predictive scores, the polygenic risk scores (PRS). So, today, we use genetic testing for diagnosis, for treatment decisions in cancer and elsewhere, and for prediction of health and disease. Many therapies are targeted, such as for example in cancer chemotherapy. And gene therapy is everywhere from metabolic disease to cancer. Hippocrates had foreseen individualized medicine, but I certainly hope he was alive today to see it happening!
2. As someone deeply involved in precision medicine, what do you see as the key benefits and challenges of integrating genetics into personalized healthcare? How do you address ethical considerations and privacy concerns in utilizing individualized genomic data?
The incorporation of genetics into personalized healthcare offers for the first time really
in the history of medicine the opportunity to titrate everything to the specifics of the individual, from prevention efforts, to diagnostic markers, to therapy interventions. However, as said above, one of the main challenges for the incorporation of genetics into personalized healthcare is protection of personal data and overall use of genomic information. The benefits of genetics informing the electronic medical or health record (EHR) of the individual are beyond any doubt for interpretation and implementation but societies and communities in general, as well as professional bodies and organizations should establish procedures, guidelines, and frameworks that will ensure ethical use of the information and protect the privacy of the individual.
3. Could you elaborate on the role of artificial intelligence and machine learning in analyzing and utilizing individualized genomic data for improving patient outcomes? How do collaborations between academia, research institutions, and pharmaceutical companies contribute to advancing precision medicine and molecular research?
The power of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in analyzing data to improve health outcomes have been presented extensivey. I will use the example of hypertension (HTN) and one recent study that used machine learning (ML) to overcome a major hurdle in its diagnosis. A study by Chen et al. used ML to link genetic data with
hormonal measurements in patients with adrenal adenomas. The study solved an old problem: how do you identify which tumor to operate on when you have more than one? ML helped identify the right tumor. So, AI and ML are already helping out and one can’t really imagine what the future holds. In pharmaceutical development, AI will be instrumental in identifying small molecules that will target genes and pathways that are affected in diseases. For the efficient use of such discoveries by the pharmaceutical industry, the tight collaboration between research institutions and industry is essential.
4. With the increasing focus on disease prevention, what strategies do you think are most effective in promoting healthy living and preventing future health issues? How can personalized genetics and precision medicine play a role in preventive care?
There is no question that where genetics will have a major impact is prevention: a healthy subject will remain healthy after the successful incorporation of genetic information into preventive diagnostic testing and health-promoting interventions in a way that are titrated to the individual’s needs. Health systems around the world will see the benefits of shifting focus from battling disease to preventing disease, in terms of total costs but also satisfaction of the population from their services. However, for that to happen there are three important steps that are summarized into one word: communication, communication, communication! First, communicating to the public the need for
prevention; second, communicating to the leadership of health systems the benefits of a strategy that prioritizes prevention; and, third, communicating to the health care personnel efficient and user-friedly protocols that can be applied at the general practitioner’s level and beyond, at home, schools, etc.
5. You have a vast experience in clinical genetics and precision medicine. How do you envision the future of healthcare, particularly in terms of personalized medicine, preventive care, and addressing societal challenges such as rare diseases?
I envision a situation where every one of us has our own genetic information in our wallet or our phone or any other small device. This information will then be readily available whenever it is needed by our healthcare provider. Our check ups will be informed by it. Any suggestions for physical activity, diet, or environmental exposures, and any medications we need to take will be informed by it. This is vastly different from the current situation for the average person and promises a real improvement in healthspan! As for rare diseases, precision medicine promises a revolution in therapy: for most patiens with rare diseases there have been no treatments for centuries. Already, there are hundreds of gene therapy trials for many rare diseases. I do hope that the cost of such treatments will also decline as technology improves.
Precision medicine in healthcare tailors treatments to individuals, but safeguarding personal data and ethical genomic use are key challenges.
6. As the Chief Scientific Officer of ELPEN Pharmaceuticals and a director of human genetics and precision medicine at IMBB, FORTH, what initiatives are you leading or involved in to advance precision medicine and molecular research? Can you share any success stories or examples where personalized genetics and precision medicine have significantly impacted patient care and treatment outcomes?
My personal experience is in the field of rare diseases. The discovery of genetic defects such as the PRKAR1A mutations in patients with Carney complex allowed for the early diagnosis, surveillance and treatment of these patients. Carney complex is a disease that among other problems predisposes to the development of heart tumors. Up to the discovery of the gene by my laboratory and the establishment of genetic testing and surveillance protocols, there were no families with Carney complex that had not lost a member, usually a child, due to sudden death caused by a heart tumor. I am proud to say, that in the last 20 years, of the hundreds of patients I know with Carney complex, I know of no sudden deaths due to a previously unknown heart tumor. This is clearly due to genetic diagnosis and implementation of preventive testing and care. There is more that needs to be done of course, such as for example gene therapy to treat recurrent heart tumors and the other manifestations of Carney complex. But precision medicine has already shown the miracles that it can accomplish by increasing lifespan of Carney complex patients to almost normal.
7. How important is it to educate both the public and healthcare professionals about personalized genetics, precision medicine, and preventive care? What steps are being taken in this regard, and how can we improve public understanding and acceptance of these technologies?
Perhaps one of our best projects is the successful establishment of the Hellenic network for precision medicine in molecular oncology (www.edimo.gr) coordinated by our IMBB, FORTH-located laboratory DIGENIA (www.digenia.gr). It envisions a comprehensive oncological care for the Greek population all the way from prevention to diagnosis and treatment based on personalized molecular information. These initiatives will undoubtedly lead to improvement of healthspan by averting neoplastic disease, as well improve lifespan by providing personalized and targeted therapies.
I mentioned before that communicating to health care providers the beneftis of implementing personalized genetics, precision medicine, and preventive care is essential. A number of healh systems are now educating their staff about personalized medicine protocols. This is essential in fields such as oncology, for example, where genetics plays a critical role for the choice of diagnostic testing, surveillance and even therapies. Slowly, but steadily, this is expanding in other fields of medicine but it has yet to be implemented widely in preventive care.
For that to happen, we do have to have the public understanding and acceptance of new technologies. The use of social media to educate the public is essential and many communities are now doing that. Most clinics have engaged in outreach efforts and information is widely available. But there is more that needs to be done. Perhaps, the best place to start is schools, primary education for example. Fortunately, many school systems are now educating young kids on the needs of prevention and what genetics means for them and their families
8. Considering your extensive background in academia and research, what advice would you give to young professionals aspiring to make a difference in the field of healthcare and precision medicine? How can they contribute to shaping the future of medical research and patient care?
I used before what Cicero said “O tempora, o mores!” which roughly translates to “What an age we live in!”.
It is a great time to be a professional today entering the field of healthcare and precision medicine. Technology advances allow for applications that were unimaginable just a few years ago. Thus, delivering care today can be very rewarding in ways that it could not be in the past. Yet, the new era has challenges, too: can we deliver these new therapies to all? Is technology accessible to all and by all? And can the complexity of the new knowledge be mastered by all staff? It is now estimated that medical knowledge doubles every 2 months or so, whereas this doubling time was counted in centuries until recently.
So, here is my advice: embrace new technology, master it, and make all you can do for all to benefit from it, regardless of costs, difficulties in access, and other challenges. And remember to protect society and the individual from the possible abuses of technology or its unethical applications.
9. Lastly, could you discuss the role of large data and predictive healthcare in shaping the future of medical research and patient care, as highlighted in the new NICHD Strategic Plan? How do you see these advancements influencing clinical practice and healthcare delivery?
While at the United States National Institutes of Helath, I co-led the strategic planning process of the National Institute of Child Health & Human Development (NICHD) (NICHD Strategic Plan 2020. Healthy pregnancies. Healthy children. Healthy and optimal lives. (nih.gov)). The plan emphasized the use of large data for predicitive care, biomedical research, and clinical practice. The creation of user-friendy, accessible databases for clinical trials, molecules, genetic information is essential for the practice of medicine in the new era, and will lead to faster implementation of machine learning and artificial intelligence technology in daily care.
The most important way these large data affect daily practice is by providing easy access to accurate information for both patients and healthcare providers, but also to any individual that needs it. I will give you an example of my daily clinical practice in genetics. The other day, I saw a patient with frequent fractures and a family history of brittle bones. I made the provisional diagnosis of a form of osteogenesis imperfecta (OI). I ordered the enetic test and a mutations was found in the COL1A1 gene which infact causes OI. Then, we searched the databases and found out that the mutation had been described previsously. We provided the patient all the information and even showed him how to access the databases himself. Within days
from when I saw the patient, he and his family have been diagnosed, they now have the tools for preimplantation genetic testing for future pregnancies, and can take control of their lifes having access to all the up-to-date information. This is the power of databases: large datasets, access to all, continuously updated. Not only useful for the clinicians but also for the patients and their families!
The
future of healthcare lies in personalized genetics, precision medicine, and preventive care.
Embracing new technology, mastering it are key steps towards shaping a healthier tomorrow.
10. In conclusion, what do you believe are the most critical areas of focus for the future of precision medicine and healthcare, and how can stakeholders across the industry collaborate to achieve these goals effectively?
In conclusion, we live at fascinating times, yet times that are transitional and with huge opportunities opening up but also great challenges. In the preceding questions, and through our answers we presented the huge opportunities and mentioned some of the challenges. The most critical areas, as is obvious from what we have said so far, are those of access,
cost, and ethics. Everybody should have access to precision medicine and modern healthcare with its preventive tools, large databases, and molecular therapies, both providers and the society as a whole (non-providers, every healthy citizen and patients). This means education, familiarity with new technologies, and bringing costs down. Affordability and costs are very important issues that are intertwined with access. And last but not least, ethics: how do the new tehcnologies get mastered without breaking privacy, how we use machine learning and artificial intelligence to society’s advantage without at the end being enslaved by non-human processes, how to make gene modification affordable
and a therapeutical opportunity for many diseases and all patients, and how to prevent it from being used for eugenics or other practices that we all seem to find unacceptable. Stakeholders individually and through their professional societies should engage actively towards addressing these issues, bringing them to the forum and coordinate their actions, informing communities of their activism and making these issues important for the everyday political discussion. At the end, it is state policies that make healthcare accessible and create the proper legislation for the protection of citizens, dissemination of new technologies and their use for the benefit of many, as well as fostering further innovation.

Professor Constantine Stratakis is an internationally known medical geneticist, endocrinologist, translational investigator and executive leader at the US National Institutes of Health. As the CSO of ELPEN, in Athens, Greece he directed the efforts to build a Research Institute. He is currently the Director of human genetics and precision medicine at IMBB, FORTH and coordinates the Hellenic Network for Precision Medicine in Molecular Oncology

Explore how AI models are being used to track and predict infectious diseases. As we approach the post-COVID-19 era, how are we preparing for the next pandemic? How will AI inform our reponse, how is AI impacting epidemic forecasting and supporting the development of vaccines? What kinds of partnerships will we see between public health, healthcare, and AI?
1. How do you envision AI integration within the broader digital health ecosystem, and what role can it play in transforming traditional healthcare delivery models?
Although the notion of AI in clinical practice seems to be new, it has been steadily and slowly impacting healthcare as whole for at a few decades. I think the recent pandemic highlighted the need for digital health and as such we have seen a renewed focus not only on digital health but AI. Certainly, the recent
advancements in technology have allowed AI to become more mainstream in its adoption but the use of AI in healthcare has been going on in the background.
There are several ways in which I think AI will continue to impact the digital health ecosystem. The embedding of machine learning and deep learning algorithms into workflows will allow for data to be processed and enable the practice of precision medicine, predictive analytics, and personalized care plans. The ability of AI to analyze vast datasets at a rapid pace will lead to better disease
detection, treatment recommendations, and ultimately better health outcomes. For example, AI can enable (and is already in practice) early disease detection through advanced imaging analysis, like identifying diabetic retinopathy in retinal images. Furthermore, AI-driven predictive models can forecast epidemic outbreaks by analyzing patterns from various data sources, including social media and travel data sets, as seen with AI systems that flagged early warnings ahead of the COVID-19 pandemic which are still in use and continuing to improve today. And AI can transform traditional healthcare delivery, by automating administrative tasks such as appointment scheduling, freeing up human resources for direct patient care.
As we see a further embedding of AI in our daily personal and professional lives, the artificial intelligence of medical things (AIoMT) will continue to learn, process, and inform the how, when, and why we provide care allowing us to intervene sooner and harnessed with more precise data to inform our clinical decisions.
2. What challenges and opportunities do you foresee in ensuring interoperability between AI technologies and existing digital health platforms within healthcare organizations?
The challenges of implementation lie in a few domains—data, drive, and demand. First and foremost is data. Data silos and various formats of health data pose a challenge for any healthcare organization who wants to implement AI into their existing systems. Furthermore, maintaining privacy and security across platforms and ensuring
data quality and consistency while navigating HIPAA is complex and challenging. A notable opportunity is the use of AI to standardize data through natural language processing, converting free-text notes into structured data. Developing standardized data standards and creating centralized data lakes can enable a more efficient exchange of data. Additionally, blockchain technology can also aid in secure data sharing. An example of interoperability enhancement is Google's Cloud Healthcare API (among others), which enables data exchange through FHIR protocols, making varied health data sets more accessible and useful for AI applications.
A second area that is challenging is drive. Resistance to drive change within established organizations can pose a significant challenge. The technical complexity of integrat-
 Dipu Patel Vice Chair for Innovation and Professor, University of Pittsburgh’s DPAS program
Dipu Patel Vice Chair for Innovation and Professor, University of Pittsburgh’s DPAS program
AI transforms clinical decision support in digital health by rapidly analyzing vast medical data for accurate diagnostic support.
ing new AI technologies with legacy systems, compounded by new platforms posed by vendors, and lack of motivation by healthcare clinicians and staff can be daunting challenges to overcome. Yet, there are significant opportunities to be leveraged. By fostering open standards and APIs and encouraging partnerships and innovation incentives for those clinicians and staff who would like to experiment, healthcare organizations can align their drive with the evolving technological landscape, paving the way for more adaptable and integrated systems.
The third area of challenge is demand. The challenges of demand are diverse and include meeting the varied needs of stakeholders, ensuring scalability of AI solutions, and navigating the intricate process of regulatory approval. However, the demand for more personalized, efficient, and patient-centered care is catalyzing the adoption of AI in healthcare. This growing demand underscores the opportunity for AI to facilitate the shift towards value-based care models, optimize patient outcomes, and bridge global healthcare gaps. By focusing on patient-centric solutions and embracing global health initiatives, AI can
significantly enhance interoperability and the overall effectiveness of digital health platforms. Ultimately, the journey towards full interoperability in digital health is complex, marked by technical, organizational, legal, and regulatory hurdles. Yet, the potential for improved patient care, innovation, and system efficiencies creates a compelling case for ongoing investment and development in this area.
3. In what ways can AI technologies be tailored to enhance the patient experience within digital health platforms, and how might this impact patient engagement and outcomes?
Patient care and experience is at the core of every healthcare organization’s mission and every provider’s heart. Tailoring AI to improve patient experience takes a multifaceted approach. Personalization of care through predictive analytics can help create highly tailored health interventions leading to improved outcomes. For example, by considering patient history, genetics, and lifestyle factors, AI can predict patient risks by analyzing patterns in historical data allowing providers to intervene early if needed and perhaps prevent complications. A right patient, right time, right intervention approach if you will.
Another way to tailor the patient experience is using AI-powered chatbots and virtual health assistants to support patient needs and questions 24/7. These can include appointment scheduling, offering medication reminders, or answering basic questions. This is especially important for populations who have limited access to care, those with mobility concerns, people whose work schedules are erratic, or those who live in remote areas.
The upside of these interventions is that they increase engagement from the patient, allowing them to feel more connected and involved in their care which can lead to improved outcomes but also a cost reduction for the organization. The efficient use of data and predictive analytics can lower admission rates, improve rates of preventive care, improve rates of patient satisfaction, and lower healthcare costs. The thoughtful investment of AI technologies can enhance the patient experience.
4. How can AI contribute to clinical decision support systems in digital health, and what steps should be taken to ensure seamless integration into the workflow of healthcare professionals?
AI's contribution to clinical decision support systems (CDSS) in digital health can be transformative. AI can enhance the capabilities of healthcare professionals to deliver high-quality care. AI algorithms excel in assimilating and interpreting vast amounts of medical data quickly and accurately, offering diagnostic support that complements human expertise. For example, machine learning models can sift through thousands of radiographic images to identify potential malignancies with accuracy, aiding in early detection and treatment. Many studies have shown the power of machine learning models in radiology and this area in medicine is certainly leading the way in clinical decision support systems. As mentioned previously, AI's capacity for synthesizing patient histories, lab results, and current research facilitates the generation of tailored treatment recommendations. Furthermore, predictive analytics applied by
AI can prognosticate patient risks, allowing for preemptive care strategies that mitigate potential adverse events.
However, realizing the full potential of AI within CDSS hinges on seamless integration into the healthcare professionals' workflow. The integration process should start with usercentered design, ensuring that AI tools are intuitive and enhance, rather than disrupt, clinical workflows. Training is also pivotal; healthcare professionals must be educated not only in the use of AI tools but also in understanding the basis of AI recommendations to trust and effectively leverage them in their clinical decision-making.
A strategic approach for AI to be effectively integrated into the healthcare environment without disrupting existing workflows is essential. Here I propose using the mnemonic "STRIDE” to help understand the basic considerations—Standardization, Training, Regulatory compliance, Interoperability, Design, and Ethics.
• Standardization of data is the foundation, ensuring that AI systems can interpret clinical data consistently.
• Training is critical, not just in the functionality of AI tools but in understanding their analytical processes, instilling confidence, and trust in their use.
• Regulatory compliance is important for all stakeholders. AI systems must adhere to healthcare regulations such as HIPAA or GDPR for safeguarding patient privacy.
• Interoperability is vital for the fluid exchange of information between AI systems and other healthcare technologies, whether they be new or legacy.
• Design must be user-centric. AI tools should be intuitive to use and meld seamlessly
with clinicians’ workflows. The same is true from the patient aspect of design.
• And last but not least, ethical deployment of AI involves addressing bias, maintaining transparency, and ensuring accountability in the algorithms that support clinical decisions.
Seamless integration requires meticulous attention to regulatory compliance at all levels as part of the "STRIDE" framework. Compliance ensures that AI tools meet legal and ethical standards, fostering trust and reliability among healthcare providers and patients.
The regulatory aspect also ensures that AI applications are developed and used in a manner that prioritizes patient safety and quality of care. Through the lens of STRIDE, each step is interconnected and reinforces the others, underscoring the notion that integration is an ongoing process that evolves with technological advances and changes in healthcare practice.
The STRIDE framework can help healthcare organizations navigate the complexities of AI integration, aligning technology with the human aspects of healthcare.
5. How can AI-driven insights contribute to the personalization of healthcare services within digital health platforms, and what considerations should be made in respecting patient privacy and consent?
Patient privacy and consent are of utmost importance in healthcare. AI-driven insights are driving and will continue to drive personalization of care on digital platforms. By analyzing large datasets, AI can surface health patterns that may not be evident to the human eye. This allows for accurate diagnoses and predicting risk patterns. The depth of analysis that AI allows will power the personalized treatment plans we recommend as clinicians. Everything from lifestyle and medication recommendations to prediction and prevention of adverse events will become fine-tuned and personalized. However, in order for this to be a reality, we have to assure a robust and secure framework to protect patient privacy and consent. Strict adherence to HIPAA and GDPR (although I think this framework will also evolve) is crucial. In order to maintain trust for the clinician to use the algorithm and data and for the patient to have confidence in the recommendation, transparency is fundamental. Patients must be clearly informed about the use of their data and the insights AI is generating.
Consent processes should be rigorous and transparent, outlining the scope and intent of data usage. Data protection measures, including encryption and anonymization, are important to safeguard against breaches. Patients should retain control over their data, with the ability to opt-out and oversee their personal information. Finally, continuous vigilance is required to avert biases within AI systems. It is crucial that the personalization of healthcare does not compromise fairness or equity. Balancing the transformative benefits of AI with a commitment to ethical data practices is critical to advancing healthcare services while maintaining patient trust and autonomy.
6. What advancements and challenges do you see in utilizing AI for remote patient monitoring within digital health, and how can it enhance the delivery of continuous and proactive care?
Remote patient monitoring is becoming the new normal in care. As algorithms become more and more sophisticated with the ability to detect and predict the potential for adverse outcomes earlier, our ability to act on them will and should shift. Patients are truly becoming partners in care by sharing their real-time data with their providers through wearable devices such as smart watches, smart phones, and other devices. AI is able to identify subtle patterns and alert clinicians to intervene earlier. For chronic disease management, AI is able to track patient metrics over time providing insights that in the past may only have been gleaned retrospectively. Examples include arrhythmia detection, continuous glucose monitoring, and heart failure exacerbations. These are just some areas where AI is truly impacting real-time management of chronic conditions through remote patient monitoring. Along with the advancements, come challenges; this is true of any tool or technology. Data privacy and security remain of utmost concern especially how and where the data is transmitted and stored. Robust cybersecurity measures should be part of any digital health platform. Furthermore, organizations should know that implementation of digital health and AI is not a “one and done” project; rather it is part of the continuous improvement process of any healthy organization. As the technology evolves, so should the algorithm and this algorithm should be continuous scrutinized for accuracy and reliability. The aim should
be to trust and verify at every stage so that patients and clinicians can continue to benefit. Continuous feedback loops between patients, caregivers, and AI systems can help refine algorithms and personalize monitoring to individual needs. Ultimately, the success of AI in remote patient monitoring hinges on a collaborative approach that aligns technology with human-centric care principles, emphasizing not just the predictive power of AI but also its role in empowering patients to take an active role in their health management.
7. In the context of telemedicine, how can AI be seamlessly integrated to enhance diagnostic accuracy, treatment recommendations, and overall virtual care experiences for patients?
In many ways, telemedicine is a perfect way to integrate AI into clinical workflows. Integration of AI into telemedicine requires intelligent systems that can interpret various types of medical data, such as symptoms, images, and test results. For example, AI-driven image analysis can assist in diagnosing many conditions, from dermatological to retinal diseases. Research in both these areas has proven fruitful and many organizations have implemented teledermatology and teleophthalmology into their telemedicine practices. This is particularly helpful in areas where a specialist is not immediately available or access to care is limited. Furthermore, AI can improve diagnostic accuracy by incorporating machine learning algorithms that learn from thousands of patients which helps in pinpointing diagnosis or patterns from symptom clusters.
Beyond diagnosis, AI can contribute to personalizing treatment recommendations.
Utilizing data from EHRs, clinical studies, and current best practices, AI systems can present healthcare providers with treatment options that are statistically successful, considering individual patient factors such as comorbidities and medication interactions; this brings the vision of personalized medicine to a reality. For example, a patient with diabetes could use a telemedicine app integrated with an AI that tracks blood sugar levels and recommends insulin dosages, adjusting for factors like diet and exercise logged within the app.
Shifting from patient care to administrative tasks; AI can streamline administrative processes, reducing wait times and eliminating unnecessary steps for patients and providers. AI chatbots can handle routine inquiries, schedule appointments, and even provide follow-up care instructions, improving patient engagement without adding to the clinical workload. An example of AI's impact on patient experience could be the integration of natural language processing tools to transcribe and summarize patient-provider conversations during a telehealth visit. This summary can then be reviewed by both parties for clarity and accuracy, ensuring mutual understanding of the treatment plan, both essential for patient adherence and satisfaction.
8. What strategies can healthcare organizations employ to adequately train and upskill their workforce in embracing and effectively utilizing AI technologies within digital health settings?
Training the workforce is one of the biggest areas of need. If you don’t have a trained workforce to use these tools and technologies, the implementation endeavor will fail.
Investment into the workforce through training and upskilling is essential. This is an area I am particularly passionate about.
A basic first step is to develop a foundational training curriculum that allows engagement of AI information and content. This curriculum should cover the basics of AI functionality, its applications within healthcare settings, and the implications for patient care. By fostering a general understanding of AI, staff can become more comfortable with its presence and potential. The next step is to provide specialized training modules for specific areas, departments, and roles. For example, clinicians might receive training on AI diagnostic tools, while administrative staff might focus on AI systems for billing and scheduling. Simulation-based training, using real-world scenarios, can allow staff to apply their learning in a controlled environment, building confidence and competence before they use these systems with actual patients.
Another, more organizational level, strategy is that of creating a culture of continuous learning. Given the rapid pace at which AI technologies evolve, healthcare organizations should establish ongoing educational initiatives that keep their workforce updated on the latest developments. This can be accomplished in several ways—workshops, seminars, webinars led by AI experts. Another way is to bring forth interdisciplinary collaborators into fold. Think beyond the healthcare industry and seek out experts and leaders who can help gain an innovative insight into the current landscape. Going further, developing mentorship programs. Mentorship programs, where AI-savvy staff help to guide their less experienced colleagues, can further enhance learning.
Throughout the training and upskilling, it is important to remember that learning takes time. Providing the right support during the learning process is key. Be patient, slow the process down, keep in mind the psychological aspects of a technological transition; not everyone is ready to adapt and adopt the moment an organization is. This is sometimes a multi-year or decades long process.
9.How should regulatory frameworks evolve to accommodate the integration of AI within digital health, ensuring both innovation and patient safety are prioritized?
Like all systems, evolution is key to remaining relevant. The same is true for regulatory frameworks. As technology evolves, the regulatory landscape will need to adapt and vice versa. A balanced approach of AI innovation in digital health while keeping in mind patient safety is key. Some work is already being done in this space such as the FDA’s Digital Health Advisory Committee and the EUs Artificial Intelligence Act; although the frameworks will need to be flexible in order to remain relevant to new and emerging technologies and tools. One approach is a tiered framework that categorizes AI application on potential risk to patients or end-users. High-risk applications (such as those part of clinical decision support) would need a more stringent review process and a post-market surveillance process to account for safety. Lower-risk AI applications should also have a robust review and oversight process but could be expedited for faster approval, still keeping in place the post-market surveillance processes.
I have mentioned transparency in several contexts and the regulatory and developer space is no different. Regulatory bodies should encourage a culture of transparency from AI developers. This can be accomplished via mandatory sharing of datasets that were used for AI training and validation, explaining the AI decision-making process (known as explainable AI, XAI). In addition, the data sets used should aimed at minimizing bias.
Collaboration between regulatory bodies, healthcare providers, AI developers, and patients is also essential. Creating channels for ongoing dialogue can help regulators stay informed about the latest developments and challenges in AI. Moreover, patient engagement is key; patients should have a voice in how their data is used and how AI is integrated into their care. As AI continues to transform healthcare, regulations must be as dynamic and intelligent as the technologies they govern, ensuring safety and fostering innovation without stifling the potential benefits AI can bring to digital health.

With over 23 years of experience, Dipu Patel, is deeply committed to medical education. Her leadership extends from academia to healthcare tech startups, where she led provider-driven, patient-centered clinical pathways. As Vice Chair for Innovation and Professor at the University of Pittsburgh’s DPAS program, she focuses on quality improvement, innovation, and digital health. She is ABAIM certified. Her passion lies in merging clinical expertise with technology to enhance patient care and education while maintaining the importance of a human touch.
AUTHOR BIO
Vascular & Endovascular surgeon. Head of Department of Minimally Invasive Vascular Surgery. Co-founder of MED-Pie group.
1. What advancements in minimally invasive interventions have had the most significant impact on patient outcomes in recent years?
In the last few years, the advancements in minimally invasive interventions have been stunning. Robotic-assisted technology, interventions guided by image fusion technology, transcatheter valve therapies, laparoscopic and thoracoscopic procedures are some of the novel tools used in minimally invasive interventions. More specifically in my field - vascular surgery – we have seen an aston-
ishing improvement in imaging quality and consequently image-guided procedures, as well as an improvement of the design and manufacturing of endovascular materials, e.g. specialized catheters, drug-coated stents and balloons, bioresorbable vascular scaffolds, intravascular ultrasound imaging (IVUS) and other special devices.
2. Could you discuss the role of patient selection criteria in ensuring successful outcomes with minimally invasive procedures?
Effective patient selection is crucial for achieving favorable outcomes with minimally invasive procedures. The severity and complexity of a patient's condition are key factors in determining their suitability for such interventions. While minimally invasive techniques are applicable to a wide range of conditions, the specifics of the disease can influence the treatment outcome. Anatomical considerations are pivotal in assessing the feasibility and safety of these procedures. Additionally, the patient's overall health status and comorbidities play a significant role, as severe comorbidities may increase the risk of complications or affect their ability to tolerate the procedure, anesthesia, and recovery. Frailer patients often fare better with minimally invasive procedures compared to the risks associated with open surgery. Evaluating the patient's functional status is essential in gauging the potential benefits of minimally invasive procedures and tailoring treatment plans accordingly. For instance, a bed-bound patient with peripheral artery disease may benefit more from a short endovascular procedure to prevent toe gangrene, rather than undergoing lengthy open bypass surgery to completely reestab-
lish normal blood flow. Understanding the patient's preferences and treatment goals is critical in shared decision-making, ensuring their satisfaction with the chosen intervention and potential outcomes. In complex cases, a multidisciplinary team approach involving specialists from various medical disciplines may be necessary to comprehensively evaluate the patient and develop a personalized treatment plan.
3. Can you share examples of how patient-centered care principles are applied in the context of minimally invasive procedures?
Patient-centered care principles are seamlessly incorporated into the sphere of minimally invasive procedures. Similar to open surgery, it is imperative for healthcare providers to ensure that patients receive comprehensive information regarding their condition and treatment options, including the potential benefits and risks associated with minimally invasive procedures. This empowers patients to actively engage in the decision-making process, considering their personal preferences and treatment objectives. The customization of treatment plans to suit the individual needs and preferences of each patient is emphasized, considering various factors as mentioned earlier. Effective communication and patient education are fundamental throughout the treatment journey. Similar to open surgery, the well-being of patients, encompassing physical, emotional, and social aspects, as well as respect for their preferences, is a central focus. In complex cases, a collaborative approach involving specialists from various medical disciplines ensures a thorough evaluation and the development
of tailored treatment plans in collaboration with the patient. Adhering to these patientcentered care principles enables healthcare providers to ensure that minimally invasive procedures are not only clinically effective but also aligned with the unique needs, preferences, and goals of each patient, ultimately resulting in enhanced outcomes and patient satisfaction.
4. What are the main challenges or limitations that healthcare providers face when transitioning from traditional surgery to minimally invasive techniques?
Transitioning from traditional surgery to minimally invasive techniques presents challenges for healthcare providers and healthcare organizations. Acquiring specialized skills and training is crucial, as minimally invasive procedures require different expertise. Access to costly equipment and technology poses financial hurdles that often halt the transition process. Identifying suitable candidates and managing potential complications also require careful consideration. Effective communication among multidisciplinary teams is essential, as is educating patients about the minimally invasive procedures, managing their expectations, and explain any additional benefits by comparing to open surgery. Despite all these challenges, successful adoption of minimally invasive techniques offers significant benefits for patients, health professionals and healthcare organizations.
5. What strategies do you employ to manage complications or unforeseen challenges during minimally invasive procedures?
During minimally invasive procedures, we employ various strategies to effectively handle complications. Most important is the meticulous preoperative planning, that is crucial for anticipating potential issues and considering factors like patient history and anatomical characteristics. Team collaboration through a clear communication protocol ensures coordination among the team members, thus facilitating prompt responses to unexpected events. All team members must remain flexible, ready to adjust the minimally invasive approach or procedure in response to complications or technical difficulties. They also rely on problem-solving skills to quickly assess situations and implement appropriate strategy changes. As mentioned before, advanced imaging and material technology aid in real-time visualization and guidance, assisting in early detection of complications. Training and drills simulating possible complications build skills and confidence, and prepares team members to manage complications if these occur in reality. Continuous quality improvement through regular outcome review allows for identification of areas for improvement.
6. From a regulatory perspective, what are the key considerations for ensuring the safety and efficacy of new minimally invasive technologies?
Initially, rigorous clinical trials are important in providing robust evidence supporting safety and effectiveness of novel minimally invasive techniques. Local regulatory agencies mandate thorough pre-market approval or clearance (FDA in the USA and CE in Europe), involving a comprehensive review of preclinical and clinical data, before these technologies can be marketed
In complex cases, collaboration among specialists ensures tailored treatment plans for patients.
and/or clinically used. Moreover, clear and comprehensive labeling and instructions for use are indispensable to ensure the safe implementation of these technologies by healthcare professionals. Manufacturers must also establish robust quality management systems to maintain consistent production standards and comply with all regulatory requirements. They must also conduct thorough assessments to identify potential hazards associated with their technology, implement appropriate risk mitigation measures, and conduct post-market surveillance and reporting of their product and technology.
7. In your opinion, what are the critical success factors for healthcare organizations looking to establish comprehensive minimally invasive surgery programs?
A number of key factors contribute to the success of healthcare organizations seek-
ing to establish minimally invasive surgery programs. First and foremost is clinical expertise and it is crucial to invest in skilled surgeons proficient in minimally invasive techniques. These surgeons should be supported by equally proficient nurses, technicians and other health professionals. The continuous training and professional development of these teams ensure proficiency and keep all team members updated with advancements in the field. Additionally, adequate investment in state-of-the-art equipment and facilities supports these programs. This includes acquiring advanced surgical instruments, imaging systems, and creating dedicated operating rooms (or hybrid rooms) tailored to the needs of minimally invasive procedures Implementing robust safety and quality protocols is essential to ensure patient safety and optimize outcomes. Compliance with evidence-based guidelines, standardizing procedures, and providing comprehensive patient care pathways are crucial components. Patient-centered care is paramount for program success, therefore prioritizing patient involvement in decisionmaking processes and addressing their preferences ensures personalized care throughout the treatment phases. Interdisciplinary collaboration within multidisciplinary teams ensures seamless care delivery and optimal patient outcomes. Leveraging data analytics and regular performance reviews enables continuous monitoring and enhancement of program quality. Establishing strong networks with referring physicians and other healthcare professionals is essential for ensuring a steady patient flow to the newly-established minimally invasive surgery program.
8. What are the key differences in patient outcomes between minimally invasive interventions and traditional open surgeries for common medical conditions?
Minimally invasive interventions typically yield a quicker recovery and less post-operative pain compared to traditional open surgeries as they are characterized by smaller incisions and reduced tissue trauma. Apart from the aesthetic benefit of small scars minimally invasive interventions carry a lower risk of complications such as blood loss and infections. While long-term outcomes significantly vary by procedure and condition, minimally invasive approaches may offer similar or better efficacy when compared to open surgery. Despite potentially higher initial costs, minimally invasive procedures may lead to overall cost savings due to shorter hospital stays, fewer complications and – in some cases - minimal risk of reintervention. Ultimately, the choice between minimally invasive and traditional open surgery hinges on factors like patient status, complexity of the case and surgeon expertise.
9. How do you address patient concerns and preferences regarding minimally invasive procedures, particularly regarding recovery time, scarring, and overall experience?
When discussing minimally invasive procedures with patients, it's important to highlight the benefits, such as quicker recovery times and minimal scarring, to address concerns about the recovery process and aesthetic outcomes. Providing patient testimonials and facilitating open communication can
Minimally invasive techniques offer significant cost savings through shorter hospital stays and reduced complications, benefiting healthcare systems and insurers alike.
further reassure individuals about the overall experience. By actively involving patients in decision-making and offering educational resources, we could help align treatment choices with patients' preferences and concerns efficiently.
10. What are the potential cost savings for healthcare systems and insurers associated with a broader adoption of minimally invasive techniques?
Expanding the use of minimally invasive techniques can result in substantial longterm cost reductions for healthcare systems and insurers. These savings are derived from shorter hospital stays, decreased complication rates, diminished requirements for blood transfusions, quicker return to everyday activities, and enhanced efficiency in healthcare resource utilization. Minimally invasive procedures frequently enable outpatient care, which additionally lowers expenses compared to inpatient surgeries. Overall, these costsaving advantages make minimally invasive
approaches financially appealing for both healthcare systems and insurers, despite the higher cost of the initial investment.
11. How do you ensure continuous quality improvement and standardization of care protocols in minimally invasive surgery across different healthcare settings?
Ensuring consistent quality improvement and standardization of care protocols in minimally invasive surgery across diverse healthcare settings involves several essential steps. This includes establishing evidence-based guidelines and providing regular training to healthcare providers. Implementing peer review and quality assurance programs enables ongoing assessment of surgical outcomes and identification of areas needing enhancement. Standardized clinical pathways and surgical checklists help maintain uniformity in care processes. Overall performance should be closely monitored by leveraging data and metric, and improvement efforts should be guided by this performance analyses. A culture of ongoing review and adaptation within an organization ensures protocols remain responsive to evolving needs and standards. These strategies collectively promote reliable, high-quality care in minimally invasive surgery across different healthcare settings.
12. What role do patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) play in evaluating the effectiveness and satisfaction levels of minimally invasive interventions?
PROMs play a vital role in assessing the
effectiveness and satisfaction levels of minimally invasive interventions. By capturing patients' perspectives on their health status and quality of life post-surgery, they provide valuable insights into treatment outcomes beyond clinical indicators. Incorporating PROMs into clinical research and practice allows healthcare providers to tailor care plans to individual needs, enhance patient satisfaction, and inform shared decisionmaking. Ultimately, they contribute to a patient-centered approach to care and support continuous quality improvement in healthcare delivery.
 AUTHOR BIO
AUTHOR BIO
Nikolaos Patelis is a Vascular & Endovascular surgeon. Head of Department of Minimally Invasive Vascular Surgery. Co-founder of MED-Pie group, advocating for technology enhanced learning (TEL) in surgery. Advisor on the use of TEL and AI in healthcare organizations bridging the gap between traditional and novel health and training services. Educator in various organizations.
Cancer is the second leading global cause of death, following cardiovascular diseases. Advances in cancer treatment have enhanced patient outcomes. However, cancer treatment can increase cardiovascular risks. Our group's research bridges oncology and cardiology. Ongoing collaboration and advocacy are imperative to reduce cardiovascular risks in cancer patients.
Nataliia Lopina Director and Founder, ClinCaseQuestPresently, oncology stands as the second leading cause of mortality globally, following cardiovascular diseases. Substantial strides have been achieved in managing various oncological conditions, largely attributed to the advancements in targeted therapy for cancer. However, a noteworthy concern arises as the cardiovascular risk escalates significantly in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy or targeted therapy, surpassing that of the general population. This heightened risk stems from increased survival rates among cancer patients and the adverse effects associated with chemotherapy and targeted treatments.
Along with the increased survival of patients with different types of oncology, special attention has recently been paid to cardiovascular complications due to the prevalence of cardiovascular diseases in the general population and the toxicity profile of targeted drugs.
Current data confirm the increased cardiovascular risk in the specific types of cancers population compared to the general population, which necessitates the widespread introduction of cardiovascular prevention strategies in such groups of patients.
Patients with cancer face a dual challenge in terms of cardiovascular health. On one hand, they can have common cardiovascular risk factors with the general population, encompassing modifiable factors such as weight, smoking status, increased sugar level,
increased cholesterol level, and increased blood pressure, as well as non-modifiable factors like gender, age, and genetics. On the other hand, the complexity arises from the fact that many drugs employed in cancer treatment exhibit cardiotoxicity. This dual burden underscores the importance of comprehensive cardiovascular monitoring and management in the oncology setting.
Cardiotoxicity is heart damage that arises from certain cancer treatments or drugs. It can develop years after cancer treatment, especially in adults who received cancer treatment during childhood. Certain types of cancer treatments have a higher risk for cardiotoxicity.
Cardiotoxicity differed depending on the type of drug.
Anthracyclines (Doxorubicin, Daunorubicin, Epirubicin) are potent chemotherapy drugs commonly used for various cancers, including breast cancer and lymphomas. They are associated with dose-dependent cardiotoxicity, leading to conditions such as cardiomyopathy and congestive heart failure.
Trastuzumab is a targeted therapy used for HER2-positive breast cancer. While highly effective in treating cancer, it can lead to cardiotoxicity, particularly when used in combination with anthracyclines.
Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs - Dasatinib, Nilotinib, Ponatinib) can cause hypertension, heart failure, accelerated atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular complications.
VEGF Inhibitors (Bevacizumab, Sunitinib, Sorafenib) associated with hypertension,
proteinuria, and an increased risk of cardiovascular events.
Proteasome Inhibitors (Bortezomib, Carfilzomib) are used in the treatment of multiple myeloma. They can lead to cardiac toxicities, including heart failure and arrhythmias.
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (Nivolumab, Pembrolizumab) have been associated with immune-related myocarditis, which can lead to serious cardiac complications.
Mitotic Inhibitors (Paclitaxel, Docetaxel) may cause arrhythmias and myocardial ischemia.
In the general population, well-established strategies for mitigating and managing cardiovascular risk, rooted in evidencebased medicine, are widely disseminated and implemented across various tiers of healthcare, spanning from family physicians to specialized institutions offering highly targeted medical care.
However, the landscape becomes more challenging when addressing the reduction of cardiovascular risks in patients with cancer. One significant hurdle is the limited accessibility to consultations with cardio-oncologists. Often, patients only seek the expertise of a cardiooncologist when severe complications have already manifested. For instance, a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia taking the tyrosine kinase inhibitor nilotinib might present with advanced atherosclerosis, leading to lower limb amputation. In such cases, the focus shifts from primary prevention, which aims to avert
cardiovascular events, to secondary prevention, aimed at managing and preventing further complications after an event has occurred.
Additionally, the drug-drug interactions pose a substantial concern. Many medications utilized in cancer treatment have the potential to interact, altering each other's pharmacokinetics and potentially intensifying toxic effects. This aspect is especially critical in the treatment of comorbid patients with cardiological pathology and cancer, where a comprehensive understanding of potential interactions is imperative.
The field of cardio-oncology is rapidly evolving globally, witnessing the emergence of specialized advisory centers and dedicated departments. Recently, collaborative efforts between cardiology and oncology societies have culminated in the development of joint clinical guidelines. These guidelines underscore the paramount importance of cardiac monitoring in cancer patients. By emphasizing proactive monitoring and the management of cardiovascular health, these guidelines aim to bridge the gap between oncology and cardiology, ensuring a more holistic and integrated approach to the care of patients facing both cancer and cardiovascular challenges.
The strategy for reducing cardiovascular risk in patients with cancer should be based on the individual patient risk assessment, general population recommendations, and cardiotoxic features of the drug used for cancer treatment. All cancer patients should be recommended a
two-stage approach for reducing cardiovascular risk. The first stage is risk assessment and the choice of appropriate cancer treatment based on cardiovascular risk assessment before starting cancer therapy. The second stage is monitoring and treatment during cancer therapy with further prevention of cardiovascular complications.
In certain instances, conventional clinical guidelines may fail to address the myriad questions that surface in routine clinical practice. Recognizing this gap, our research group endeavored to address the challenges by publishing the article titled "A New Paradigm of Cardio-Hematological Monitoring in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients Treated With Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors" in 2022 (Lopina N, Dmytrenko I, Hamov D, Lopin D, Dyagil I. Cureus. 2022 Jun 8;14(6):e25766. doi: 10.7759/ cureus.25766. PMID: 35812557; PMCID: PMC9270100. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ pmc/articles/PMC9270100/). This research aims to reduce cardiovascular risk in patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML), offering potential enhancements to the prognosis within this specific population grappling with blood cancer.
When clinical recommendations prove insufficient in navigating the complexities of routine clinical cases, healthcare providers often rely on their experience, standard treatment, and prevention algorithms for the general population. Additionally, aligning an individual patient's risk profile with the cardiotoxicity attributes of specific drugs becomes crucial. This confirms the necessity of the development
of personalized strategies encompassing prevention, monitoring, and treatment for cancer patients, thereby mitigating cardiovascular risk and ultimately enhancing prognosis.
Our research group in Ukraine is actively engaged in advocating for increased awareness of the toxicity associated with cancer therapy, overcoming different types of cancer drug toxicity, and the concurrent increase of treatment tolerance. This involves active participation in national and international conferences, and conducting lectures for healthcare professionals from various specialties, including patient involvement in educational initiatives. Also, we are actively involved in developing written
algorithms for delivering medical assistance to the blood cancer patient’s population and are currently testing interprofessional protocols for providing medical care to cancer patients.
In collaboration with the Charitable Foundation "Kraplya Krovi" (Drop of Blood), dedicated to safeguarding the rights of patients with various forms of cancer, we have supported the implementation of the first strategies for cardiac and vascular prevention in Ukraine, particularly among patients with blood cancer. Despite the challenging circumstances posed by the ongoing war in Ukraine, our commitment to caring for patients and ensuring their access to adequate medical care remains unwavering.

NATALIIA LOPINA, a prominent Cardiooncologist and Clinical Simulation Training Platform Director with a decade of impactful experience. Over the last eight years, she has specialized in overcoming diverse drug toxicities in patients with oncohematological diseases. She is committed to patient safety, showcasing dedication to advancing medical care and improving patients' outcomes.
AUTHOR BIO
Book Description: This video-atlas aims to be a reference multimedia book for Thoracic Surgeons. Mainly focused on operative technical aspects, each individual segmentectomy and many combinations are described. Each chapter opens with anatomical 3D reconstructions of the segment and its bronchoscopic anatomy. Then, the main steps for performing the procedure are described in HD video-clips and figures. Expert authors highlight specifical tips & tricks for successfully performing the resection and include anatomical variations, also illustrated with HD video-clips.
This illustrated guide provides Thoracic Surgeons with an incredibly useful tool for learning and improving their technique in sublobar resections.
1. Can you share a bit about your journey to becoming a Consultant Thoracic Surgeon, and what inspired you to specialize in minimally invasive thoracic surgery?
As you well know, the path to becoming a consultant surgeon is not easy… After studying at the multi-centennial University of Valladolid (the oldest Medical School in Spain, founded in 1404), I passed the national MIR exam to access our specialized medical training program.
Then I moved to the beautiful city of Valencia to invest the next 5 years in my specific training as a surgeon, at the General University Hospital. I think it took a few more years to acquire a
 Santiago Figueroa MD, Consultant Thoracic Surgeon, Department of Thoracic Surgery, Clinical University Hospital of Valencia
Santiago Figueroa MD, Consultant Thoracic Surgeon, Department of Thoracic Surgery, Clinical University Hospital of Valencia
certain "surgical solvency", once I moved to my current position, at the Clinical University Hospital of Valencia. Here I had the opportunity to develop a minimally invasive surgery program, as well as a progressive incorporation of anatomical segmentectomies into our clinical practice. What inspired me to follow this path were the clear advantages we observe in the postsurgical recovery of our patients through these approaches and techniques, without a doubt some of the most relevant achievements of recent decades to reduce pain, risk of complications and hospital stay.
2. As the Coordinator of the Teaching Committee in the Spanish Society of Thoracic Surgery, how has your role influenced your approach to educating fellow surgeons?
Well, before acquiring this responsibility I already had experience in training residents, but of course now I see everything from a broader perspective and I think I better understand the needs of the new generations. At the Spanish Society of Thoracic Surgery we try to offer a multidisciplinary teaching plan, with special emphasis on the development of technical skills but also extensive oncological knowledge, scientific communication strategies, bioethics, artificial intelligence.
3. Your book, "The Video-Atlas of VATS Pulmonary Sublobar Resections," is focused on operative technical aspects. What motivated you to create a multimedia reference book specifically for Thoracic Surgeons?
Growing adoption of sublobar lung resections in lung cancer treatment highlights the need for mastery among European and American Thoracic Surgeons.
The four editors of the Video-Atlas shared a concern: we wanted to offer a publication that unified all the technical knowledge around anatomical lung segmentectomies. To date, no one had carried out a similar project in this format, including detailed videos of each procedure, so the challenge was even greater. But we thought the effort was worth it, to provide a valuable tool for the global community of Thoracic Surgeons, especially considering that these surgical techniques are on the rise and learning them is not easy without adequate guidance. We surgeons love to operate, so there is no greater motivation than helping your colleagues operate better.
4. Could you elaborate on the importance of minimally invasive techniques in thoracic surgery and how your book contributes to the field?
As I mentioned before, minimally invasive lung resection techniques have made a key contribution to improving the results of our surgeries, with a significant reduction in morbidity and mortality. For example, we have reduced the risk of complications or death after an anatomical lung resection by half, as well as improved postoperative pain rates and decreased hospital stays. Our book fundamentally contributes to the technical mastery of the most complex type of lung resection, which is often a challenge even for experienced surgeons. In this way, we hope to provide greater confidence and security when performing these procedures.
5. The book features anatomical 3D reconstructions and bronchoscopic anatomy illustrations for each segmentectomy. How do these visual elements enhance the learning experience for the readers?
Extensive knowledge of intrapulmonary anatomy is essential to perform a segmentectomy with guaranteed success. That is why we decided to include these 3D reconstructions and bronchoscopic images: to help readers in this sense and encourage them to delve deeper into the exciting world of segmental anatomy.
6. The main steps of the procedures are illustrated in high-definition video clips and figures. How do you believe this multimedia approach benefits thoracic surgeons in understanding and mastering the techniques? Some previous publications have addressed
the surgical technique of segmentectomies through text and static images, but we wanted to make a difference with absolute prominence of the videos, since we think it’s the best way to teach the different steps of each surgery in a precise, comprehensive and pleasant way. As an added benefit, this allows for synchronized narration by the authors, further enriching the learning experience.
7. In your book, expert authors provide specific tips & tricks for successful resections. Can you share an example of a particularly valuable tip that you believe could significantly impact a surgeon's practice?
Wow, that's a great but difficult question... I'll choose two tips, actually related: focus on your patients' results, not your own ego and look for windows, not mirrors to inspire you.
Minimally invasive lung resection techniques have greatly improved surgical outcomes, significantly reducing morbidity and mortality.
8. Anatomical variations are also highlighted in HD video clips. How crucial do you think it is for surgeons to be well-versed in handling variations, and how does your book assist in this aspect?
Anatomical variations are really the key to sublobar resections. A high percentage of mistakes and complications in these procedures are explained by misinterpretation of the anatomy. So a thorough description of all these variations is made in each chapter of the video-atlas, not only mentioning them, but also describing how to handle them correctly.
9. How do you envision your book being utilized by thoracic surgeons in their daily practice and training?
Anatomical sublobar lung resections still represent a relative low percentage of the surgeries used in the treatment of lung cancer in our environment, but the scientific evidence published in recent years places it on a clear upward trend. So European and American Thoracic Surgeons are increasingly aware of the need to master these procedures. Our work can become a "bedside book" to help both trainees and more experienced surgeons in this task.
10. In what ways does the Video-Atlas serve as a valuable tool for both learning and improving surgical techniques in sub-lobar resections?
Highlighting again what has been said: the Video-Atlas presents a thorough review of
the most frequent anatomical variations of segmental lung anatomy, it describes step by step the recommended technique for each segmentectomy, including tips and tricks based on the experience of the different authors and it also offers a video-summary of each complete procedure. The learning curve for these procedures can be long and even frustrating sometimes, so our goal is to make it easier.
11. Given the dynamic nature of medical advancements, how do you see the field of minimally invasive thoracic surgery evolving in the coming years, and how might this impact future editions or companion materials for your book?
Well, everything seems to indicate that technological advances in the field of Thoracic Surgery have only just begun, so possibly robotic surgery is the closest revolution in the short term. Although the current generations of surgical robots have not demonstrated conclusive advantages in the specific field of lung resection surgery, no one doubts this will change very soon. So perhaps our next edition of the Video-Atlas will focus on this approach, it is something that we editors have not decided yet.
12. Are there any upcoming projects or areas of research that you are excited to explore within the realm of thoracic surgery?
Maybe we could have another full interview to answer this question!
In summary, I would say that Thoracic Surgery is experiencing an exciting stage of development in many ways, so very
diverse areas of research can be proposed. Personally, I find the most interesting those related to lung cancer screening and new trends in combined treatment with immunotherapy, although we cannot leave aside everything related to artificial intelligence, which is going to revolutionize our way of understanding Medicine.
13. As we conclude, what message or key takeaway would you like to convey to thoracic surgeons and readers who are considering delving into "The VideoAtlas of VATS Pulmonary Sublobar Resections"?
First of all, I would honestly recommend that they analyze what the real impact of developing an anatomical sublobar resections program may be in their clinical practice. There are certain environments in the world where the indications for these procedures remain quite limited.
Now, to all those interested in learning these techniques, which require deep anatomical knowledge and a long learning

curve, I would strongly recommend trusting our work as a valuable tool to help them in their professional development. This VideoAtlas has been created with a very pragmatic approach, based on the difficulties that we editors ourselves have encountered along our way. And as far as we know, there is no published work with similar characteristics to date.
14. Is there anything else you would like to share with our readers about your book or your experiences as a thoracic surgeon and author?
Perhaps just a reflection about piracy and illegal access to scientific content: Of course our priority when publishing this book was to reach as many Thoracic Surgeons as possible, but from the perspective of the Editorial Team one realizes the damage that the illegal distribution of the content does. In a global world like the one we live in, we can only call for individual responsibility, so that it is possible to continue developing projects like this one.
AUTHOR BIOAnd, of course, thank you all for your interest in our work. We have put a lot of effort and enthusiasm into it during the three years it has taken to publish it, and we trust it will become a really useful tool for many colleagues around the globe.
Santiago Figueroa is a Consultant Thoracic Surgeon working at the Clinical University Hospital of Valencia, Spain. After finishing his international training, he developed the minimally invasive thoracic surgery program of his institution. One year ago he was elected as Coordinator of the Teaching Committee in the Spanish Society of Thoracic Surgery.

EUROPEANHHM with its keen interest across the length and breadth of the healthcare world aims to provide premium, cutting-edge & reliable healthcare content to its subscribes base in the European region.
These days, healthcare management is in extremely high demand
Patients are treated for greater health in the surgical discipline of medicine
Healthcare providers have been compelled to look for cutting-edge technologies
With its Healthcare IT Solutions, information technology has propelled the healthcare sector.

As a result of the development of medial sciences, we are now enjoying better and long lives.
One of the most valuable markets in the world is the diagnostics sector.
It’s crucial to have a wide range of operations & facilities to give patients better treatments.
20 - 21 May 2024 | CA, USA
https://www.may24.healthcareinnovation. marcusevans-summits.com/
About Event: The Healthcare Innovation & Transformation Summit is an invitation-only, premium Summit bringing leading senior level healthcare executives and innovative suppliers and solution providers together. The Summit’s content is aligned with key clinical trial challenges and interests, relevant market developments, and practical and progressive ideas and strategies adopted by successful pioneers.
Listed Under: Information Technology
30-31 MAY 2024 | BRLIN, GERMANY
https://emdsummit.com/
About Event: The European Medical Device Summit sets the benchmark for industry collaboration and idea exchange. This event offers valuable insights and tactics to enhance the professional growth of executives engaged in medical device aspects such as design, product development, innovation, technology and quality/ regulatory matters.
Listed Under: Technology, Equipment & Devices
06-08 May 2024 | Barcelona, Spain
https://neurodisordersconference.com/
About Event: The summit will provide a unique opportunity to neuroscientists and physicians to share their research and experiences with the leaders in their fields. The program includes keynote speeches from internationally renowned scientists. Each of these speakers helped to shape the modern concepts of neuroscience.
Listed Under: Surgical Speciality


20-22 June 2024 | Paris, France
https://heart.magnusconferences.com/
About Event: The congress will spotlight ongoing cardiology research, explore innovative technologies in heart failure treatment, and shed light on advancements in managing cardiovascular diseases. This is an opportunity to engage with esteemed academicians, scientists, healthcare professionals, and cardiologists, fostering discussions on topics such as heart disease treatment, cardio medicine, pediatric cardiology, heart failure, and electrocardiography.
Listed Under: Medical Sciences
24 -26 June 2024 | Paris, France
https://infectiouscongress.com/
About Event: This event understanding the causes, transmission, and dynamics of infectious diseases helps in developing strategies for prevention, control, and treatment. Infectious diseases research is essential for safeguarding public health, advancing medical science, and addressing global health challenges. It plays a crucial role in preventing and controlling the spread of infectious agents, improving healthcare outcomes, and promoting overall well-being on a global scale.
Listed Under: Medical Science
7 – 11 September 2024| Florence, Italy
https://www.esp-congress.org/
About Event: The ECP 2024 is dedicated to provide up-to-date insight into the whole spectrum of modern diagnostic and translational tools and achievements that characterize Pathology and its contribution to innovative diagnostics
Listed Under: Diagnostics
16-18 September 2024 | Paris, France
https://www.spectrumconferences.com/2024/isnh
About Event: ISNH2024 is all about shaping the future of nursing and healthcare. We're bringing together top researchers, industry experts, policymakers, and enthusiasts to discuss the latest trends, tackle challenges, and explore new ideas in these fields.
Listed Under: HealthCare Management

09-10 May 2024 | Barcelona, Spain
https://www.medigy.com/event/2024/05/09/ meetingsint-7th-international-conference-on-digitalhealth/
About Event: This groundbreaking event explores the latest innovations, challenges, and opportunities in the realm of digital health. Engage with keynote speeches, thought-provoking panel discussions, hands-on workshops, and cutting-edge poster presentations. Network with professionals, researchers, and policymakers, and seize the
chance to drive transformative changes in healthcare.
Listed Under: Information Technology
11-12 September 2024 | Basel, Switzerland
https://intelligenthealth.ai/
About Event: Intelligent Health is THE only largescale, global summit that purely focuses on AI in healthcare and brings together the world’s brightest AI health brains from pharmaceutical, biotech, medtech, health provisions, clinicians, tech companies, startups, investment, and science to advance discussions on how to apply AI and drive technological collaboration in healthcare.
Listed Under: Technology, Equipment & Devices
09-11 September 2024 |Dubai, UAE
https://www.continuumforums.com/2024/phhmforum
About Event: The main agenda of this conference is to bring together world-leading academics, practitioners, industry leaders, policymakers, and business professionals from Public Health and Health Care Management to develop practical solutions for current challenges in these fields.
Listed Under: Healthcare Management
01-02 July 2024| Toronto, Canada
https://cancer-events.com/#
About Event: This is going to be the largest and most promising international conference bridging the gaps between the intellectuals from across the globe to enlighten their research and findings at the conference where the program includes Clinical Oncologist and whole medical team involved in cancer patient care, researchers, professional, early career individuals and patient advocates.
Listed Under: Surgical Speciality

Abbott recently received U.S. FDA approval for its innovative TriClip™ transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (TEER) system, targeting tricuspid regurgitation (TR). The FDA's decision, backed by a 13 to 1 vote from the Circulatory System Devices Panel, marks a significant milestone in heart valve treatment.
The tricuspid valve regulates blood flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle in the heart. When this valve fails to close properly, it leads to tricuspid regurgitation (TR), causing blood to flow backward and putting extra strain on the heart. This condition can result in symptoms like fatigue and breathlessness, and if untreated, it can lead to serious complications like atrial fibrillation, heart failure, and even death.
TriClip utilizes TEER technology, delivered through a leg vein, to clip together tricuspid valve leaflets and correct blood flow without open-heart surgery. Patients typically spend just one day in the hospital post-TriClip, quickly returning home.
TriClip, using the clip-based technology similar to Abbott's successful MitraClip™ device, has treated over 200,000 patients with mitral regurgitation. However, TriClip is uniquely tailored for the intricate anatomy of the tricuspid valve.
Abbott boasts the most extensive range of structural heart solutions in the industry. Alongside TriClip, its pioneering minimally invasive treatments encompass groundbreaking technologies like MitraClip and the Amplatzer Piccolo™ Occluder for pediatric heart conditions, along with the Navitor™ transcatheter aortic valve implantation system for aortic stenosis. Abbott remains dedicated to meeting the unique needs of patients with structural heart diseases,

LifeScale AST, an advanced diagnostic platform, swiftly evaluates crucial antibiotics to identify the most effective treatment for severe bloodstream infections. This technology empowers healthcare providers to enhance patient outcomes, minimize treatment duration and costs, and promote responsible antibiotic use.
The LifeScale AST system offers several key features:
• Swift results: LifeScale AST provides results within 5 hours, significantly reducing the time to select optimal antibiotic therapy. It tests a range of antibiotics, including those effective against multi-drug-resistant bacteria.
• Precision: Using population profiling, LifeScale AST measures the masses of individual bacteria via microfluidic sensors, ensuring fast and accurate AST results.
• Efficient workflow: With a user-friendly interface and automated processes, LifeScale AST streamlines laboratory operations, allowing healthcare professionals to prioritize patient care.
Affinity Biosensors, known for groundbreaking healthcare diagnostics, celebrates FDA clearance for its LifeScale AST system. This achievement equips healthcare professionals with a vital tool for swiftly managing bacteremia through rapid antibiotic susceptibility test (AST) results. pushing the boundaries of care to enhance people's quality of life.
Cardio Diagnostics Holdings, Inc., a company specializing in AI-driven precision cardiovascular medicine, has announced a strategic partnership with Navierre. Navierre is an innovative digital health technology platform that transforms patient access to healthcare, offering comprehensive care navigation, wellness, and chronic care management services from infancy to old age. This collaboration aims to broaden access to Cardio Diagnostics' cutting-edge AI-enabled precision cardiovascular diagnostic tests.
With heart disease remaining the top global cause of death, there's an urgent need for accessible and innovative clinical cardiovascular solutions. Current methods like CT imaging for assessing and diagnosing heart disease face scalability challenges due to specialized infrastructure, especially in rural areas of the US. In contrast, Cardio Diagnostics' tests like Epi+Gen CHD and PrecisionCHD require only a blood sample, easily collected in various settings including at-home or through mobile phlebotomy. This scalability, coupled with the booming telehealth sector, positions Cardio Diagnostics and Navierre to transform patient cardiovascular care by enhancing early detection, accessible specialty care, and personalized prevention.
Cardio Diagnostics' AI-driven solutions, such as the Epi+Gen CHD and PrecisionCHD tests, utilize advanced epigenetic and genetic science to offer personalized risk assessments for coronary heart disease (CHD) or evaluate CHD status. By detecting risks early and uncovering their underlying causes, these tests offer actionable insights for patients and clinicians, enabling proactive prevention and management strategies that enhance outcomes and save lives. The partnership with Navierre expands access to these transformative tools, bridging gaps in specialty cardiovascular care for a wider audience.

AngioDynamics, Inc., a pioneering medical technology firm dedicated to restoring healthy blood flow, broadening cancer treatment alternatives, and enhancing patient well-being, disclosed FDA clearance for the AlphaVac F1885 System. This clearance extends its application to treating pulmonary embolism (PE), offering significant utility in critical medical situations involving PE.
The FDA's expanded indication permits the use of the AlphaVac F1885 System in treating PE, widening its scope for non-surgical removal of thrombi or emboli from venous vessels. This extension offers more treatment choices for PE patients, reducing thrombus load and enhancing right ventricular function.
The AlphaVac F1885 System, an innovative primary device, is presently approved for thromboemboli removal from venous systems and PE treatment. It comprises an ergonomic handle, an 18F cannula with an 85-degree angle, an obturator, and a waste bag assembly. The APEX-AV Study aimed to gather safety and efficacy data specifically for PE clearance.
In the United States, pulmonary embolism (PE) impacts approximately 900,000 individuals annually and ranks as the third primary cause of cardiovascular mortality. Patients with sub-massive or intermediate-risk PE constitute 35% to 55% of hospitalized PE cases and face mortality rates
ranging from 3% to 14%.
AbbaDox and Radiology Imaging Associates have collaborated in a groundbreaking partnership aimed at revolutionizing operational and patient care standards in Florida and the US Virgin Islands. Through AbbaDox's CareFlow RIS platform, this alliance combines strengths to enhance care quality and operational efficiency across 17 locations, processing more than 600,000 annual studies.

AbbaDox's platform will streamline operations by replacing multiple-point solutions and manual processes. This transition marks a significant step towards modernization and efficiency, particularly in critical areas like appointment scheduling and automated patient communications. The platform's specialized workflows for breast and lung health, coupled with AI-driven follow-up recommendations, are poised to elevate the quality of patient care significantly. By replacing two separate RIS systems, AbbaDox eliminates inefficiencies and complexities within Radiology Imaging Associates, establishing a new standard for seamless, efficient, and patientcentric radiology practices.
Following Lake Medical Imaging's successful use of AbbaDox's solutions, which notably improved operational efficiency and patient satisfaction, Radiology Imaging Associates is positioned for similar success. This partnership is expected to boost scheduling efficiency, minimize patient wait times, and generate significant cost savings, establishing a new standard for technological excellence in outpatient imaging centers.
Medtronic plc, renowned for its advancements in healthcare technology, has revealed encouraging clinical trial findings for Sphere-360™. This investigational catheter, employing pulsed field (PF) energy, demonstrated both safety and efficacy in treating patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AFib).
The Sphere-360 catheter aims to streamline atrial fibrillation procedures, offering improved efficiency and durable lesions. Its innovative design features a large, flexible lattice tip for efficient energy delivery, eliminating the need for multiple rotations in one spot. The catheter seamlessly integrates with the Affera™ Mapping and Ablation System, providing comprehensive visualization and electroanatomical mapping. This makes it a comprehensive singleshot solution for mapping, ablation, and validation in cardiac procedures.
The Sphere-360 PFA catheter features:
• Consistent and efficient energy delivery across its entire 34mm flexible lattice tip
• Full integration with the Affera Mapping and Ablation System, allowing for minimal to no fluoroscopy during procedures
• Adaptability to different pulmonary vein anatomies by adjusting to various shapes
• Real-time local impedance data for assessing catheter-tissue proximity
• Over-the-wire design for easy positioning and a streamlined workflow
• Compatibility with a compact 8.5Fr sheath
Atrial fibrillation stands as one of the most prevalent and inadequately treated heart rhythm disorders, impacting over 60 million individuals globally. AFib is a progressive condition, with the potential to worsen over time and elevate the risk of severe complications such as heart failure, stroke, and increased mortality. While antiarrhythmic drug (AAD) therapy has traditionally been the primary initial treatment, it proves ineffective in about half
of patients undergoing drug therapy to manage AFib.
GE Healthcare Launches Caption AI Software for Rapid Cardiac Assessments on Vscan Air SL Handheld Ultrasound, offering Real-time guidance and automated ejection fraction estimation for clinicians.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains the top global cause of death, with its prevalence projected to rise due to aging populations and population growth. Detecting heart disease early is crucial for better patient outcomes, yet rapid echocardiographic assessments at point-of-care settings can be challenging in resource-limited facilities. Vscan Air SL with Caption AI aims to simplify cardiac imaging, making it accessible even for non-expert ultrasound users, thus aiding in quick heart assessments.
Caption AI offers live visual guidance for probe movements, featuring a quality meter to ensure optimal image acquisition. It includes AutoEF for instant left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) calculation upon image capture. Moreover, AutoCapture and Save Best Clip features enable efficient scanning, capturing the highest-quality images from each view.
The ultraportable Vscan Air SL delivers exceptional imaging performance with industry-leading single crystal transducer technology, offering superior depth, resolution, and sensitivity. The integration of Caption AI adds to GE Healthcare's legacy and innovation in handheld ultrasound, following the introduction of the pioneering Vscan in 2010 as the first color, pocket-sized ultrasound device. This advancement is making next-generation ultrasound care accessible to a broader range of patients.
Analytics for Life, Inc. and CorVista Health Inc. have announced FDA clearance for the CorVista System with Pulmonary Hypertension (PH) Add-On Module. This marks the first FDA-cleared, machine-learning pointof-care technology capable of assessing the likelihood of elevated mean arterial pulmonary pressure (mPAP), a key indicator of pulmonary hypertension (PH).
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a progressive condition affecting lung blood vessels, leading to increased strain on the heart to supply blood to the lungs. It impacts about 1% of the global population, with over half of heart failure patients potentially affected—most notably those in areas lacking advanced cardiovascular care (80%). Despite diagnostic advancements, PH remains challenging to detect due to symptom overlaps with other heart and lung disorders. Limited early detection and treatment options contribute to rising mortality rates among PH patients, underscoring the importance of ongoing diagnostic innovation. The CorVista System with PH Add-On addresses this need, aiming to facilitate
early diagnosis and improve patient outcomes in PH detection and management.
The non-invasive CorVista System has recently gained clearance for assessing significant coronary artery disease.
Pulmonary arterial hypertension is particularly aggressive, leading to right ventricular pressure/ volume overload, right ventricular failure, and often premature mortality.
The CorVista System, available by prescription only, is a non-invasive point-of-care solution designed to analyze cardiac and hemodynamic signals in symptomatic patients using machine learning. It predicts the likelihood of cardiovascular diseases without the need for radiation, contrast agents, injections, fasting, or exercise. The CorVista® Analysis is swiftly accessible in a secure web portal after the test, aiding physicians in promptly diagnosing and treating patients with suspected cardiovascular disease, thereby facilitating better treatment decisions. FDA clearance has been obtained for the CorVista System with CAD and PH Add-Ons for marketing in the US. It is developed and manufactured by Analytics For Life, Inc., and licensed to CorVista Health, Inc.
Are you ready to dive into the future of healthcare? Join us at the Healthcare Innovation & Transformation Summit, an exclusive gathering of senior-level healthcare executives, innovative suppliers, and solution providers.
Date: May 20 - May 21, 2024
Location: Four Seasons Hotel, Westlake Village, CA, USA
The summit is designed to address key challenges in clinical trials, highlight market developments, and showcase practical strategies adopted by healthcare pioneers. Here's a sneak peek at our key topics for 2024:
• The AI Prescription: Explore how intelligent innovations are transforming healthcare, from diagnosis to treatment.
• Harnessing The Value Of Value-Based Care: Learn strategies for successful adoption and implementation of value-based care models.
• Telehealth and Digital Innovation: Discover how digital technologies are empowering patients and revolutionizing doctor-patient interactions.
• Sustainability in Healthcare: Dive into costefficient solutions that drive long-term healthcare transformation while focusing on sustainability.
• Ensuring Security In Healthcare Transformation: Navigate the complex landscape of data and privacy challenges in healthcare.
• Holistic Approaches To Healthcare Transformation: Embrace an integrated approach to innovation that encompasses all aspects of healthcare delivery.
Connect with leading healthcare executives from America's largest hospitals and healthcare systems. Our platform facilitates meaningful partnerships between healthcare facilities and
innovative suppliers, ensuring that solutions meet the industry's evolving needs.
Experience a dynamic program featuring visionary keynote presentations, real-life case studies, and interactive forums led by industry experts. Network with like-minded professionals and gain indispensable insights into the future of healthcare transformation.
Don't miss out on this opportunity to be part of a transformative journey in healthcare innovation. Register now and join us at the Healthcare Innovation & Transformation Summit 2024!

"41%
of event professionals are putting on more events in 2023 than they originally planned."
Don't be left behind... We are here to help!

Get ready to explore the future of patient-centered healthcare at the Healthcare Patient Experience & Engagement Summit. This invitation-only event brings together senior-level healthcare executives, innovative suppliers, and solution providers for two days of essential insights and strategic collaborations.
Date: May 20 - 21, 2024
Location: Four Seasons Hotel, Westlake Village, CA, USA
Our summit is designed to address key challenges in patient experience and engagement, aligning with market developments and showcasing progressive strategies adopted by industry pioneers. Here's a glimpse of our key topics for 2024:
• Metrics Matters: Dive into the importance of measuring data to enhance and improve the patient experience.
• The Value of The CXO Role: Discover the responsibilities and impact of the chief experience officer in healthcare organizations.
• Tackling Burnout and Stress: Explore initiatives aimed at supporting the well-being of healthcare workers and reducing burnout.
• AI In Healthcare: Learn about the integration of artificial intelligence while maintaining the human connection in patient care.
• Vocalizing The Patient’s Voice: Adopt patientcentered care principles and practices to prioritize patient needs and preferences.
• Leading Better Patient Outcomes: Revolutionize the patient experience and engagement to drive better healthcare outcomes.
Connect with senior-level healthcare executives representing America's largest hospitals and healthcare systems. Our platform facilitates strategic partnerships between healthcare facilities and innovative suppliers, driving impactful solutions for patient experience and engagement.
Experience a dynamic program featuring visionary keynote presentations, real-life case studies, and interactive forums led by industry experts. Network with peers and gain indispensable insights into shaping the future of patient-centered healthcare.
Don't miss this exclusive opportunity to be part of a transformative dialogue in healthcare patient experience and engagement. Register now and join us at the Healthcare Patient Experience & Engagement Summit 2024!



Aspiring to be leading journals in the B2B landscape of Healthcare-Industry covering Medical Science, Business & Technology and all the latest innovations.
Introducing a group of highly focused magazines for the American and European markets.
Poised for bi-annual issuance, our new magazines bring a fresh outlook towards insightful and pragmatic Healthcare-Industry reporting.