










In the fast-changing world of drug development, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is bringing about exciting and transformative changes. AI is not just a tool, it’s a revolutionary force that is reshaping the pharma industry. From finding new compounds to recruiting trial participants, designing study plans, and analysing large amounts of data, AI's impact is deep and far-reaching.
The promise of AI lies in its ability to accelerate and enhance the drug development pipeline, bringing the efficiencies that were once the realm of imagination. Imagine a world where the difficult task of finding new compounds is made easier by smart algorithms, where clinical trials are carefully designed and adjusted in real-time using predictive data, and where recruiting patients becomes more inclusive and precise. This is the future that AI offers, and it is one we must work hard to achieve.
However, with this great power comes great responsibility. The integration of AI into drug development is not without its challenges. We must carefully examine and address the risks and biases in AI systems to ensure they are used ethically and fairly. It is crucial that we balance the huge potential of AI with its complexities.
In this special edition of Pharma Focus Europe, we explore the many ways AI is changing drug development. We look at ground breaking innovations, real-world applications, and the challenges we must overcome. Experts and thought leaders share their insights, giving a thorough overview of the current situation and a visionary look into the future.
As you immerse yourself in these pages, I invite you to reflect on the transformative power of AI and its capacity to redefine our approach to drug development. Let us embrace this technological renaissance with a commitment to innovation, integrity, and inclusivity, ensuring that the benefits of AI are realized in a manner that upholds the highest standards of ethical practice.
Thank you for being a vital part of the Pharma Focus Europe community. We eagerly anticipate the continued exchange of ideas and knowledge, as together, we are navigating the ever-evolving global pharmaceutical landscape.
If you have a perspective, an idea, or a story to share, we welcome your contributions to our upcoming issues. Whether it’s an article highlighting emerging trends, an interview with a thought leader, or unique insights into the Pharmaceutical ecosystem, your wisdom can guide others on their Pharmaceutical journey. Share your voice with us via email at: editorial@pharmafocuseurope.com
Thank you for joining us in exploring innovations in the pharma industry.
Stay tuned for more in our upcoming editions!
N D Vijaya Lakshmi Editor08 Revolutionizing Medicine: The Pivotal Role of Artificial Intelligence in Drug Discovery and Medical Device Design
Mena Abdelsayed, Research Assistant Professor, Lankenau Institute for Medical Research
16 Nutraceuticals Unveiled A Holistic Odyssey to Wellness
Arun Om Lal, President, Hexagon Nutrition Limited
22 Accelerating the Drug Development Process
Joerg Birkenfeld, Chief Scientific Officer, BioCopy AG
28 Unlocking Capsules Potential: Expediting Drug Development in a Fast-Moving Market
Jnanadeva Bhat, Head-R&D-Formulation Development, ACG
Manali Dalvi, Lead-R&D, ACG
34 Lean Supply Chain Management in Pharma Sector
Deepak Khurana, Vice President Procurement & SCM, Suven Pharmaceuticals
50 Applying AI and ML to Optimise Processes and Enhance Patient Safety in Pharmacovigilance
Dr Bianca Piachaud-Moustakis, Lead Writer, PharmaVision


Donna Snyder MD, MBE, Executive Physician, WCG
56 Gen AI in PV and Regulatory Affairs Marty Boom, Global Head of Regulatory & Safety, Navitas Life Sciences
ADCs and their Drug Development Process Kishore Hotha, Global Vice President, R&D, Veranova











Alessio piccoli Director & Head, Business Development Europe presso Aragen Italy
Amine Bekkali Director, Medfields, UAE
Dmitrii Vitalievich Kriuchkov
Executive Director Axon Clinical Trial Lab Russia
Gustavo Samojeden CEO, Eriochem S.A Argentina
Hassan Mostafa Mohamed Chairman & Chief Executive Officer ReyadaPro Saudi Arabia
Hoda Gamal
Director of Regulatory and Corporate Affairs Middle East and Africa, Allied associate, Egypt
Joaquin D. Campbell Global Director Managed Access Services Spain
Josipa Ljubicic QA Director / Principal GCP and GVP auditor, Proqlea Ltd Croatia
Juris Hmelnickis CEO, Grindeks Latvia
Nicoleta Grecu Director, Pharmacovigilance Clinical Quality Assurance Romania

Nigel Cryer FRSC
Global Corporate Quality Audit Head
Sanofi Pasteur France


Paola Antonini
Chief Scientific Officer, Meditrial Global CRO Italy
Pinheiro Neto Joao
Chief Executive Officer
Meu Doutor Angola



Shamal Jeewantha Fernando
Managing Director, Slim Pharmaceuticals ( Pvt) Ltd Srilanka
Svetoslav Valentinov Tsenov
Senior Pharma Executive and Global Transformation Lead Bulgaria
Tamara Miller
Senior Vice President, Product Development, Actinogen Medical Limited, Sydney



Teresa Derbiszewska Clinical Quality Director G42 Healthcare/IROS
Thitisak Kitthaweesin
Chief of Phramongkutklao Center of Academic and International Relations Administration, Thailand
Vicknesh Krishnan
Associate Medical Director at Fresenius Medical Care Malaysia Sdn Bhd Malaysia
EDITOR
Vijaya Lakshmi N D
EDITORIAL TEAM
Sarah Richards
Debi Jones
Harry Callum
Supraja BR
ART DIRECTOR
M Abdul Hannan
PRODUCT MANAGER
Jeff Kenney
ASSISTANT MANAGER
David Nelson
Peter Thomas
BUSINESS EVENTS
Sussane Vincent
CIRCULATIONTEAM
Sam Smith
SUBSCRIPTIONS IN-CHARGE
Vijay Kumar Gaddam
HEAD-OPERATIONS
Sivala VNR

www.pharmafocuseurope.com
©Ochre Digi Media Private Limited. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, photocopying or otherwise, without prior permission of the publisher and copyright owner. Whilst every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of the information in this publication, the publisher accepts no responsibility for errors or omissions. The products and services advertised are not endorsed by or connected with the publisher or its associates. The editorial opinions expressed in this publication are those of individual authors and not necessarily those of the publisher or of its associates.
Copies of Pharma Focus Europe can be purchased at the indicated cover prices. For bulk order reprints minimum order required is 500 copies, POA. LinkedIn
Ochre Digi Media www.ochre-media.com Magazine Subscribe





Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized the field of scientific applications, particularly in biotechnology and medicine. By leveraging AI, medical devices and drugs are now designed and optimized more efficiently, accelerating the drug discovery process and competitive analysis. My expertise in biotechnology underscores AI's transformative role in advancing medical technology, from streamlining market research with large language models to enhancing drug and device design. AI not only saves time and costs by predicting efficacy and toxicity but also aids in structuring clinical trials and patient recruitment, making it an indispensable tool in modern medical innovation.
Mena Abdelsayed Research Assistant Professor, Lankenau Institute for Medical ResearchIn the rapidly evolving landscape of healthcare and medical research, the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has marked a transformative era, fundamentally altering the paradigms of drug discovery and medical
device design. As we stand on the brink of this technological revolution, it becomes imperative to understand the depth and breadth of AI's impact. From streamlining the arduous process of drug development to facilitating the intricate design of life-saving medical devices, AI has emerged not just as a tool but as a beacon of innovation, guiding the future of healthcare towards unprecedented horizons. This exploration delves into the multifaceted role of AI, shedding light on how it is reshaping the fields of biotechnology and medicine, promising a future where healthcare solutions are more accessible, effective, and personalized.
The significance of AI in the medical field cannot be overstated. By harnessing the power of advanced algorithms and machine learning, researchers and developers are able to navigate the complex biological and chemical data with newfound precision and speed. This synergy between AI and medical science is not just enhancing the efficiency of existing processes but is also uncovering possibilities previously deemed unattainable.
From the meticulous engineering of cellular DNA to the construction of vast infrastructures governing cities and healthcare systems, AI's contribution is universal, serving as a catalyst for breakthroughs across the spectrum of scientific application. As we delve deeper into the themes of AI's role in medical device and drug design, market research, and clinical trials, the narrative unfolds to reveal a compelling vision of the future, underscored
AI has emerged not just as a tool but as a beacon of innovation, guiding the future of healthcare towards unprecedented horizons.
by data, evidence, and real-world applications that highlight AI's indispensable value in advancing medical technology.
The integration of AI into the medical field marks a significant advancement in how medical devices and drugs are designed and optimized. AI's ability to process and analyze vast amounts of data rapidly enables more efficient identification of potential drug candidates and device innovations. According to a study by the McKinsey Global Institute, AI can significantly cut both the time and cost associated with the drug discovery process (McKinsey Global Institute, 2020). By leveraging predictive models, AI can forecast the efficacy and potential toxicity of compounds before they are synthesized in the lab, thus reducing the need for costly and time-consuming experimental trials.
AI technologies, especially large language models, have revolutionized market research and competitive analysis in the pharmaceutical industry. These models can sift through extensive databases and public records to gather insights on the development stages of drugs, patent landscapes, and the competitive positioning of products. A report by Deloitte highlighted how AI tools could reduce the time spent on analyzing the pharmaceutical landscape from months to just a few days, providing a strategic edge to companies in a highly competitive market (Deloitte, 2019).
Within the realm of market research and competitive analysis, the precision and efficiency afforded by AI are not merely conveniences but necessities in the face of the pharmaceutical industry's competitive and fast-paced nature. The integration of AI enables companies to conduct thorough analyses of global market trends, regulatory landscapes, and emerging therapeutic areas with a level of speed and accuracy that was previously unimaginable. This rapid processing capability allows for real-time decision-making and strategic planning, empowering companies to adapt swiftly to market changes and capitalize on new opportunities. Furthermore, AI-driven analytics offer a granular view of the competitive environment, enabling firms to identify niche markets and underserved patient populations. This strategic advantage
AI has led to breakthroughs in personalized medicine by tailoring treatments to individual genetic makeup.
is crucial for the differentiation of products in a crowded marketplace, ensuring that innovations not only meet the highest standards of efficacy and safety but also address unmet medical needs. Through the lens of AI, the pharmaceutical industry is witnessing a paradigm shift in how market intelligence is gathered and analyzed, setting a new standard for strategic excellence in healthcare innovation.
The advent of AI in market research and competitive analysis also heralds a new age of consumer-centric product development in the pharmaceutical industry. By leveraging AI-driven sentiment analysis and consumer behavior modeling, companies can now gain deeper insights into patient needs, preferences, and expectations. This wealth of information enables pharmaceutical companies to tailor
their product development and marketing strategies to better meet the demands of their target audiences, thereby enhancing patient engagement and satisfaction. AI’s ability to process and analyze social media data, patient forums, and online health communities in realtime provides a dynamic and comprehensive view of the market landscape. This not only facilitates more informed decision-making but also enables companies to stay ahead of emerging healthcare trends and adapt their products accordingly. Such consumerfocused approaches are transforming the way pharmaceutical products are marketed and delivered, ensuring that they not only address specific health conditions but also resonate with the broader aspirations and concerns of the patients they aim to serve.
AI's impact extends beyond initial research and into the very design of drugs and medical devices. By analyzing complex biological data and chemical structures, AI algorithms can predict how modifications to chemical groups and molecular structures might affect a drug's performance. This capability is particularly promising for personalized medicine, where treatments can be tailored to individual patients based on genetic factors. The Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling published a study demonstrating how AI could accurately predict the outcomes of chemical reactions, paving the way for more innovative and effective drug formulations (Journal of
Chemical Information and Modeling, 2018).
The enhancement of drug and device design through AI transcends traditional methodologies, introducing a level of innovation and precision that is transforming the landscape of medical research. AI's capability to analyze and interpret complex biological data has led to significant breakthroughs in the design of personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to the unique genetic makeup of individual patients. This approach not only increases the efficacy of treatments but also minimizes adverse effects, heralding a new era of patientcentric healthcare. Moreover, AI's application in biomaterials and device engineering is paving the way for the development of smart medical devices that can adapt and respond to patient needs in real-time, enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life. The use of AI in simulating and modeling drug interactions at the molecular level further accelerates the identification of promising drug candidates, reducing the dependency on trial-and-error methods and dramatically speeding up the drug development process. This shift towards AI-integrated design processes signifies a move from a one-size-fits-all approach to a more nuanced and effective strategy in medical treatment and device innovation, emphasizing the critical role of AI in shaping the future of healthcare solutions.
In the quest for more sustainable and environmentally friendly healthcare solutions, AI is also playing a pivotal role in the green
synthesis of pharmaceuticals and the development of biodegradable medical devices. By employing AI algorithms to predict the most efficient synthesis pathways, researchers can minimize the use of hazardous chemicals and reduce waste in drug production processes. This approach not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also leads to cost savings and improved safety for both the manufacturing personnel and the end-users. Additionally, AI's ability to analyze the properties and interactions of biodegradable materials is facilitating the creation of medical devices that can safely decompose within the body or the environment, eliminating the need for surgical removal and reducing environmental pollution. These advancements underscore AI's potential to drive innovation not just in the effectiveness and precision of medical treatments and devices, but also in their sustainability and ecological impact, marking a significant step forward in the integration of healthcare and environmental stewardship.
The application of AI in designing clinical trials and recruiting suitable patient populations is another area where its potential is being realized. AI can identify patterns and correlations in medical data that may not be apparent to human researchers, helping to structure clinical trials more effectively and ensuring that they are more likely to
yield valuable results. Additionally, AI can assist in patient recruitment by analyzing patient data to identify those who meet the specific criteria for a trial. A study published in Nature Medicine highlighted the use of AI to predict patient eligibility for clinical trials, significantly speeding up the recruitment process (Nature Medicine, 2021).
AI algorithms excel in identifying suitable candidates for clinical trials by analyzing vast datasets of patient information, including electronic health records (EHRs), genetic data, and previous medical history. This precision in patient selection not only accelerates the recruitment process but also increases the likelihood of successful trial outcomes by ensuring that participants closely match the study criteria. Furthermore, AI can optimize trial designs by predicting potential challenges and identifying the most effective methodologies, thereby reducing trial durations and costs. This proactive approach to trial planning and execution is instrumental in bringing groundbreaking therapies to the market more swiftly and safely.
Moreover, AI's role extends beyond the initial phases of clinical trials, offering continuous insights throughout the study. For example, AI-driven tools can monitor patient data in real time, flagging adverse reactions or significant outcomes as they occur. This real-time monitoring capability enhances patient safety and ensures that critical decisions can be made swiftly, potentially saving lives. Additionally, AI can analyze
interim trial results to suggest modifications in trial protocols, optimizing the study's effectiveness and efficiency. The integration of AI in clinical trials represents a paradigm shift towards more adaptive, patient-focused research methodologies. By leveraging AI, researchers can not only streamline the development process but also significantly enhance the precision and relevance of their findings, ultimately leading to more effective and individualized patient care.
The advent of artificial intelligence in scientific applications, especially in biotechnology and medicine, is a leap forward in the quest to develop and optimize medical devices and drugs. By enhancing the efficiency of drug discovery processes, accelerating market research and competitive analysis, improving
AUTHOR BIOMena Abdelsayed currently holds the position of research assistant professor at the Lankenau Institute for Medical Research. After obtaining his Ph.D. in Cardiac Electrophysiology from Simon Fraser University in Canada, he pursued postdoctoral studies in cardiovascular medicine at Stanford University. His extensive publication record reflects his pioneering work in the discovery of medical devices and drugs, which are direct outcomes of his innovative ideas.
drug and device design, and streamlining clinical trials and patient recruitment, AI is setting a new standard in medical research and development. As AI continues to evolve, its integration into these processes promises to not only save time and money but also to lead to the development of treatments that are more effective, safer, and more personalized than ever before. This evolution underscores the necessity of leveraging AI across all facets of drug discovery and medical device design, ensuring that resources are optimized and that the innovations brought to market meet the true needs of patients. The future of medical research and development is inextricably linked with the advancements in artificial intelligence, heralding a new era of innovation and efficiency in healthcare.

PMMI Business Intelligence surveyed pharmaceutical manufacturers in late 2023 and early 2024 to track trends since the 2022 report on Pharmaceutical Manufacturing. Amid projected growth, the industry faces opportunities and challenges in meeting marketplace demands.
Top Machine Types by Share of the Pharmaceutical Market (total

Delving into the realm of nutraceuticals, this article illuminates the fusion of nutrition and pharmaceuticals as a cornerstone of modern health consciousness. From its inception by Stephen De Felice to its transformative impact amidst COVID-19, the piece navigates through regulatory complexities, market dynamics, and emerging innovations. Embracing overall wellness, it advocates for informed consumer choices and proactive healthcare paradigms.
Arun Om Lal President Hexagon Nutrition LimitedIn an era where health-consciousness is on the rise and preventative medicine takes center stage, the concept of nutraceuticals emerges as a beacon of hope for individuals seeking holistic well-being. Coined by Stephen DE Felice in 1989, the term "nutraceutical" represents
the fusion of nutrition and pharmaceuticals, encapsulating a diverse array of products aimed at providing medical or health benefits, with a primary focus on prevention and proactive health management.
At its core, nutraceuticals embody the ancient wisdom that "food is thy medicine." This philosophy underscores the belief that optimal health can be achieved through a balanced diet supplemented with functional foods, dietary supplements, and specialized nutritional products. By harnessing the therapeutic properties of food components, nutraceuticals offer a natural and sustainable approach to health maintenance and disease prevention.
The landscape of health management has seen a paradigm shift, with a growing emphasis on preventive measures rather than reactive treatments. One of the key tenets of nutraceuticals is integrative health, which integrates conventional medical practices with complementary approaches such as herbal remedies, dietary supplements, and lifestyle interventions. This holistic approach recognizes the interconnectedness of body, mind, and spirit, emphasizing the importance of addressing underlying imbalances to promote overall well-being.
The COVID-19 pandemic has served as a catalyst for rethinking health priorities, with a heightened focus on immunity.
The COVID-19 pandemic has served as a catalyst for rethinking health priorities, with a heightened focus on immunity, weight management, and overall wellness. This newfound awareness has accelerated the adoption of nutraceuticals as individuals seek proactive measures to bolster their immune systems and mitigate the risk of lifestyle-related diseases.
Recognizing the growing importance of nutraceuticals, regulatory bodies such as the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) have introduced comprehensive frameworks to regulate the production, distribution, and labeling of these products. The Food Safety and Standards (Health Supplements, Nutraceuticals, Food for Special Dietary Use, and Food for Special Medical
Purpose) Regulations, 2022, aim to ensure the safety and efficacy of nutraceuticals while providing consumers with transparent information.
Nutraceuticals encompass a wide range of products tailored to specific health needs, including health supplements, functional foods, dietary supplements, and foods for medical purposes. Functional foods, fortified with bioactive compounds and phytonutrients, offer health benefits beyond basic nutrition, while dietary supplements provide concentrated doses of essential nutrients to support overall health and wellbeing.
The global market for functional foods is experiencing robust growth, with a projected CAGR of 8.93% from 2023 to 2032. By 2030, the market is estimated to reach approximately USD 586.1 billion, driven by increasing health consciousness and demand for nutritionally enriched products. North America and the Asia Pacific region hold significant revenue shares, indicating a widespread adoption of functional foods.
Dietary supplements, on the other hand, are witnessing even more rapid expansion, with a projected CAGR of 9.1% from 2023 to 2032. By 2032, the global market size is
expected to surpass USD 390.5 billion, fueled by rising consumer interest in preventive healthcare and supplementation. North America remains a dominant market player, capturing 34.2% of the revenue share in 2023.
Meanwhile, the market for food for special dietary use is characterized by steady growth, with a projected CAGR of 10.6% from 2023 to 2032. By 2030, the global market size is forecasted to reach approximately USD 22.9 billion, driven by the dietary management of disease-related medical conditions. North America retains a significant revenue share, reflecting the prevalence of specialized nutritional needs in the region.
1. Regulatory Hurdles: The industry faces challenges due to a complex regulatory environment, necessitating governmental intervention to strengthen regulations regarding production, distribution, and safety testing of nutraceutical products.
2. Misleading Claims: There's a need to address claims regarding the effectiveness of dietary supplements, ensuring accuracy and transparency in marketing messages to consumers.
3. Lack of Knowledge: Despite a positive attitude towards nutraceuticals, there's a prevalent lack of adequate knowledge among consumers, highlighting the importance of education and awareness initiatives.
4. Counterfeit Products: The market sees an influx of counterfeit and fake supplements, manufactured using low-cost, non-standard materials that evade regulatory approval, posing risks to consumer health.
5. Consumer Distrust: Deceptive advertising and communication strategies have contributed to growing consumer distrust towards the nutraceutical sector, emphasizing the need for transparency and integrity in marketing practices.
Innovative delivery formats, including gummies, chewable, and flavored supplements, are reshaping the nutraceutical market, catering to diverse consumer preferences and lifestyles. Manufacturers are leveraging these trends to create visually appealing and Instagram-worthy products, particularly targeting millennials and healthconscious consumers.
Hexagon Nutrition Limited stands at the forefront of the nutraceutical revolution, offering innovative solutions for the entire family through its flagship product, NUTRONE. As part of a global partnership focused on staple fortification, Hexagon is committed to enhancing nutritional outcomes and promoting self-care through fortified food products.
In conclusion, the nutraceutical revolution heralds a new era in health management, emphasizing the proactive integration of nutrition and medicine. As we navigate the complexities of modern healthcare, innovation, education, and regulatory diligence are pivotal in realizing the full potential of nutraceuticals. By making informed choices and embracing a holistic approach to wellness, individuals can embark on a journey towards self-care and preventive medicine, ensuring a healthier future for generations to come.

Arun Om Lal is President at Hexagon Nutrition Limited Corporate Affairs and Communication Building Bridges Between People, I build cross-sectoral partnership and facilitate progress for stakeholders/unapologetic extrovert. A visionary leader with an outstanding track record of successful business strategies, Mr. Arun Om Lal has cultivated staunch credibility in the Nutriution Industry.
The pharmaceutical and medical communications industry relies heavily on the use and dissemination of scientific journals, research papers, medical reports, and other publications, all of which are protected by copyright. These materials are the backbone of research, development, and collaboration, with journal articles providing insights into drug safety and side effects, case studies informing new treatment strategies, research papers sparking drug discovery pathways and regulatory reports shaping the future of patient care. This knowledge exchange ultimately accelerates innovation by ensuring reliable content is reused ethically and responsibly.
The CLA Pharmaceutical Licence is a collective licence, covering millions of works from thousands of publishers, including works from over 40 territories worldwide. This licence offers a solution to the industry, simplifying content sharing for research development, regulatory processes, and internal collaboration, as well as collaboration with external partners.
Developed in consultation with the industry, this licence is fully tailored for pharmaceutical, life sciences, biosciences, and medical communications organisations. An extension to the main CLA Business Licence, it offers additional permissions designed for healthcare companies' everyday information and regulatory needs, including:
• Permission to make copies from millions of works from thousands of publishers, including from over 40 territories worldwide.
•External sharing of single licensed copies with healthcare providers, patients, and carers.
•Regulatory submissions and patent applications in any jurisdiction. Understanding reuse rights and copyright compliance is critical. We discussed these complexities with Leslie Lansman, Global Permissions Manager at Springer Nature, exploring how the CLA Pharmaceutical Licence safeguards companies and promotes ethical content sharing.
•Published content provides tangible value to pharmaceutical, life science, and medical communications professionals: Access to reliable, accurate, and up-to-date STM content is essential for pharmaceutical and medcomms professionals to share, use and reference. The CLA Pharmaceutical Licence facilitates the use of this valuable content by simplifying copyright compliance and ensuring professionals can readily access and share the most relevant and verified information.
•The CLA Pharmaceutical Licence streamlines content sharing and enhances reliability: It eliminates the need to contact rights holders directly, reducing administrative burdens and saving valuable

time. The licence's clear guidelines ensure ease of use and promote confidence in sharing accurate and verified content. By working with publishers, CLA ensures that the content shared under the licence is subject to rigorous research integrity standards, further enhancing the reliability of scientific information in the pharmaceutical industry.
•Mitigate risk and support collaboration: The CLA Pharmaceutical Licence clearly defines sharing limits, enabling pharmaceutical and medcomms professionals to easily determine when additional permissions are necessary. This proactive approach prevents unintentional copyright infringement, which can lead to costly legal disputes and damage valuable relationships with publishers. By adhering to the licence's guidelines, pharmaceutical companies not only avoid potential legal issues but also foster a collaborative environment with publishers who are eager to support the legal and effective sharing of verified information.
•Dispelling copyright misconceptions: Pharmaceutical and medcomms companies demonstrate a commitment to ethical research by ensuring their employees use verified versions of articles. This is crucial in an industry where decisions based on inaccurate or misleading information can have significant consequences. The CLA Pharmaceutical Licence helps clarify copyright rules and dispel common misconceptions, such as the belief that paraphrasing or using "free to read" content equates to permission for reuse. By educating employees on copyright law and the licence's provisions, companies can foster a culture of respect for intellectual property and ensure compliance with legal requirements.
•Ensuring integrity and accuracy of scientific communication: Licences, like the CLA Pharmaceutical Licence, ensure the accurate dissemination and attribution of scientific content, upholding the integrity of research and preventing the spread of outdated or problematic information.
•Future of STM publisher and pharmaceutical industry partnership: Publishers are committed to responsible content management and fostering collaboration with users who have legitimate reuse interests. Licences, such as the CLA Pharmaceutical Licence, ensure ongoing compliance and access to the latest scientific information.
But how can pharmaceutical and medcomms organisations ensure that their content reuse is ethical and compliant? How does CLA’s Pharmaceutical Licence streamline content sharing for the sector?
Read the full Q&A with Springer Nature’s Leslie Lansman and learn more about how the CLA Pharmaceutical Licence can help ensure that your organisation can stay compliant here: https://link.cla.co.uk/pharmafocus


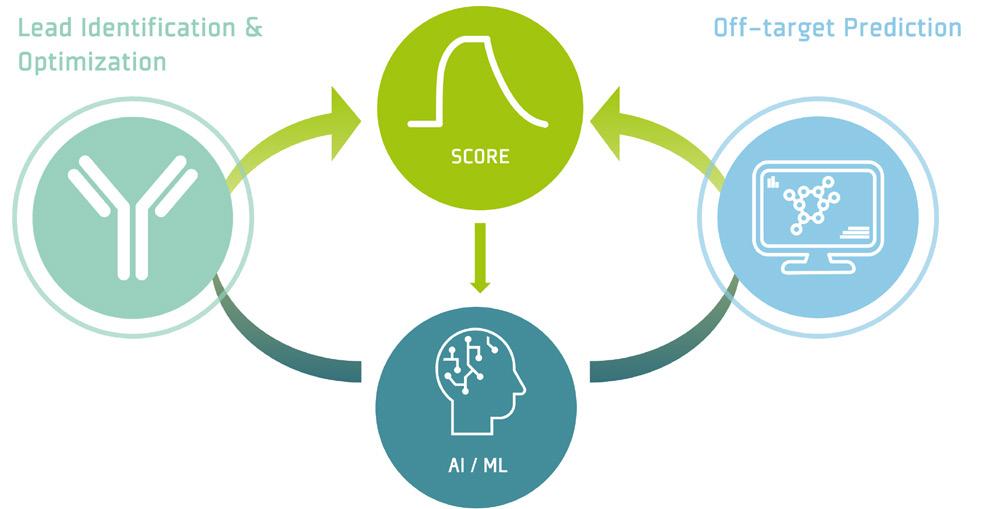
Synergy between high throughput-pHLA (peptide Human Leukozyte Antigen) screening technology on the one hand and AI-driven antibody design with end-toend automated protein optimization accelerates the development of next-generation T-cell engagers for previously unexplored tumor targets.
Joerg Birkenfeld Chief Scientific Officer BioCopy AGThe body's immune system exhibits a remarkable ability to scrutinize a cell's interior, a function of central importance. This scrutiny enables the detection of changes indicative of the transformation from a normal cell to a rapidly multiplying cancer cell. The human immune system has developed an intricate mechanism where every intracellular protein is presented on the
cell's surface for immune surveillance. Proteins are broken down into peptides within the cell, binding to human leukocyte antigen (HLA) molecules and forming peptide HLA complexes (pHLA). If the amount of presented peptide is altered or unusual peptides are presented, cytotoxic T-cells recognize it through their T-cell receptors, selectively eliminating the transformed tumor cell.
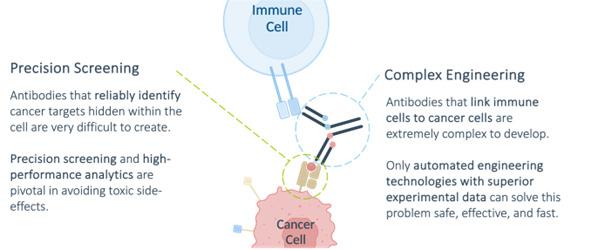
Despite being the most abundant surface markers on cancer cells, pHLA complexes present challenges for targeted cancer immunotherapies due to variable expression levels and marginal distinctions from those found in normal cells. This complicates the development of pHLA-targeting therapeutics, especially bi-specific T-cell engagers (TCEs) designed to redirect cytotoxic T-cells towards tumor sites. (Figure 1).
First, TCEs must precisely target cancerspecific pHLA complexes with the utmost specificity to avoid off-target effects, preventing severe toxicity in the patient. Second, the pHLA-targeting moiety needs to be combined with a T-cell targeting moiety to form a bi-specific modality. This is commonly achieved by engineering two distinct monoclonal antibodies — one directed at the cancer-specific pHLA complex and the other at a T-cell-specific protein like CD3 — into a single bi-specific antibody. Since bi-specific T-cell engaging antibodies do not naturally occur, their technical development requires extensive protein engineering efforts. The goal is to achieve a manufacturable, stable, and soluble compound which can be produced in substantial quantities for medical applications. The optimization of bi-specific
T-cell engagers for pre-clinical and clinical development is a process that typically needs several years.
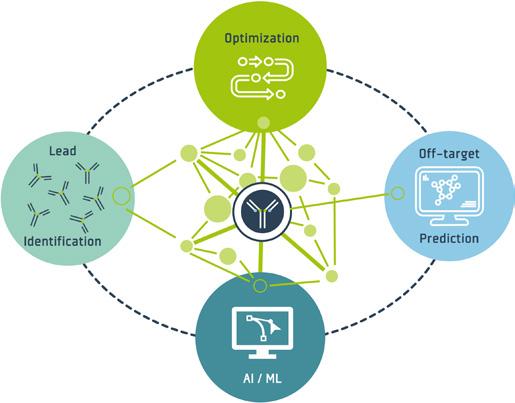
This combination of technologies may well be a transformative shift in the progression of next-generation pHLA-targeting T-cell engagers, aiming for superior safety and increased efficiency. This commitment is driven by the utilization of modern screening technology for ultra-high throughput pHLA and the automated protein engineering platform for unparalleled speed and efficiency in drug optimization. Both technologies are seamlessly integrated within a closed loop that incorporates artificial intelligence, enhancing the predictive capability for the design of pHLA-targeting TCEs with optimal developability and highest safety standards.
Achieving precise discrimination of cancer cells without affecting healthy tissue is crucial for the development of T-cell engagers (TCEs).
This requires accurate characterization of the pHLA-targeting antibody, considering its binding properties not only to the target cancer pHLA but also to other pHLAs resembling the target structure. Specialized technology is essential to meet these demands.
Precision screening is key for evaluating antibody binding to pHLA complexes, leveraging advanced microsystems technology and cutting-edge microarray chips. These technologies ensure exceptional accuracy in characterizing the binding properties of antibodies to pHLA complexes. The screening chips embed thousands of pHLA complexes, facilitating rapid and precise measurement of antibody binding to all relevant pHLA complexes in the body, enhanced by highly specialized bioinformatic workflows.
To initiate the process, in silico predictions are generated to identify pHLA complexes closely resembling the target pHLA. Those predicted pHLAs, together with rationally designed pHLA complexes, undergo precise
measurement. The gathered results are augmented with additional experimental and omics data, allowing a precise bioinformatic prediction for the toxicity profile of a pHLAtargeting TCE. This risk assessment serves as a basis for informed decision making in the drug development process regarding safety and effectiveness.
This technology serves as a cornerstone of developing next generation TCEs. The measurement data enables AI-driven predictions, establishing a closed loop that facilitates comprehensive antibody characterization and optimization across multiple cycles, all powered by the automated platform.
In addition to recognizing the target pHLA molecule on cancer cells, the new antibodies must activate the body's immune cells against the identified tumor. To achieve this goal, the pHLA-binding antibodies are transformed into more complex structures known as bi-specific antibodies. Those antibodies possess a risk of unsuitability for development due to challenges in meeting industrial requirements for large-scale production, stable storage, and eventual use as a formulable drug. This often results in the failure of complex molecule developments at early stages.
These challenges can specifically be addressed with a fully automated and AI-powered platform for antibody optimization (2). The platform initiates the drug optimization process by in silico designing tens of thousands of bi-specific antibody variants. It seamlessly integrates the in-silico 'digital design' stage with the physical wet-lab stages within an end-toend automated process. Using a parallelized approach, the automated platform produces up to 25,000 individual in silico-designed bi-specific antibody molecules. Each molecule is expressed in its desired soluble drugproduct format within an isolated minibioreactor-like compartment, allowing simultaneous unbiased assessment of multiple functional and biophysical properties crucial for technical development, including yield, potency, stability, and solubility for each molecular design.
The automated platform accelerates drug development by more than 24 months,
providing a substantial advantage over traditional optimization approaches. The platform's unique ability to preserve data on all variants ensures an accelerated learning, invaluable for refining the drug development process. As the process mirrors the final industrial drug production process, identified candidates undergo de-risking for progression into large-scale production and subsequent development through commercial manufacturing. The foundational concepts and technologies have been developed over many years by leading scientists, validated within the Big Pharma environment.
In order to ensure that the optimized candidates meet safety requirements, the physical data from the optimization platform are fully integrated with the off-target pHLA screening data. This combination enhances
Platform
the identification of developable bi-specific antibodies. Furthermore, it enables the deep understanding of design principles underlying those antibodies, leading to enhanced efficacy and improved developability while maintaining high molecular safety standards. These insights are systematically incorporated into subsequent optimization cycles, streamlining the overall development process. This approach accelerates the identification of developable drug candidates from years to months compared to standard semi-automated and iterative design approaches. Additionally, it generates data sets of unprecedented quality and quantity and enables training of artificial intelligence for predicting improved designs of bi-specific pHLA-targeting TCEs with enhanced safety and efficacy.

The combination of these two technologies generates a unique "data authority," providing the capability to develop proprietary artificial intelligence (AI).
This integration also enables the development of new AI-based methods to accurately predict the design of novel pHLAtargeting TCEs. Harnessing AI capabilities empowers drug makers to precisely predict off-target toxicity and the developability of complex bi-specific antibodies. As a result, development timelines can be reduced significantly, and development processes will be streamlined continuously.
In summary, the innovative approach to combine precision screening, highthroughput engineering, and AI integration, can lead to a paradigm-shift in next-generation biologics development, particularly in immuno-
oncology. The technologies promise enhanced safety, efficiency, and reduced development timelines so that patient safety can truly be prioritized and drug development may even be revolutionized.
(1) Krämer, S. et al. Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 31;13(1):5290. doi: 10.1038/s41598-02332384-z.
(2) Furtmann, N. et al. Mabs .
2021 Jan-Dec;13(1):1955433. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2021.1955433.
(3) roPROTix (Biopharma Dealmakers (Biopharm Deal) ISSN 2730-6283
 AUTHOR BIO
AUTHOR BIO
Jörg Birkenfeld, PhD, is a molecular biologist with extensive experience in biological drug screening, antibody engineering and lab automation. He has worked for major pharma and biotech companies for more than 20 years and heads the R&D department of BioCopy AG as CSO.
In the race to meet the increasing demand for new pharmaceutical products, capsules as a preferred choice for many drug developments offer a transformative solution to the challenges associated with the process. Delve into the myriad ways capsules streamline the process, alleviating time constraints and resource burdens while meeting the demands of a rapidly evolving industry. This article explores the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of capsules in accelerating the journey of new drug entities from research to market.
Jnanadeva Bhat Head-R&D-Formulation Development, ACG Manali Dalvi Lead-R&D, ACGIn today's ever-evolving global context, the demand for novel medications to combat emerging pathogens and rare diseases has reached unprecedented levels. The intensified focus on addressing these challenges has propelled continuous advancements in drug development. However, the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries are facing numerous hurdles in bringing novel active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) to market as life-saving medicinal products. The primary challenge lies in finding a molecule that not only effectively targets the desired condition but also meets stringent safety and efficacy standards. Nevertheless, this objective represents just

one aspect of the complex process. Equally critical is formulating and precisely delivering the molecule to its intended site of action.
Drug discovery and the subsequent development process are often a lengthy, expensive, and incremental process. The pharmaceutical sector invests billions in this endeavour, underscoring its significance, with substantial resources allocated to rigorous screening and testing protocols. Despite significant efforts, accurately predicting the timeline from conceptualization to market availability remains a formidable challenge. In this landscape, capsules emerge as a beacon of promise, offering a versatile pathway to expedite various stages of drug development. They streamline manufacturing processes, reinforce proof-of-concept demonstrations, and help mitigate the demand for expensive materials and testing protocols.
Capsules play a pivotal role in modern pharmaceutical innovation by supporting drug development across all stages, from preclinical research to market release, and continuing more during its lifecycle. With the typical drug development process spanning a lengthy duration of 12 to 15 years, the utilization of capsules emerges as a favoured strategy, presenting scientists with an expedited pathway to market entry. Capsules serve as a cornerstone in the initial phases of concept formulation, offering a minimal yet effective solution amidst the intricacies of early-stage development. Their versatility simplifies the product development process, enabling researchers to navigate
complexities with greater ease and efficiency, ultimately driving innovation and progress in drug development.
The journey of drug development begins with the synthesis of a novel molecular entity (NME), marking the discovery of compounds of interest. However, the real test lies in evaluating these compounds for efficacy and safety. This involves initial thorough testing on animals before even considering human trials. The aim is to sift through a multitude of byproducts and pinpoint the most promising candidates for deeper investigation.
Capsules as a preferred choice for drug development, offer a straightforward solution to the challenge of administering NMEs to non-human subjects, as they can contribute to the efficiency and precision of the testing process. They enable precise dosing, ensuring accurate measurement and delivery of NMEs in predefined amounts, which is essential for reliable data interpretation. They provide a protective environment for NMEs, particularly those sensitive to moisture or acid. By encapsulating these compounds directly into the capsule shell, researchers can ensure the stability of the substances during delivery to the gastrointestinal tract in the early stage of development. This rationalizes the formulation process by eliminating the need for additional steps like coating or extensive formulation
efforts. This not only saves time but also reduces costs associated with the preclinical testing phase.
Additionally administering capsules to animals is generally less stressful than alternative methods. The ease of capsule administration reduces potential discomfort for the animals, contributing to more consistent and humane preclinical testing. The availability of capsules in different sizes enables tailored dosing based on the specific needs of the experiment and the size of the animals involved in preclinical studies, thereby increasing adaptability.
In some instances where candidate compounds are costly during the early stages of selection and synthesis, limiting the usage of API for initial evaluation, precision dosing through capsules for clinical trials proves to be an advantageous option. This approach facilitates the exploration and innovation in the early stages of drug development. They enable direct testing of products under investigation for clinical efficacy without the need for extensive formulation efforts. In Phase 1 clinical trials, capsules containing very small amounts of the drug compound can be directly administered to human subjects for safety testing. This technique helps in the rapid manufacturing of drugs products by placing pure drug in capsules for oral and pulmonary dosing in Phase 1 studies. This is particularly beneficial for highly potent, low-dose applications where precision
dosing is essential, and can be extended to other products. This process eliminates the need for excipient blends and associated testing and evaluation, minimizing the timelines for the first human study compared to conventional formulation routes. By bypassing specific formulation steps like excipient compatibility testing, companies can gather critical clinical trial data sooner. This early data helps in identifying viable candidates and meeting aggressive project timelines effectively.
Furthermore, this approach provides formulators with the time to address environmental and physicochemical challenges associated with the pure drug, which are necessary for formulation development. Conducting physicochemical studies concurrently with clinical studies allows formulators to optimize formulation parameters while clinical trials are ongoing. This parallel approach reduces the overall timeline of the
Accelerates time-to-market
Enables seamless scalability
Enhances brand recognition
Boosts patient preference
Streamlines manufacturing processes
Offers potential patent extensions
drug development process by overlapping activities that would traditionally be sequential. It is advantageous in circumstances where there is an urgent need for the medication, such as in the case of emerging pathogens or rare diseases.
Available in various sizes and colour, capsules facilitate easy identification and blinding protocols crucial for clinical trials. Researchers can effortlessly distinguish between different formulations, doses, or placebos, ensuring accurate data collection while maintaining participant blinding, thus enhancing the integrity and reliability of clinical trial outcomes. This versatility not only facilitates logistical aspects but also contributes significantly to the efficiency and rigor of the clinical trial process.
3. Formulation feasibility
In drug development, feasibility is a paramount concern as researchers strive to establish proof of concept and evaluate the fundamental characteristics of molecules. When focusing on oral delivery systems, capsules emerge as a highly advantageous dosage form supporting the drug development process. Their benefit encompasses ensuring accurate dosing, protecting drugs from environmental factors, and simplifying manufacturing with easy filling methods to expedite the encapsulation of active ingredients. This eliminates the need for complex machinery or intricate development procedures, allowing researchers to swiftly encapsulate medications through manual
or semi-automatic means. Consequently, this approach reduces time to market and eliminates the need for machinery investment during the early phases of development, compared to other dosage forms.
Capsules provide versatility in accommodating various medication forms, including powders, liquids, semisolids, pellets, mini tablets, and granules, facilitating a wide range of delivery formats. This flexibility enables formulators to efficiently achieve desired pharmaceutical actions by experimenting with different formulations and delivery options within a single dosage form. Additionally, capsules allow for the customization of formulations by combining multiple active ingredients into a single dosage form, particularly beneficial for combination therapies targeting specific conditions.
For drugs categorized under biopharmaceutical class II (BCS II), liquid filling in hard capsules enables the use of APIs that may be difficult to incorporate into solid dosage forms. Furthermore, in some cases, capsules exhibit improved bioavailability due to factors such as better dissolution characteristics, enhanced absorption, or protection from enzymatic degradation in the gastrointestinal tract. Overall, capsules play a pivotal role in expediting drug development processes while offering versatility and efficiency in formulation design.
4. Scalability and manufacturing support
From a manufacturing standpoint, hard
capsules present notable advantages in production phase and enhance the efficiency of drug development. Unlike tablets, which typically involve intricate manufacturing steps like granulation, drying, and compaction, capsules make these processes easier. This dosage form not only decreases the number of steps involved but also reduces the time and resources necessary for manufacturing. Consequently, hard capsules offer a more efficient and cost-effective solution for pharmaceutical companies aiming to bring their products to market swiftly.
The efficient manufacturing process of capsules accelerates validation and CMC (Chemical, Manufacturing, and Control) activities. During validation, they ensure that the manufacturing process consistently produces capsules of high quality, which facilitates the reliability of capsule production. Similarly, CMC activities, which encompass the documentation and regulatory aspects of manufacturing, draw significant benefits from the upfront nature of the capsule manufacturing process. Capsules inherently offer a simplified approach to production, reducing the complexity associated with regulatory compliance. This process enables pharmaceutical companies to navigate through regulatory requirements more smoothly, ensuring timely approvals and adherence to quality standards.
They also facilitate scale-up, allowing for a seamless transition from small-scale production to larger volumes. Their standardization and
consistency in production make them ideal for scaling up manufacturing operations while maintaining product quality and integrity. As demand for a drug increases during its progression through various stages of development and eventual market release, capsules offer the flexibility to meet these escalating production requirements without compromising product quality or integrity.
Capsules offer substantial advantages in bolstering brand recognition and extending patent longevity. Opting for capsules as the preferred dosage form empowers innovator companies to distinguish their products in a crowded market. With capsules available in diverse sizes, colours, shapes, and printing options, they serve as a canvas for branding initiatives, allowing for distinctive appearances that resonate with both consumers and healthcare professionals. This customization capability ensures instant recognition of the brand and fosters consumer loyalty over time. Capsules offer protection against counterfeiting, safeguarding the manufacturer's compound from being replicated and sold in the market. With distinctive printing options such as the brand name, strength, or logo prominently displayed on the capsule body, products stand out in crowded markets, making them easily identifiable to consumers.
Additionally, capsules enable frequent product releases, fostering brand awareness and
anticipation among consumers. It facilitates easy integration of new products into the lineup, simplifying testing process strategies by enabling formulation modifications that extend the patent life of a drug. By reformulating a medication into a capsule form or developing innovative capsule technologies, pharmaceutical companies can obtain new patents or extend existing ones. These patents can cover aspects such as the capsule formulation, manufacturing processes, or specialized delivery systems, providing additional protection and exclusivity for the product.
The journey of drug development, from concept to real-world application, has encountered formidable challenges. To meet the imperative of shortening development timelines, pharmaceutical companies have implemented various supportive systems, striving to adhere to stipulated timeframes. Amidst these challenges, capsules have emerged as a catalyst for acceleration, facilitating the entire process. Renowned for their simplicity and efficiency, capsules as a dosage form offer a promising solution to expedite drug development while minimizing expenditures. By leveraging the agility and innovation enabled by capsules, researchers can effectively navigate the pressures of a rapidly evolving market, ensuring timely delivery of pharmaceutical innovations to meet critical healthcare needs.
AUTHOR BIO
Dr. Jnanadeva Bhat is Head –Formulation R&D (Pharma & Nutra) at ACG Group. Jnanadeva has been associated with the pharmaceutical industry for more than two and a half decades. As a product formulator, he has worked on various dosage forms that include tablets, soft gelatin and hard capsules, injectables, and lyophilized formulations. At ACG, he heads the formulation R&D lab where he primarily leads new product development projects and customer interface.

Manali is part of the Capsules R&D team at ACG. Her primary responsibilities include writing and publishing of scientific research articles and developing segmented solutions and technical content as integral component of Thought leadership programs. She is actively engaged in various research activities pertinent to the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical sectors. She is also involved in all the Industry and Institute related collaborations and research activities.

Lean Supply Chain Management in Pharmaceutical Industry is of great concern as it involves Patients’ lives. Drug Shortages occur very often & cause severe supply chain disruptions. Lean Supply Chain management starts before time drug is manufactured. The article will cover different aspects of Lean Supply Chain, Challenges in implementing LSC, Implementation of Lean Supply Chain in the industry.
Deepak Khurana Vice President Procurement & SCM, Suven PharmaceuticalsIn the pharmaceutical industry, where efficiency and adaptability are crucial, companies face unique challenges ranging from stringent regulations to complex manufacturing processes. To overcome these hurdles and deliver life-saving medications efficiently, many pharmaceutical firms are turning to lean supply
One significant advantage of lean supply chain management in pharmaceuticals is the reduction of lead times. By minimizing non-value-added activities and optimizing processes, companies can accelerate the
delivery of medications from production to distribution, enhancing customer satisfaction and responsiveness to market demands. Shorter lead times also reduce the risk of drug shortages, ensuring consistent availability of essential medications to patients. Additionally, lean principles promote inventory optimization, helping companies to manage stock levels efficiently while reducing holding costs and the risk of product expiration or obsolescence. This agile approach allows companies to adapt quickly to market changes and customer preferences. Furthermore, lean supply chain management contributes to improved quality and compliance within the chain management principles. Originating from the Toyota Production System, lean management focuses on eliminating waste, optimizing processes, and improving overall efficiency throughout the supply chain. While adoption has been slower in pharmaceuticals due to industry-specific characteristics and regulatory constraints, companies are increasingly embracing lean practices to streamline operations and ensure sustainable growth.
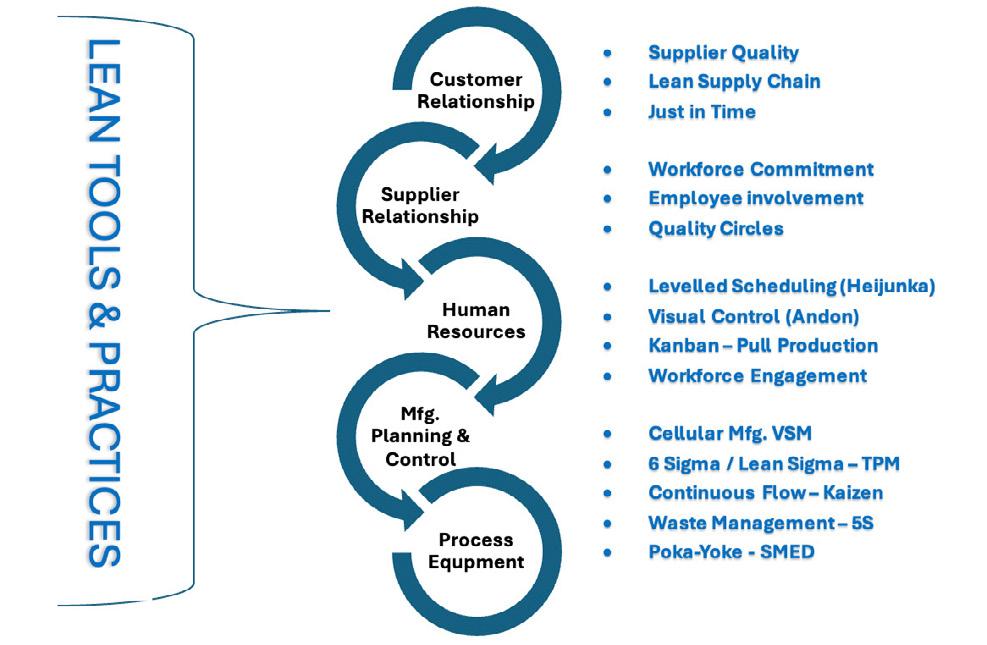
pharmaceutical sector. By standardizing processes, implementing rigorous quality control measures, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, companies can maintain the integrity and safety of their products across the supply chain. This aspect is crucial in an industry where product quality and regulatory adherence are paramount.
Lean supply chain management promotes collaboration and transparency among supply chain partners, facilitating optimization of processes and innovation. Through strong relationships with suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and other stakeholders, companies can share information, pool resources, and solve problems jointly, enhancing operational efficiency and resilience against disruptions. This approach has significant potential to transform the pharmaceutical sector by improving efficiency, resilience, and customer satisfaction. However, successful implementation requires commitment, collaboration, and a culture of continuous improvement. With increasing competition and evolving market dynamics, firms are prioritizing efficient supply chain management to accelerate innovation, enhance customer value, optimize resource utilization, reduce costs, and boost profitability.
Supply chains have become more complex, involving forward and backward flows of materials, information, and funds among multiple operating units. In the generic pharmaceutical industry, supply chains typically include manufacturing raw materials,
AI transforms drug development, from identifying compounds to recruiting participants and analyzing data.
pharmaceutical manufacturing, distribution centers, retail pharmacies/hospitals, and patients. Economic shifts have prompted restructuring of supply chains in response to the sector's unique challenges, including strict regulations and the critical nature of pharmaceutical products.
Supply chain management (SCM) in the pharmaceutical industry aims to produce the right product, for the right customer, in the right amount, and at the right time. However, the complexity of industrial processes, characterized by numerous variables and nonlinear dynamics, poses challenges in modeling their behavior. System dynamics (SD) methodology emerges as a suitable technique for depicting interactions among various factors in supply chain modeling.
Let's explore the various benefits of Lean Supply Chain Management (LSCM) within the pharmaceutical sector:
LSCM practices streamline processes, decreasing the time it takes for medications to reach patients. This is particularly crucial for time-sensitive treatments like cancer therapies or organ transplants. By minimizing delays and inefficiencies, LSCM ensures prompt delivery of life-saving medications, potentially enhancing treatment outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Techniques such as Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory management minimize excess inventory and maintain optimal stock levels. This reduces carrying costs and the risk of inventory obsolescence. JIT also ensures materials are available precisely when needed, enhancing efficiency and reducing waste.
LSCM fosters continuous improvement, driving efforts to identify and eliminate defects and errors. Rigorous quality control measures and process optimization enhance product safety and quality, reducing costs associated with recalls and rework.
Real-time data sharing provides stakeholders
with comprehensive visibility into inventory levels, production status, and demand forecasts. Tools like Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, and Replenishment (CPFR) facilitate effective collaboration, aligning production with demand and minimizing stockouts or excess inventory.
Lean organizations are more agile and responsive to market changes and disruptions. LSCM enables quick adjustments to production, distribution, and sourcing decisions, allowing companies to capitalize on opportunities and maintain a competitive edge.
Overall, LSCM empowers pharmaceutical companies to optimize operations, improve product quality, and deliver medications more efficiently. By streamlining processes, optimizing inventory, improving quality, enhancing visibility, and increasing agility, LSCM enables companies to meet market demands and ensure timely delivery of medications to patients.
Implementing Lean Supply Chain Management (LSCM) in the pharmaceutical sector faces challenges that must be addressed. These include regulatory compliance, as the industry is highly regulated with strict requirements like Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and FDA oversight. Adapting lean principles to meet regulatory standards without compromising efficiency is essential.
Additionally, data integration across disparate systems and fostering a cultural shift towards collaboration and continuous improvement are critical.
Transitioning from traditional, siloed approaches to a collaborative, cross-functional model requires a significant cultural shift within pharmaceutical organizations. Embracing LSCM principles necessitates fostering a culture of continuous improvement and employee engagement. Leadership support, training programs, and clear communication are essential for overcoming resistance to change and driving successful LSCM adoption.
Overcoming these challenges is essential to fully realize the benefits of LSCM in improving efficiency, quality, and resilience in pharmaceutical supply chains.
Certainly, let's delve deeper into each of the modern technologies used for Lean supply chain management in the pharmaceutical sector:
Modern technologies are transforming Lean supply chain management in the pharmaceutical sector:
Track and Trace Systems: Utilize barcode or RFID technology to monitor pharmaceutical products' movement, enhancing visibility and enabling quick responses to issues.
Temperature Monitoring Devices:
Ensure temperature-sensitive products' safety and efficacy by continuously monitoring storage conditions and providing real-time alerts.
Serialization and Authentication Solutions:
Combat counterfeit drugs by assigning unique identifiers to drug units and implementing authentication technologies like holographic labels.
Supply
Aggregate data from various sources to provide real-time insights into inventory levels, demand forecasts, and supplier performance, facilitating proactive decision-making.
Digital
Streamline supply chain processes through cloud-based technologies, enabling seamless collaboration and automating manual tasks.
Predictive Analytics and Forecasting Tools:
Use advanced algorithms to predict demand patterns, optimize inventory levels, and identify potential disruptions, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Blockchain Technology:
Enhance traceability and authenticity by recording transactions securely, reducing the risk of counterfeit medications and ensuring patient safety.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Automate repetitive tasks like order processing, reducing errors, and freeing up human resources for strategic activities, enhancing overall productivity.
By incorporating these technologies, pharmaceutical companies can achieve Lean supply chain management practices, improving efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring medication quality and safety.
Six Sigma plays a pivotal role in ensuring quality control, navigating regulatory compliance, and optimizing processes in the pharmaceutical manufacturing industry. Firstly, it emphasizes stringent quality control measures, including rigorous testing of raw materials and final products to meet predefined quality standards, ensuring adherence to regulatory mandates.
Secondly, Six Sigma aids in navigating complex regulatory frameworks by aligning operations with standards set by regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA. This is achieved through meticulous documentation, standardized procedures, and utilizing tools like Process Validation and Change Control.
Optimizing processes for efficiency is another core aspect of Six Sigma implementation. By identifying inefficiencies and minimizing waste, pharmaceutical companies can streamline production workflows, reduce cycle times, and enhance resource utilization, leading to cost savings and increased competitiveness.
Data-driven decision-making is facilitated by Six Sigma methodologies, utilizing statistical tools for data analysis to discern trends, correlations, and root causes of variation, thus informing proactive decision-making to elevate product quality and operational efficiency.
Moreover, fostering a culture of continuous improvement is crucial, encouraging innovation, collaboration, and accountability among employees to identify improvement opportunities and drive implementation.
Lastly, Six Sigma prioritizes risk management by providing tools like Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to anticipate potential failure modes and systematically manage risks throughout the product lifecycle.
An example of successful Six Sigma application in the pharmaceutical sector is seen in supply chain optimization, where a
prominent pharmaceutical firm used Six Sigma to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance efficiency, resulting in significant benefits for patients and stakeholders. Overall, implementing Six Sigma in pharmaceutical manufacturing offers numerous benefits, including increased efficiency, reduced waste, improved risk management, and ultimately, better outcomes for patients.
In the pharmaceutical industry, managing the supply chain efficiently is crucial not only for business performance but also for ensuring healthcare continuity. Disruptions can have far-reaching consequences, impacting healthcare delivery and patient well-being. Therefore, pharmaceutical companies must develop and improve supply chain models
suited to the industry's complexities. These include strict regulations, quality assurance standards, temperature-sensitive transportation, and international logistics management amidst globalization.
The Lean Supply Chain model offers an effective strategy for addressing challenges in the pharmaceutical sector by focusing on waste reduction and maximizing value. Borrowed from manufacturing, this methodology revolves around five key principles: defining value, mapping the value stream, creating flow, establishing pull, and striving for perfection.
In the pharmaceutical industry, these principles translate into specifying drug quality requirements, outlining the production process from raw materials to finished products, ensuring continuous production, aligning production with demand, and continually
improving processes. Implementing Lean principles promises significant cost reductions and increased efficiency in pharmaceutical supply chains. By eliminating unnecessary processes, reducing supply chain length, and encouraging cross-functional collaboration, performance can be greatly improved.
The Agile Supply Chain Model presents another effective strategy, particularly suited for an industry characterized by volatile demand patterns. With a focus on responsiveness and flexibility, the Agile model emphasizes quick decision-making, adaptable sourcing, and robust data analytics. This model resonates well with the pharmaceutical sector's emphasis on customer-centricity. It enables companies to swiftly respond to demand fluctuations and evolving customer needs, critical in a field where patient requirements can change rapidly.
Augmented by sophisticated predictive analytics, the agile model empowers pharmaceutical companies to accurately forecast demand and adjust supply chain operations accordingly. Agility facilitates swift product launches, providing a competitive edge in a dynamic market.
Recognizing the merits of both Lean and Agile models, a Hybrid Supply Chain Model, blending elements of both approaches, offers a nuanced and resilient solution for the pharmaceutical industry. The Hybrid model integrates Lean's efficiency and waste reduction with Agile's flexibility and adaptability. For instance, stable, high-volume products may benefit from a Lean approach, while agile strategies suit innovative, fast-changing products. This hybridization allows for cost-effective operations and agile response to evolving demands.
Digitalization and advanced analytics are pivotal in achieving efficient supply chain management, offering real-time visibility, predictive capabilities, and automated decisionmaking. Technologies like IoT, blockchain, and AI streamline operations, enhance transparency, and improve decision-making. For instance, IoT devices monitor shipments, blockchain ensures secure transactions, and AI refines demand forecasting. Advanced analytics leverage big data and machine learning to drive optimization by identifying bottlenecks and optimizing sourcing, logistics, and inventory management.
In conclusion, the adoption of lean supply chain management stands as a pivotal opportunity poised to revolutionize the pharmaceutical sector profoundly. By embracing the fundamental tenets of lean principles and systematically optimizing processes, pharmaceutical companies have the potential to usher in a new era marked by heightened efficiency, resilience, and elevated levels of customer satisfaction. This paradigm shift promises to yield multifaceted benefits, ranging from streamlining operational workflows to reducing overhead costs and mitigating risks across the intricate web of the supply chain. The essence of lean supply chain management lies in its ability to strip away inefficiencies and redundancies, paving the way for leaner, more agile operations. Through a
concerted effort to eliminate wasteful practices and streamline workflows, pharmaceutical companies can achieve significant cost savings while simultaneously enhancing the quality and reliability of their products. Moreover, by adopting lean methodologies, companies can foster a culture of continuous improvement, perpetually striving for excellence in every facet of their operations.

Deepak Khurana CPSCM a seasonal supply chain management professional with 3 decades of experience in Strategic & Operational Procurement & Supply Chain Management. Highly Knowledgeable, strategically focused, mentor and performance driven leader. Lead various Organization’s Procurement & Supply Chain Management portfolios specially, Pharmaceutical Drug Discover & API Manufacturing.



Artificial Intelligence (AI) has the potential to impact all areas of drug development from the identification of viable compounds to the recruitment of participants, design of the protocol, analysis of data and everything in between. AI may have transformative effects on drug development if potential risks and biases are appreciated.
Although Artificial Intelligence (AI) took root in the mid twentieth century shortly after the advent of computers, AI has rapidly advanced over the last several years as computers have grown their capacity to handle and analyze large datasets at a speed much faster than the human mind. Release of the ChatGPT (Generative Pretrained
Donna Snyder MD, MBE, Executive Physician, WCGTransformer) chatbot in November 2022 introduced the public to the pervasive power of one application of AI, Large Language Models (LLM). It is no wonder that AI currently has and will have an impact on the development of pharmaceutical products. As these tools become more powerful, it is imperative to understand where AI might be implemented
and recognize the benefits and risks of AI’s use in drug and biologic products research.
Before clinical research can begin, promising candidate drugs must be identified. Many large pharmaceutical companies and some start-ups are using AI as part of the drug discovery process. One example of its use in drug discovery is the development of tools to identify molecules or proteins based on a causal relationship between a target and a disease. This may take the form of a literature-based search to identify relevant target/disease pairs or an analysis of an inferred reaction using tools such as SPIDER (self-organizing map-based prediction of drug equivalence relationships). Other areas where AI may play a role are the evaluation of drug-drug interactions, optimizing compounds using predictive models, and evaluating disease mechanisms. One of the challenges with the use of AI in drug discovery is, because of the variability and variety of datasets available for analysis to develop models, researchers may have difficulty having confidence that the predictions are accurate. Currently deep learning models (DLM) are complex and may not be transparent or easily interpretable. Methods must be developed to optimize and query these models to help ensure the accuracy of the model’s results.
Once a viable compound has been identified, AI can aid evaluation of the product in non-clinical animal models. AI models to
evaluate the toxicity of products before use in a human participant may speed up product development and reduce the number of animals needed to conduct the research. Computational tools can also be used to predict pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) responses of drug products prior to investigation in humans or in animals. Using AI/ML (machine learning) recurrent neural network models to complement traditional PK/PD methods may improve the predictive accuracy of the data prior to use in clinical trials especially when dealing with complex PK/PD data analysis sets.
AI has the potential to impact all aspects of clinical trial design and operation, such as site selection, recruitment of participants, selection of eligible participants, stratification when appropriate, dose selection and optimization, study adherence, study retention, and data analysis. AI can also be used to enable predictions of disease outcomes or progression to improve study design. Recruiting sufficient participants to complete the clinical trial is paramount, so appropriate site selection is key to a successful trial. Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) can be screened using AI to identify sites that will have the most eligible participants, or algorithms could be used to evaluate site performance to establish which sites might be more likely to stay on schedule or fall behind. One concern noted when using automated methods to screen for eligible sites
is that the sites with smaller populations or low volumes of clinical trials could be missed using these methods.
Regarding recruitment, AI can shorten the time to enrollment in clinical trials, reduce workload by as much as 90%, and improve the accuracy of identification of appropriate study participants. Rather than researchers needing to manually extract data, AI systems can rapidly sort through EMRs using natural language processing (NLP) methods and select appropriate participants and assemble study cohorts. Neural NLP can analyze notes and free text to further evaluate the appropriateness of enrolling certain individuals in a trial. Barriers to implementing the use of AI in participant recruitment are difficulties in merging participant information when the data is dispersed throughout different departments and institutions, and the lack of clear guidelines on how the data is processed and identified by the AI system (e.g., Is it relying on an AI model to identify participants which may have unidentified biases?). Incorporating a description within the protocol of how AI is used as part of recruitment would be instrumental in helping understand and evaluate the reliability and efficiency of recruitment using AI methods and should be encouraged.
Enrichment is a process whereby participants
AI has the potential to streamline drug discovery, protocol design and implementation, study analysis and safety monitoring
are selected for trials based on specific characteristics that make them more likely to respond to a treatment. If AI predictive models could select participants to enrich a trial, the number of participants needed to complete the trial may be reduced. As a result, the trial may be easier to complete because of increased efficiency and feasibility. However, the drawback to such an approach may be that the results of the study might not be generalizable. This is not a drawback related to the use of AI in clinical trials per se, but an overall issue with enrichment. As precision medicine becomes more mainstream and more products are targeted to individuals with specific genetic or disease characteristics, this may become less of a concern.
AI models and methods could be used to further refine dosing within a trial, or help
establish dosing for special populations, such as children, where rigorous PK/PD studies may be challenging due to ethical concerns. As modeling and simulation algorithms are refined, potentially effective doses can be identified for use in clinical trials. In pediatric studies, data from adults may be used to predict the doses in children eliminating the need for dedicated PK trials. Studies can be developed using an adaptive approach to minimize the number of participants needed to evaluate safety and effectiveness of the product and this can streamline product development. For example, nonparametric Bayesian learning can help with dose selection using Bayesian logistic regression models that allow datadriven borrowing across multiple populations to improve the accuracy of the estimation of the optimal dosing level.
Once participants are enrolled in the clinical trial, it is important to ensure that they are engaged in the trial and willing to adhere to study requirements. AI tools may help with this process by improving communication, evaluating drug compliance, and accurately collecting data on study outcome measures. For example, smart phone applications (apps) might send medication reminders and might even use facial recognition to evaluate whether a drug has been taken. Smart pill boxes can track whether medication has been accessed. Chatbots can provide personalized text messages to participants to keep them
interested in the research and robotic assistants can help with disease management. According to one article, the use of AI robotic assistants had helped children with self-management of diabetes and insulin control. Passive collection of data through clinical practice or digital health trackers might also automate collection of data to eliminate or reduce the number of study visits required. Use of these tools may result in better clinical outcomes, better data collection and less attrition, and may help participants remain engaged in the trial.
However, some limitations may exist when incorporating AI tools as part of research procedures. Some participants may have problems using the platforms or may have performance anxiety related to use. Others may not trust the app or prefer talking to a real person about their health rather than a computer. This may result in less diversity in the clinical trial because only those who have experience using apps overall may be comfortable using them in the context of a clinical trial. Participants with cognitive delay, from lower socioeconomic backgrounds, or on multiple drugs, who might be at risk for non-adherence, may find these systems harder to use than traditional methods.
Data management and analysis are critical aspects of clinical trials. AI tools can be used to integrate data within a clinical trial by
converting data to compatible formats and imputing missing data elements. Duplicate entries can be removed, and data can be better curated for analysis. AI can also be used to monitor the quality of data more effectively from studies and sites. This is done using a technique called “smart monitoring” where AI/ML tools are developed that learn from trial data as it accumulates through a series of cross-database checks. An advanced form of risk-based management using these AI tools could be developed that improves efficiency and reduces cost. If quality is improved this could have a “transformative effect on [the] sponsor’s ability to protect patient safety, reduce trial duration, and trial cost.” Safety signals can be assessed using AI/ML models that evaluate various sources, such as social media, or digital health tracking information, while clinical trials are in progress. Such evaluations may not be possible using traditional methods. Regulatory agencies are evaluating how AI/ML might be used to process individual case safety reports and detect and evaluate safety findings when conducting post-marketing safety surveillance.
Finally, AI may be used to facilitate protocol design. Digital twins have been proposed to either replace or reduce the number of participants that will be assigned to a placebo arm of a trial. “A digital twin is a computer simulation that allows [researchers] to generate biologically realistic data of a target patient.” Participants may be more interested
in participating since they know they will be more likely to receive the study treatment. Studies may be easier to complete because fewer participants are necessary to complete the trial. Other examples using AI to facilitate study design include evaluating previous trial designs to see what designs are more likely to be successful and using those designs for new studies.
AI has the potential to significantly improve the efficiency, speed, and safety of clinical trials and of drug development, but as already alluded to within this article, there are potential risks and harms that may be introduced when using these technologies in clinical research. The output generated by an AI model is only as good as the data that is used to build the model. For example, an AI model used to identify participants for a trial that does not pull from a heterogeneous, and racially diverse set of potential participants may bias the study results. Or an AI model used to generate molecules that might be effective in a particular disease condition must draw from robust, reliable datasets on the molecule’s potential action or composition to generate viable compounds. Additionally, a certain level of detail in the data may be necessary to construct a valid AI model, but this may require utilizing data that might be considered private. An individual’s confidential information might be inadvertently compromised. Unlike ChatGPT, created by pulling data from public
sources, private sources (such as EMRs) may be required to develop models for research. Adequate protections must be in place to de-identify that information so that it does not result in harm to participants.
Members of the European Parliament passed the European Union AI Act in March 2024, and the United States (US) issued an executive order in October 2023 to establish guidelines that may ultimately lead to regulations for the safe and trustworthy use of AI in the US. These initiatives should provide, over time, significant oversight of AI development and implementation. Meanwhile, given the pace at which AI technology is being implemented, it is imperative that models used in research are developed with a focus on transparency, or knowing how the model is constructed, accountability, or explaining why certain decisions are made to create the model, and responsibility to protect the privacy and confidentiality of the data employed, to prevent any inadvertent harms associated with the use of AI. There also appears to be consensus that including the human element whenever possible in the loop may raise trust levels when AI is utilized in place of processes that might typically be performed by humans.
In summary, AI has the potential to accelerate the drug development process by streamlining many aspects of drug discovery, protocol
design and implementation, study analysis and safety monitoring, and innumerable areas in between these steps. However, it is important to recognize that in addition to the benefits, there may be harms associated with the use of these tools. Understanding the various areas where AI may impact the drug development process and considering the impact on individuals and the research enterprise in general are the first steps in ensuring that AI has a positive impact in drug and biological product development.
References are available at www.pharmafocuseurope.com
 AUTHOR BIO
AUTHOR BIO
Donna Snyder, MD, MBE, is the Executive Physician of WCG providing guidance on medicine, research, and regulations. Before WCG, Dr. Snyder served as Senior Pediatric Ethicist, in the Office of Pediatric Therapeutics, at the U.S. FDA. She is a board-certified pediatrician with experience in pediatric practice and research ethics.
Changes in public awareness, combined with changes in technology are demanding innovative approaches to drive forward pharmacovigilance processes and the analysis of adverse event reporting. Advances in AI/ML applications are presenting biopharmaceutical companies with opportunities to navigate an evolving pharmacovigilance landscape by optimising capabilities and achieve investigation maturity, leading to richer insights.
Dr Bianca Piachaud-Moustakis Lead Writer, PharmaVisionOne of the principal objectives of clinical studies is to test the safety of drugs and ascertain potential Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) in the study population. However, it is only feasible to study a few
hundred or thousands of participants at any given time. Furthermore, these studies are performed under controlled clinical conditions that may not represent every real-world situation or circumstance. The limitations of these traditional approaches do not allow for all ADRs to be identified before a drug is made available on the market, thus mandating the need for drugs to be constantly monitored post-launch. According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), “the long-term monitoring of existing drugs is crucial, because potential ADRs, interactions, and other risk factors, may only emerge many years or even decades after the drug initially received market authorization”.
Pharmacovigilance (PV) is dedicated to the long-term monitoring of drug safety beyond market authorization, and is defined by the WHO as “the science and activities relating to the detection, assessment, understanding and prevention of adverse effects or any other medicine-related problem”. Every biopharmaceutical company has a legal responsibility to collect, process, and report details of Adverse Events (AEs), and other product safety information to healthcare regulators. It is common for patients to report the incidence of AEs to their healthcare practitioner, who then informs the relevant manufacturer, and subsequently, the regulator.
The COVID-19 pandemic raised public awareness of the importance of biopharmaceutical innovation and drug safety, and specifically the need for reporting the side effects of the newly developed vaccines. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), for example, received over one million COVID-19 vaccine AE reports in the first year, while the European Medicines Agency (EMA) received a million reports from the five vaccines used over two years (based on 868 million doses). Changes in public awareness, combined with changes in technology are demanding innovative approaches to drive forward PV processes and AE analysis.
The COVID-19 pandemic was undoubtedly a catalyst for change as it brought to the fore changes that were already beginning to impact the traditional PV landscape due to:
Evolving disease complexity: Growth in new product portfolios and therapy areas has led to a surge in global databases, leaving the biopharmaceutical industry saturated with data.
Complex regulatory requirements: Healthcare regulators are incorporating processes and standards that explore Real-World Evidence (RWE) for signals and drug safety information.
Increasing cost burdens due to rising safety reporting volumes: The processing of Individual Case Safety Reports (ICSR) is a time-consuming and costly process as
it requires significant resources across manual workflows. In 2019, Pfizer processed approximately 1.4 million AE reports globally. In 2021, GSK, estimated a mean cost of US$33 per processed case report, while other pharmaceutical companies approximated their costs to be even higher. The exponential rise in safety reporting volumes is placing an increasing cost and human resource burden on biopharmaceutical companies.
Exponentially rising number of data points: The International Society of Pharmacovigilance (ISoP) has highlighted the exponential rise in ADR-related data inflow from a variety of sources that include patient/healthcare professional AE reporting; RWE studies; data generated from connected medical devices; and information derived from social media platforms that are increasingly being used to share personal health-related insights.
Other sources such as spontaneous reports, chatbot interactions, Electronic Health Records (EHRs), emails, published literature, patient registries, claims data, and postapproval safety studies are also contributing to a surge in data. Data published by the US FDA in 2021 indicated that over 2.2 million AEs were submitted to the regulatory body’s Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS), up from 500,000 in 2009. This highlights the burden not only shared by the regulatory agencies, but also by the industry in terms of rising ICSR processing.
Applying AI and ML in pharmacovigilance optimizes processes and enhances patient safety by navigating evolving landscapes and analyzing adverse event reporting.
AI and ML to pharmacovigilance
PV is fundamentally a data-driven field that requires the collection, management, and analysis of data gathered from a wide range of disparate sources. The central challenge for PV is the ability to extract meaningful insights from large volumes of heterogeneous data, quickly and reliably to find safety signals that require attention. To aid this process, Artificial Intelligence (AI) powered by advancements in Machine Learning (ML) is being used to optimize processes and find solutions to many of the core problems confronting PV.
According to Gosh et al. (2020), current areas of AI activities in the field of PV include
“digital media screening; extracting and classifying data from source documents; checking for duplicate reports; case validation, triage and initial assessment; data entry; medical assessment, including causality; narrative writing; and coding AE concepts into standardized terminology”.
In general terms, AI/ML has the potential to impact, and is being explored across three broad areas of PV activities that include data ingestion-related tasks, signal detection activities, and ‘other’ applications that include analysing social media posts and integrating data sources with multiple analytical approaches to gain richer insights.
According to Ball et al. (2022), an ICSR contains “information on the patient, the AE, the suspect medical products, the reporter, and, for ICSRs submitted by industry, information on the company that holds the application or license for the drug”. Providing complete and accurate reporting of ICSRs is critical to the understanding of a drug’s safety profile, and as such, applying AI/ML to improve the efficiency and scientific value of ICSR case reporting is a major area of interest for the biopharmaceutical industry.
AI and ML applications are well suited to extracting and organizing the information contained in ICSRs that take the form of structured, semi-structured and unstructured data, all of which are needed to make
a clinical assessment. Once extracted, this catalogued information can then be submitted to a drug safety specialist for review and confirmation, or correction. This ‘augmented intelligence’ serves as input for subsequent rounds of ML to be applied to AE case processing, which in turn, serves to improve the algorithms, increase consistency, and reduce errors. Such applications have the potential to significantly enhance the efficiency of the current PV operating model by automating the routine and manual tasks associated with PV, decreasing overall costs. With case volumes growing at a rate of 10–15 percent per year, a survey published by Deloitte (2019) noted that 90 percent of companies working with PV are looking for solutions to cut the costs of case processing through automation.
Signal Detection Activities: The WHO defines a safety signal as “reported information on a possible causal relationship between an adverse event and a drug, of which the relationship is unknown or incompletely documented previously”. The practice of signal detection is typically targeted at marketed drugs where a safety concern may be new in nature (having not been identified previously in pre-marketing phases), or is a novel pattern of already known ADRs (relating to factors such as severity, highrisk sub-populations, and frequency). Signal detection involves the analysis of a wide range of sources that include case-by-
case assessment of ICSRs, or the mining of pharmacovigilance databases comprising Real World Data (RWD) derived from clinical trials, EHRs, biomedical literature, and spontaneous reporting, to name a few.
The databases may be owned by a pharmaceutical company, a drug regulatory authority, or a large healthcare provider. For example, VigiBase, the WHO global database of medicines-induced reported side effects contains reports of ADRs submitted by national pharmacovigilance centres participating in the WHO Programme for International Drug Monitoring (WHO PIDM) whose purpose is to ensure that early signs of previously unknown medicines-related safety problems are identified as rapidly as possible. Vigibase is the largest database of its kind in the world, with over 30 million reports of suspected medicinal adverse effects submitted by member countries of the WHO PIDM. Sophisticated ML techniques, such as Lasso shrinkage regression, Bayesian borrowing algorithms, and temporal scan statistics are being applied for signal detection.
With the emergence of Web 2.0 and social media platforms, there has been a significant rise in user-generated content in the form of blogs, forums, and social media posts that are published on the Internet. Concurrent with this, advances in AI technologies are giving rise to powerful methods and
AI/ML in pharmacovigilance offer efficient data management, signal detection, and social media monitoring for enhanced drug safety.
algorithms that led to the creation of Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques, which enable the processing and understanding of human-generated text. Text mining, which is generally defined as the analysis of textual data (unstructured or semi-structured text), emerged from the need to analyse large amounts of text containing human language. The principal task of signal extraction from social media “consists in the identification of drugs and symptoms (entity recognition) and of the relationship between them”. Since more patients use social media platforms to express their responses to medication regimens, this medium has become an important source of information for biopharmaceutical companies and regulators in recent years.
Although colloquial terminology, including acronyms, emojis, hashtags, images and slang, together with duplicate reporting (such as parallel posting on multiple platforms), makes it challenging to mine social media data, NLP enables the analysis of multi-formatted AERs to extract meaningful health insights. Novartis, for example, developed AE Brain which analyses and processes social media posts to identify potential AEs, and based on the content and context, predict whether they contain reports of AEs. AE Brain processes around 15,000 messages per week, thereby improving the quality of safety information derived by the company, and reducing the burden of manual repetitive work.
Advances in AI/ML applications are presenting biopharmaceutical companies with opportunities to improve their overall PV capabilities and achieve investigation maturity through investment in nextgeneration digital learning systems that can increase efficiency and generate richer insights. Given that risk minimization measures can be initiated faster, and with greater accuracy, the application of AI/ML in PV has the potential to further promote and protect the health and well-being of patients, which is the overall objective of a successful PV strategy.
 AUTHOR BIO
AUTHOR BIO
Dr Bianca Piachaud-Moustakis is lead writer at PharmaVision, and a freelance business and technology writer based in Exeter, UK, with over 20 years’ experience covering the pharmaceuticals, healthcare and MedTech industries. She has authored/ co-written over 50 publications including peer-reviewed papers, articles, reports, book chapters, and a book published in 2004.

Our article will explore targeted applications of Gen AI within Pharmacovigilance and regulatory affairs, highlighting its potential to streamline processes, improve decision-making, and ultimately, drive better outcomes for all stakeholders.
Marty Boom Global Head of Regulatory & Safety, Navitas Life Sciences1. How has Generative AI impacted pharmacovigilance (PV) and regulatory affairs in the life sciences industry?
Generative AI has already started transforming many industries, and the impact on the life sciences is no different. We’ve seen use cases of how Gen AI can impact clinical trials. Similarly, we expect Gen AI to positively impact domains like Regulatory Affairs (RA)
& Pharmacovigilance (PV) by optimizing workflows and helping humans focus on value added tasks thereby enhancing efficiency of the processes. This is also evident from the survey data collected from our proprietary industry networks related to Regulatory & PV (pvnet®, pvconnect®, pvtech®, & rimnet®)
Any process that involves going through multiple data sources, structured and unstructured content, large amounts of data, and summarizing & generating new content will be served by Gen AI. Additionally, content creation for training purposes is another area where Gen AI will have a significant impact.
2. What challenges has Navitas Life Sciences faced in integrating Generative AI into PV and regulatory processes, and how were they addressed?
We need to be aware of the following challenges when it comes to applying Gen AI for Regulatory & Safety processes.
• Ensuring regulatory compliance (that hasn’t necessarily kept up with the latest developments in the AI space)
• Protecting proprietary information
• Eliminating systemic bias & ensuring fairness
• Ensuring traceability of content generated
• Ensuring consistency of output
• Complying with Data privacy and security. Navitas Life Sciences has addressed most of these challenges by incorporating human expertise to provide necessary
oversight, implementing continuous learning mechanisms, ensuring robust data privacy measures, and developing adaptable AI systems to keep pace with regulatory changes. We have over 250 professionals who are experts at working with 100+ Health Authorities, and whose expertise may be leveraged to optimize the use of AI in its PV and regulatory processes, ensuring regulatory compliance, accuracy, and security.
3. How does Navitas Life Sciences ensure ethical AI use and patient privacy in leveraging AI technologies?
Navitas Life Sciences takes ethical AI use and patient privacy very seriously. These are critical to AI adoption in the life sciences industry. We use these principles right from the design stage through to the validation of the systems & processes we use. Having necessary human oversight ensures that ethical dilemmas are resolved in a conventional manner.
4. Can you share insights into how Generative AI has transformed adverse event reporting and improved patient safety or reporting accuracy?
Generative AI has a significant impact on adverse event reporting. Here are some insights into how it has transformed adverse event reporting and improved patient safety and reporting accuracy:
Generative AI enables improved chat and search experiences for customers, enhancing interactions through platforms like Medical Information Call Center (MICC) and website intake. This ensures better understanding and faster resolution of queries related to adverse events, contributing to overall patient safety.
Natural language processing (NLP) is utilized to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of safety applications. Generative AI aids in case creation from unstructured data sources, such as medical reports or patient narratives. It also assists in generating case narratives and automating follow-ups to healthcare professionals, ensuring that adverse events are reported comprehensively and promptly.
Generative AI automates various tasks and processes within PV, saving time and resources for businesses and organizations. This includes fully automated non-serious case processing and building aggregate reports, among other tasks, streamlining the reporting process and improving overall efficiency.
Through conversational interfaces and summarizations, Generative AI enables the exploration of vast amounts of unstructured data. This includes social monitoring,
automatic coding of medical events, identification of lab results, past medication, and historical conditions. By analyzing this data, potential adverse events can be detected more accurately and promptly.
Generative AI allows for the analysis of complex data from multiple sources, helping businesses and researchers uncover safety signals, hidden patterns, and trends. This enhances risk-benefit analysis by providing deeper insights into the safety profiles of drugs or medical products, ultimately improving patient safety.
Generative AI has revolutionized adverse event reporting by streamlining processes, improving accuracy, and enabling the exploration and analysis of vast amounts of data, ultimately leading to better patient safety and more informed decision-making in the life sciences industry.
Generative AI has revolutionized regulatory submissions and approvals by automating various tasks and processes, thereby enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and compliance. Some of the use cases for Regulatory Automation are highlighted below:
• Content Authoring: Authoring of regulatory documents like CSR, Summary reports, and generation of structured data from clinical trial documents
AI algorithms will detect trends in safety signals well before manual processes, enabling quicker response and intervention
• Clinical trial data summarization: It helps in summarizing complex clinical trial data, converting tabular data into text format, and preparing patient summary reports for each study.
• Converting protocol into Informed Consent Forms (ICF): Generative AI automates the generation of ICF based on study protocols.
• Document search and retrieval: Generative AI enables quick document retrieval based on keywords, improving efficiency during the regulatory submission process.
6. How has Generative AI improved the management and analysis of vast datasets in PV and regulatory affairs, impacting decision-making?
Generative AI has significantly enhanced the management and analysis of vast datasets in PV and regulatory affairs, leading to more informed decision-making.
In regulatory intelligence, Generative AI provides up-to-date information on evolving regulations through regulatory updates and alerts. This ensures that regulatory strategies remain compliant and adaptable to the everchanging landscape.
In the PV domain, Gen AI helps in areas like literature monitoring & surveillance, aggregate report writing & signal detection and management. All these involve going through large amounts of data - both structured and unstructured.
7. What emerging trends or innovations in Generative AI do you believe will further revolutionize PV and regulatory affairs?
Some of the emerging trends in this space include:
Replacement of Search Engine with AI: AI approaches will replace traditional search engines, ensuring that content is served by AI algorithms tailored to specific needs.
Increased Role of Gen AI in Decision-Making:
Generative AI will play a major role in decision-making processes, providing insights and recommendations based on data analysis.
Early Detection of Safety Signals:
AI algorithms will detect trends in safety signals well before manual processes, enabling quicker response and intervention.
Touch-less PV Case Processing & Increased reporting of Adverse Events (AEs):
There will be a move towards developing nearly touch-less PV case processing as most of the data can be created or generated by Gen AI systems or programs. Gen AI’s ability to make sense of vast amounts of unstructured
data can lead to greater reporting of AE information from social media monitoring & literature monitoring.
Auto-Generation of Reports & Narrative information:
Generative AI will facilitate automatic generation of reports based on underlying case data, medical knowledge, regulatory inputs, and social media feedback. However, it is important to have a human in the loop to provide necessary oversight.
8. How should individuals and organizations adapt to meet the demands of integrating AI into pharmacovigilance and regulatory affairs?
Adopting AI is a significant change for both individuals and organizations. AI will result in greater automation & more efficient processes. This frees up human resources to be redeployed in high value-add activities. However, this is only possible if organizations and employees accept and adapt to the new environment quickly. Investments in education, change management and partnerships among various participants enable adoption of this change. Organizations should critically re-visit existing processes in RA & PV to see if AI can help perform these activities more effectively and efficiently. It´s difficult to find new team members who come “fully trained or educated” on AI. The education system is lagging behind. I do think that it offers an opportunity for my current team, but it requires individual team
members to embrace AI and invest in getting themselves trained in using AI tools.
9. How do partnerships between regulatory bodies, industry, and academia foster innovation in AI applications in healthcare?
Regulatory bodies play an active role in this space, issuing guidelines for the use of AI and other innovative technologies. Additionally, there are proof-of-concepts (POCs) between industry and regulatory bodies in these areas for reviewing and approving new drug applications. Navitas Life Sciences is at the forefront in promoting AI for the life sciences industry through its industry forums and partnerships with best-in-class technology vendors in the RA & PV domains. Discussions and free exchange of information related to AI in these forums help in greater understanding and adoption, leading to innovative uses of AI to solve industry pain points.
10. What leadership principles guide promoting an innovative culture at Navitas Life Sciences amidst technological transformation?
Navitas Life Sciences invests in technology initiatives based on quality and productivity gains, focusing on timelines and efforts. We track these metrics for each tech innovation project. Additionally, besides internal productivity gains, Navitas Life Sciences looks for opportunities where our clients can directly experience the benefits of these projects.
11. How do Navitas Life Sciences’ Generative AI initiatives align with broader sustainability goals within the pharmaceutical industry?
I think the link between Generative AI and Sustainability is, in our situation, a bit more vague or less tangible. One can always say that productivity gains expected from investments in Gen AI will contribute to the sustainability goals of the industry but, like I said, this is not very tangible.
12. What advice would you offer to companies navigating the complexities of effectively integration of Gen AI into their PV and Reg strategies based on your experience?
Implementing Gen AI into PV and Reg operations can be a complex and expensive project. Organizations would do well to focus on the business cases in Regulatory & PV that can deliver value through leveraging Gen AI,
rather than be carried away by the technology itself. Once a potential ROI is established, a cross-functional group comprising various stakeholders from Business, IT (& legal) can look at how to progress with these initiatives. It is essential to plan these projects progressively, with small improvements in each project phase bearing in mind that we haven´t yet got all the regulatory frameworks in place to make big steps in a safe manner. AI projects will require multi-year engagements. Many life sciences organizations have also utilized the services of external consultant organizations like Navitas Life Sciences to bring in expertise and make these initiatives more successful.

Marty Boom is a seasoned leader with over two decades of experience in regulatory affairs, pharmacovigilance, and management consulting within the life sciences industry. As the Global Head of Regulatory & Safety at Navitas Life Sciences, he has demonstrated expertise in integrating diverse business units, leading large teams across multiple countries, and providing strategic guidance to top pharmaceutical companies.

One of the fastest-growing modalities in the pharmaceutical industry, antibodydrug conjugates (ADCs), combines a targeted antibody with a cytotoxic payload to offer numerous therapeutic benefits. Veranova’s experts have a deep understanding of the challenges involved in ADC development and have explored how advanced techniques such as preparative chromatography can help streamline the process.
Kishore Hotha Global Vice President, AR&D Lab OperationsCan you describe the current landscape of ADCs in terms of their therapeutic potential and market impact?
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) have made great progress in recent years, targeting more than 260 recognized antigens today. The landscape is becoming more diverse, beyond conventional antibody-based conjugates to peptide-drug conjugates, radio conjugates, and other cutting-edge modalities. This scientific and commercial promise is reflected in the more than a dozen ADCs that have already received US approval. Leading the effort are Daichi Sankyo and AstraZeneca with Enhertu, sales of which hit $1.6 billion in 2022, and,
based on current projections, are expected to reach an astounding $9 billion by 2028. By utilizing these changing development methodologies, it is anticipated that the ADC industry, with its immense potential, will grow to around $30 billion by 2028.
Q2 - What are the primary challenges faced during the development of ADCs, especially regarding efficacy, safety, and manufacturing scalability?
Developing ADCs is a complex endeavour where precision medicine intersects with advanced drug delivery systems. During development, one must select the most suitable target antigens for the specific ADC – those primarily expressed on the intended tumour cells – to prevent cross-reactivity with healthy cells. The precision of the ADC also comes from the expertly engineered linker, which allows the antibodies in the compound to be released at the site of the tumour and not before. The drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) is crucial to ensure ADC performance.
Regarding safety, the specificity of the ADC is of the utmost importance to minimize toxicity to non-cancerous cells. One must constantly calibrate the therapeutic window and determine the proper dosing requirements through rigorous clinical studies. Additionally, there is always the potential for immunogenicity—the immune system can recognize and react against the ADC, which can limit its effectiveness and pose safety risks.
The manufacturing stage demands high precision to ensure each batch is consistent, especially when upscaling production. Quality control becomes more challenging as the scale increases, and all components of the ADC need to be tested and observed, from the DAR to the purity of the product. The components of ADCs often require specialized handling and storage, which can get more logistically complicated as volume increases. The process is like a symphony of finely tuned instruments - all must work harmoniously to afford the best patient benefits.
Q3 - How do you approach selecting antibody targets and cytotoxic payloads to optimize ADC effectiveness?
When developing ADCs, choosing the antibody target and the cytotoxic payload is pivotal for ensuring therapeutic effectiveness while minimizing risks. The ideal antibody target, an antigen, is predominantly expressed on tumour cells, minimizing exposure to healthy cells and enhancing the delivery precision of the cytotoxic payload. Such target antigens should be readily externalizable upon ADC binding, allowing the entry of the cytotoxic agent into the cancer cell. These targets must also be accessible and not obscured by the tumour microenvironment. They are essential to the survival or proliferation of cancer cells, making them the most effective point of attack. The cytotoxic payload must be highly potent, allowing maximum efficacy at lower
ADCs have become a beacon of hope in cancer treatment, with a market projected to reach $30 billion by 2028.
doses and reducing potential side effects. The payload's mechanism should be chosen for its action on the targeted cancer. Integrating the payload with the antibody via the linker is also crucial; the linker must stabilize the bond in the bloodstream and allow for the timely release of the payload inside the target cell. Key factors such as the DAR require optimization to balance effective drug delivery with maintaining the antibody’s functionality. Additionally, the linker’s design must ensure that the ADC remains stable until reaching the target site. Finally, the scalability of the manufacturing process is essential to transition ADCs from the lab to commercial production, encompassing every stage from antibody production and payload-linking to purification, ensuring a steady supply for clinical use.
Q4 - What role does bioconjugation chemistry play in ADC development, and what are the critical considerations in designing stable and effective linkers?
Bioconjugation chemistry is essential in developing ADCs, as it enables the precise attachment of potent cytotoxic drugs to antibodies targeted at cancer cells. This integration transforms the antibody into a particular vehicle, delivering lethal doses to tumour cells. The process involves various strategies for covalently bonding the drug to the antibody, each tailored to preserve the antibody's targeting capabilities while ensuring effective drug linkage.
The role of bioconjugation chemistry extends to designing and synthesizing linkers that connect the cytotoxic payload to the antibody. These linkers are engineered to be robust enough to withstand the bloodstream's environment and prevent the premature release of the drug, which could lead to side effects. However, they must also be sensitive to the specific conditions within tumour cells, such as acidic pH or enzymatic activities, to release the drug precisely where needed. The design of these linkers considers several factors, including stability to prevent breakdown before reaching the target site, cleavability for drug release inside the tumour cell, and biocompatibility to ensure the linker does not detract from the antibody’s function.
Considerations for linker design also include the physical properties of the linker,
Q5 - Can you discuss the importance of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (PK/PD) studies in evaluating ADCs' performance in preclinical and clinical settings?
Pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) studies are vital in developing ADCs and are crucial in the preclinical and clinical phases. PK studies track how the body processes the ADC, while PD studies examine the biological effects and interactions with target cells. The insights we get from these studies refine the ADC design for efficacy and safety.
In clinical trials, PK/PD studies act as a patient safety mechanism by monitoring drug behaviour and identifying potential side effects. The drug exposure is correlated to the tumour response, which enables customized dosing based on individual patient factors such as metabolism and disease severity. This can enhance treatment outcomes and reduce adverse effects.
Recent FDA guidelines emphasize the importance of PK/PD studies, recommending best practices for dosing selection, linker stability assessment, and immunogenicity evaluation. Adherence to these guidelines ensures that the studies are robust, yielding reliable data that can be used to optimize ADC development and improve patient safety and efficacy.
PK/PD studies are essential throughout ADC development. Providing crucial data for dosage decisions, assessing drug delivery and action, and ensuring safety, efficacy, and a systematic approach is vital for successful ADC development into cancer treatments.
such as its length and flexibility, which can affect how the drug interacts with its target inside the cell. Additionally, the conjugation site on the antibody molecule is significant; the chosen site can influence the overall stability, efficacy, and distribution of the ADC within the body. By addressing these complex factors, bioconjugation chemistry helps optimize ADCs, making them potent and selective treatments for cancer.
Q6 - How do you navigate regulatory challenges specific to ADCs, such as characterization, stability, and safety assessments?
Navigating regulatory challenges specific to ADCs demands meticulous compliance with stringent standards focused on characterization, stability, and safety assessments. These challenges arise from ADCs' complex nature, combining small molecule and biologic drug properties.
Characterization requires understanding an ADC's antibody, drug, and linker using sophisticated analytical techniques like mass spectrometry and HPLC. Regulatory bodies require data on an ADC's molecular profile, including DAR, attachment sites, the distribution of conjugate species, unconjugated impurities, unreacted drug, site-specific conjugation, and heterogeneity within the product.
Stability testing is crucial for maintaining efficacy and safety over the ADC's shelf life. These tests involve physical, chemical, and biological assessments. Safety evaluations for ADCs are more complex than for traditional therapeutics due to their dual mechanism of action and the potential for off-target effects. They are essential to how well the ADC deals under stress and involve toxicological studies in relevant animal models, considering acute and chronic toxicity, immunogenicity, and PK/PD.
Companies should engage with regulators early in development and clarify expectations using pre-IND (Investigational New Drug) meetings. These conversations can guide the ADC and help clarify regulatory expectations for a successful IND application. Comprehensive risk management strategies, including robust quality controls and detailed documentation of all development processes, are essential to address regulators' concerns regarding ADCs.
Addressing the regulatory challenges of ADCs requires a thorough understanding of their complex nature and a strategic approach to development that incorporates advanced analytical techniques, rigorous stability
and safety studies, and proactive regulatory engagement to ensure safe and effective ADCs are brought to market.
Q7 - What strategies do you employ to enhance ADC manufacturing processes, including scale-up and production efficiency?
Optimizing ADC production for scale-up entails strategic adoption of key technologies and methodologies. These include but are not limited to:
Implementing modern conjugation techniques. Newer methods like click chemistry or enzymatic approaches enhance DAR's reaction speed, yield, and precision, which are crucial for uniformity and efficacy.
Enhancing manufacturing through automation. Automated systems streamline operations, reduce errors, and boost capacity. Continuous manufacturing (CM) minimizes downtime and increases output efficiency.
Utilize cutting-edge monitoring. Process analytical technology (PAT) ensures continuous quality monitoring, enabling immediate adjustments. High-throughput screening accelerates development and optimizes manufacturing parameters.
Efficient supply chain and inventory management. Early supplier collaboration ensures high-quality materials. Just-in-time inventory systems minimize storage costs and align supply with production needs. Apply global project management to standardize processes and anticipate geopolitical impacts.
Linker stability and manufacturing scalability are pivotal for ADC success, ensuring targeted efficacy and consistent supply.
Scalability and flexibility in process design. Single-use systems enable quicker setups and minimize contamination risks. Design of Experiment (DoE) optimizes process parameters for robust and scalable manufacturing. Standardize quality control across facilities, update regulatory strategies, and robustly manage intellectual property, integrating continuous training and expert consultations to maintain high standards and secure operations. Regular cost and efficiency evaluations. Ongoing economic analysis ensures practical, cost-efficient enhancements, supporting sustainable scale-up and commercialization. This approach refines ADC manufacturing, effectively meeting regulatory standards and commercial demands.
Q8 - In your experience, what are the critical factors influencing the success or failure of ADC clinical trials?
In my understanding, the success or failure of clinical trials for ADCs hinges on critical factors across their development, from preclinical stages to regulatory compliance.
Linker stability is one of the most crucial factors for maintaining ADC integrity and ensuring targeted drug release within tumour cells. It helps avoid premature release and potential side effects. Optimization of the DAR balances efficacy and safety without compromising targeting or increasing toxicity. Additionally, manufacturing scalability ensures sufficient ADC production for clinical trials and potential commercial distribution, maintaining consistency and quality. These factors collectively influence the trajectory of ADC clinical trials. Thoroughly addressing each aspect—from meticulous ADC design and rigorous preclinical testing to strategic clinical trial planning and robust patient monitoring— enhances the potential for successful outcomes, ultimately aiming to bring practical and safe cancer therapies to patients.
Q9 - How do you leverage advanced analytical techniques, such as mass spectrometry and chromatography, to characterize ADCs and ensure quality control?
Advanced analytical techniques such as mass spectrometry (MS) and various forms of chromatography play a pivotal role in the development, characterization, and quality control of ADCs. These techniques provide essential data that ensure the structural integrity, efficacy, and safety of ADCs throughout their lifecycle from development to manufacturing. Intact mass analysis uses mass spectrometry to determine the ADC molecular weight.
This method captures the composite structure of the antibody, linker, and conjugated drug molecules and is crucial for finding the DAR ratio calculation, ensuring consistent drug attachment. Conversely, subunit analysis entails MS analysis of ADC subunits acquired post enzymatic digestion. This approach allows for detailed mapping of conjugation sites and evaluation of the distribution of DAR across different ADC molecules, facilitating the assessment of uniformity and expected activity of the ADC. High-resolution MS utilizes high-resolution accurate mass spectrometry to achieve precise mass measurements of the ADC and its components. This capability is invaluable for detecting and identifying potential impurities or modifications within the molecule and ensuring quality control. We offer state-of-the-art chromatography and advanced manufacturing techniques used for purification and separation, which are challenging in ADCs due to their complex nature. These advanced techniques include Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography (RP-LC), where ADC components are separated based on their hydrophobicity, proving particularly useful in synthesizing linkers and cytotoxic payloads and their chemical conjugation process.
Q10 - Could you elaborate on the potential synergies between ADCs and other therapeutic modalities, such as immunotherapy or targeted therapies?
ADCs offer promising synergies with other therapeutic modalities, such as immunotherapy and targeted therapies. These combinations can enhance treatment efficacy, overcome drug resistance, and potentially improve patient outcomes by targeting cancer from multiple angles. Integrating ADCs with other cancer therapies is a promising, potentially revolutionizing treatment option. By addressing tumours on various fronts, these combinations aim to improve patients' survival rates and quality of life, significantly impacting the future of cancer treatment.
Tumours often create an immunosuppressive environment that inhibits the immune system's ability to fight cancer effectively. ADCs can counteract this by killing tumour cells and releasing tumour antigens, activating the immune system. This enhancement is particularly synergistic with checkpoint inhibitors, which bolster T-cell responses against cancer cells. As cancer cells can develop resistance to targeted therapies, combining ADCs with these treatments can enhance therapeutic effectiveness. ADCs target different molecular pathways or tumour markers, potentially outmanoeuvring cancer's adaptive resistances.
Prioritizing patient-centric processes and combining ADCs with other therapies aligns with this ethos. Meticulous research is crucial for optimal combination strategies, determining effective sequences and dosing for maximum benefit and patient safety. However, combining therapies can sometimes increase side effects,
requiring careful patient monitoring and expertise. Leveraging the genetic profile of a patient’s tumour can inform tailored treatment strategies, employing specific combinations of ADCs and other therapies that target the unique characteristics of the cancer, thereby enhancing personalized medicine in oncology.
Q11 - What advancements do you foresee in the next decade in ADC technology and drug development strategies?
The next decade promises promising advancements in ADC technology and drug development strategies, which will transform oncology treatments by enhancing efficacy, safety, and specificity.
Researchers are expanding beyond traditional cytotoxins to explore novel payloads with diverse mechanisms of action. These include agents that target specific signalling pathways within cancer cells, radioisotopes for localized radiation therapy, and alternative mechanisms that induce tumour cell death. Additionally, ADCs are being developed with two antigen-binding domains to simultaneously target different molecules on the cancer cell. This approach enhances targeting specificity and may help overcome resistance mechanisms. Another pioneering method is to combine two different cytotoxic drugs, each with distinct mechanisms of action, in a single molecule. This strategy aims to broaden the therapeutic window and reduce the potential for resistance.
We have also seen some exciting advances in linker chemistry, such as biodegradable and triggered-release linkers. Biodegradable linkers degrade under specific tumour microenvironment conditions, improving the precise drug release and minimizing side effects from premature payload release. Triggered-release linkers are responsive to external stimuli such as light or ultrasound, enabling controlled drug release at the tumour site upon activation.
Manufacturing and analytical advancements are also anticipated in ADCs and will play a pivotal role in producing more complex ADCs with enhanced consistency and quality.
By integrating these advancements, the next decade in ADC development promises to deliver more sophisticated, effective, and patientspecific therapies. The focus on improving every aspect of ADC technology—from targeting and payload delivery to safety and manufacturing— underscores a shift towards more precise and effective cancer treatments.
Q12 - Considering the competitive landscape, what strategies do you recommend for companies looking to enter or expand their presence in the ADC market?
I strongly feel that the competitive ADC market needs a multifaceted strategy centered around scientific innovation, operational efficiency, and strategic collaborations.
Scientific innovation and differentiation are crucial. Companies should target novel
antigens and mechanisms, focusing on discovering and targeting unique cancer antigens and integrating novel cytotoxic payloads for distinct mechanisms of action. This may involve developing bispecific ADCs or exploring synergistic combinations with immunotherapies to enhance targeting specificity and treatment efficacy. Additionally, linker chemistry innovation can improve drug release stability and control. As such, developing linkers that respond to specific tumour microenvironment triggers or external stimuli is essential.
Operational excellence and development strategies also play a pivotal role. Prioritizing thorough preclinical studies and advancing rapidly into early-phase clinical trials establish the safety and efficacy of ADC candidates, attracting investors and partners. Moreover, investing in scalable, costeffective manufacturing processes ensures consistent and reliable ADC supply for clinical development and commercialization.
Strategic collaboration and market preparation are also crucial. Partnerships between pharmaceutical companies and academic institutions could accelerate development timelines and enhance innovation. Antibody engineering can be used to develop particular antibodies, and investing in advanced analytical technologies for precise ADC characterization and quality control is also vital. Regulatory navigation and commercial strategy are essential. Maintaining proactive engagement with regulatory bodies to navigate
the evolving landscape and articulate a clear value proposition that differentiates your ADC from existing therapies is more critical than ever as this modality picks up speed. Robust commercialization strategies that address pricing, market access, and healthcare stakeholder partnerships will also be essential. By strategically addressing these elements, I believe companies can effectively compete in the ADC market, leveraging scientific advancements to deliver innovative cancer treatments and ensure readiness for future opportunities and challenges in the evolving oncology landscape.

Dr. Kishore Hotha has shaped the scientific business strategies of several companies. Over two decades in the pharmaceutical and CDMO landscape, with extensive expertise in developing drug substances and productsparticularly in small molecules, HPAPI, drug linkers, ADCs, and complex drug dosage forms - Dr. Hotha has authored over 50 scientific research publications and serves on several editorial boards. He received his Ph.D. from Jawaharlal Nehru Technological (JNT) University and MBA from Southern New Hampshire University and has held leadership positions at Lupin and Dr. Reddy’s in Research & Development.
Decentralized and virtual clinical trials, with pharmacies as collaborators, mark a significant transformation in medical research methodologies, utilizing digital tools for remote trial management. They overcome traditional obstacles such as geographical limitations and promote patient engagement through remote monitoring and telemedicine, with pharmacies managing medication dispensing and adherence. By dispersing trial operations, these trials streamline procedures, cut costs, and boost efficiency, ultimately expediting medical breakthroughs and broadening access to experimental therapies. Integration of telemedicine improves patient access and participation, ultimately accelerating medical innovation and the development of experimental therapies.
 Josipa Ljubicic Chief Executive Officer Proqlea Ltd
Josipa Ljubicic Chief Executive Officer Proqlea Ltd
Introduction
According to the National Centre for Biotechnology Information, 30% of participants drop out during clinical trials, causing harm to the study. This can be prevented by solutions involving virtual clinical trials. [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3684189/]
Drop out can be prevented by implementation of decentralized and virtual clinical trials. The traditional approach to clinical trials requires a clinical study site, which is usually a hospital, where participants are recruited, experimental drugs are administered, interviews with patients are conducted, data is managed, and documents are signed. Some (or all) of these processes can be done remotely using technology. Such clinical trials are called decentralized or virtual clinical trials.
An elderly patient volunteer lives several hours' drive away from the study site. Instead of spending time and energy traveling there, they sign up for a virtual telemedicine system and talk to their doctor online about their experience with the new medicine. They monitor some symptoms themselves with devices they have on hand, then fill out forms and surveys by themselves, without waiting in a long line. The medication is available in their local pharmacy, where it has been delivered from the site.
The patient has now saved time, money, and labour of travel, while the study site has gained all information needed, using minimal staff.
Virtual and decentralized clinical trials have the potential to contribute to clinical research in several ways: overcoming geographical limitations, increasing patient engagement, streamlining procedures, cutting costs, saving money... and ultimately boosting efficiency and aiding in reaching medical breakthroughs, all with the help of technological innovations, good network connectivity, and a more accepting attitude towards technology.
For a clinical trial to be of high quality, diversity in patients are needed. Potential patients are unlikely to be located in the same area, and as such Clinical Trial face
geographical limitations. Patients who must travel several hours to the clinical site, have to arrive at a specific time, and then have to spend several hours there as well, may not join the Clinical Trial due to stress or burden of travel, they may drop out of it, or they may not be as compliant due to dissatisfaction. Since clinical trials should be conducted for the patient, i.e., the patient should be the focus, this creates difficulties in the quality of research.
In Clinical Trial patient engagement issues are typically lack of awareness, limited access to information and resources, patient burden and inconvenience and lack of diversity and inclusion. Potential patients will never participate in clinical trials if they are not aware of them. Some patients are not sufficiently informed about the trial process and their rights, so they are not interested. Furthermore, if patients want to inform themselves, they may not have access to disease and medication data, and current study status due to legal regulations or data privacy regulations. If patients agree to participate in the study, they bear a certain burden, such as the waste of time and burden of travel mentioned earlier, and complex treatment procedures. Finally, individuals from marginalized communities often do not participate in clinical trials, so the drug is not tested for all groups because it is often not easily accessible to them (e.g., patients over 65 years old, patients with disabilities, people of colour).
Clinical trials sometimes face operational inefficiencies. Sometimes processes within clinical trials are not optimized for productivity, cost reduction, time efficiency, and quality of collected data. Common challenges include participation retention, when patients do not follow up after the trial, resulting in a lack of staff and resources, and problems in data management when multiple incompatible data storage systems are used.
The concept of decentralized or virtual clinical trials is not new, but it was developed further after the global COVID-19 pandemic. Decentralized and Virtual Clinical Trials involve the use of digital health technology to enable remote participation by patients. Decentralized systems do use a central site, which can be confusing due to the name, but not all processes are conducted at the same site; they may occur at other local smaller sites or remotely from home. A virtual clinical trial would be a type of decentralized clinical trial that is fully remote and online. In practice, most clinical trials operate using a hybrid model, incorporating remote technology for some aspects of the trials
The key word here is technology. Various software and hardware solutions can replace
or enhance some processes of clinical trials, showcasing benefits of decentralized and virtual clinical trials.
1)
In theory, a patient should only need to visit the clinical site once to meet with the doctor and understand the procedure. After that, other obligations, such as receiving medication, completing questionnaires, or consulting with the doctor, can be done remotely from their home, at a local site much closer to them, with the help of nearby pharmacies.
Today, remote monitoring and telemedicine encompass much more than just talking to patients via webcam. Modern systems are used not only for communication but also for collecting data. They are adaptable for both patients and professionals and can independently measure symptoms such as high blood pressure, diabetes, weight loss or gain, heart conditions, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sleep apnea, and asthma. Example of technology used for remote monitoring is weight scales, pulse oximeters, blood glucose meters, and blood pressure monitors. With today's global connectivity, widespread use of technology, and falling prices, technology is more accessible and affordable than ever before.
Patients can independently educate themselves about their rights and the trial process using a digital platform containing all necessary information and resources. After being informed, the investigator verifies whether the patient agrees with everything. This allows the patient time and agency to make decisions independently, without external influence, and frees up the investigator's time for other processes.
All this leads to streamlining of procedures and cutting costs, boosting efficiency and expediting medical breakthroughs.
Pharmacies can recruit diverse and local patients by reaching out to them directly. They hold real-world evidence data which are useful. Some companies have the finance to use advanced machine learning algorithms to design betters’ studies.
For patients who are in the process of clinical research, pharmacies can offer directto-patient services, with shipments of drugs or medical devices in smart packaging directly to patients.
Instead of the patient traveling to the clinical centre where the study is conducted, the medication is delivered to a local pharmacy where everything is familiar to the patient and they can pick up the medication without traveling and waiting for a long time.
Here are some real-world examples of successful decentralized and virtual clinical trials
The Michael J. Fox Foundation Virtual Study
This study enrolled individuals with and without Parkinson's disease using the Fox Trial Finder, a clinical trial matching tool. More than 160 participants from 39 sites across the country took part in the study. Since Parkinson's disease is typically diagnosed visually, the virtual platform allowed investigators to remotely examine participants via videoconferencing, eliminating the need for travel. This approach provided wide geographic representation and included individuals who otherwise wouldn't have been able to participate. A follow-up evaluation showed high participant satisfaction, with 90% expressing satisfaction with the trial, 80% indicating a willingness to join a similar future trial, and 85% stating they would be more able to participate if it could be done remotely.
This study will conduct follow-ups with participants from two large, multicenter Phase 3 Parkinson's disease studies (Steady PD III and Sure PD3) via annual virtual visits using web-based video conferencing. Participants in the AT-HOME PD study will also provide self-reported outcomes quarterly
through Fox Insight, an online clinical study platform, and submit monthly assessment data on tremor, gait, voice, and balance collected via a smartphone.
This study aims to investigate the linkage between the leucine-rich repeated kinase (LRRK2) genetic mutation and Parkinson's disease by recruiting a national cohort of carriers. Due to the rarity of the LRRK2 mutation, a traditional study would necessitate multiple sites worldwide. Instead, leveraging the Fox Insight online platform, the study successfully recruited 300 participants, including 50 with Parkinson's disease. Participants will be followed remotely with annual virtual Parkinson's disease examinations.
Virtual trials present several advantages over traditional studies, notably in their participant-centered approach. The geographic reach of virtual trials is not constrained by the location of participants but by their internet access. These trials offer additional benefits such as comfort, convenience, and confidentiality for participants. They also streamline the initiation process, enable more frequent participant assessments, and simplify the management of multiple Institutional Review Boards (IRBs).
Case studies indicate that virtual trials could significantly reduce costs in the long
term. Despite the availability of tools to conduct virtual trials, the primary barriers to their widespread adoption appear to be a lack of creativity and determination within the industry. By overcoming these challenges, virtual trials have the potential to revolutionize the field of clinical research.
AUTHOR BIOJosipa has over 20 years of experience in the pharmaceutical industry and is an expert in QA (Quality Assurance). She has helped more than 150 companies establish effective QMS and has hosted over 320 audits and regulatory inspections. Her expertise extends to clinical trials, focusing on innovative products for rare diseases. Josipa has advised leading pharmaceutical companies throughout the clinical trial process. Under her leadership, Proqlea became a full-service CRO, promoting high-quality products. She is currently working on establishing the first clinical trial hub for the EU and Balkan region.


 Satish (Kumar) Singh Vice President, Astria Therapeutics, Inc
Satish (Kumar) Singh Vice President, Astria Therapeutics, Inc
 Atanas Koulov Chief Scientific Officer Clear Solutions Laboratories
Atanas Koulov Chief Scientific Officer Clear Solutions Laboratories
Surfactants in Biopharmaceutical Development addresses the progress, challenges, and opportunities in surfactant research in the context of the development of biologic therapeutics. The book covers a broad range of important fundamental topics as they relate directly to biopharmaceutical development including synthesis of surfactants, mechanisms of protein stabilization by surfactants, as well as practical considerations for the use of surfactants in biomanufacturing. The book also provides an overview of the state-of-the-art analytical technology and methods for quantification and characterization of surfactants, as well as deep- dive into one of the hottest topics in biopharmaceutical development today - surfactant degradation and its impact to drug product quality and stability. Special attention is given to critical aspects of biopharmaceutical development, like control strategies and current regulatory aspects of paramount importance for biopharmaceutical companies and regulators.
The chapters are authored by subject matter experts, thus providing an up-to-date coverage of, and thinking on the topics involved.

What motivated you to delve into the topic of surfactants in biopharmaceutical development, and how does your book contribute to this field?
Satish
Whereas the former are focused on speed and simplicity of operation (in addition to accuracy, precision and robustness), the latter are typically more sophisticated and focused on selectivity.
Interestingly, mass spectrometry coupled with liquid chromatography, has made significant advances in both groups of methods, albeit in different implementations. Another highlight is the utility of lipase activity assays to aid protein purification process development and control thus helping prevent surfactant degradation challenges in the drug product.
The criticality of this excipient as well as the challenges posed by it has led to a flurry of research on multiple aspects of these materials. This prompted us to summarize the knowledge being generated in the readily accessible form of a book.
The book covers analytical techniques for quantifying and characterizing surfactants. Can you highlight some of these techniques and their relevance in biopharmaceutical development?
Surfactants are a critical excipient in the stabilization / formulation of biologic drug products or biopharmaceuticals. In a recent review, it was estimated that more than 97% of antibodies approved after 2009, contain surfactants. Atanas
Extensive coverage of this critical topic is provided in a dedicated chapter, but also throughout the entire book. It is important to highlight the distinction between analytical methods for quantification versus characterization, as their divergent goals determine very different analytical target profiles.

Pharma Focus Europe
Can you discuss some key challenges with surfactant as it relates to stabilizing biologic therapeutics, and how does your book address these challenges?
The key challenges with surfactants relate to their own instability if not handled properly, the analytical difficulties posed by their heterogeneity and their degradation mechanisms, and the relatively low concentrations at which they are used. Fundamental understanding of their function is critical to the proper use of these excipients.
Finally, most formulation scientists are likely unaware of how these materials are synthesized and their biological fate. The book covers all these topics and provides a compilation of the latest research, and a great introduction to the newcomer in the field.
What control strategies or quality assurance measures do you recommend for ensuring the consistent performance of surfactants in biopharmaceutical formulations?
A well-designed phase-appropriate surfactant control strategy is critical for ensuring program success and preventing unforeseen delays, technical and regulatory hurdles.
A comprehensive control strategy has three main components: a) surfactant raw material control (including raw material sourcing, control, storage and handling), b) process control (including drug substance and drug product in-process control), and c) drug product control and characterization (drug product quality control for release and stability testing, as well as additional “extended characterization” tests, such as surfactant profiling and particle monitoring).


Most importantly, a strong product and process development effort is needed to provide the foundation for the control strategy. For example, a limited but focused effort on protein purification evaluation and host-cell protein species, even in early stages of development, can pay off in the long run.
In your opinion, what are the most significant advancements or breakthroughs in surfactant synthesis that have impacted biopharmaceutical development?
Advancements in synthesis relate primarily to moving away from animal-derived raw materials (fatty acids) and improved control of process as well as final purification (for pharma grade), thus resulting in tighter control of critical quality attributes (e.g. peroxide value, acid value, fatty acid distribution, impurities etc.) and better batch to batch consistency. Various grades of surfactants have also been introduced as the understanding of their function has improved.
From a regulatory perspective, what considerations should companies keep in mind when using surfactants in biopharmaceutical products, especially regarding product safety and efficacy?
Dr. Rao of the FDA has provided an excellent overview of the scientific and regulatory considerations in a chapter of the book. From a product safety and efficacy perspective, it is important to justify the need for and the level of the surfactant to be used. A control strategy has to be elaborated and justified, consistent with current guidelines, such as the recently published ICH Q14.
Analytical methods must be in place to follow this excipient at release and also on stability to ensure product quality and function of the surfactant at end of shelf-life. The bottom line is – this is a critical excipient in your product. It must be controlled as such.
How do surfactants influence the quality and stability of drug products, and what are some best practices for managing surfactantrelated issues?
This question goes to the heart of the scope of the book. While all formulators understand the need for addition of surfactants, the quality of surfactant can significantly impact the long-term stability of the protein product. Surfactant excipient that has oxidation products in it, can enhance the rate of oxidation of the protein.


Thus, protecting the excipient from heat, light, and oxygen is important, and this understanding must also be communicated to manufacturing personnel who actually handle the ingredient and create the formulation on the shop floor. Hydrolytic degradation of the surfactant due to host cell protein related enzymatic species, can lead to particle formation as well as loss of protective function.
Trace amounts of such lipolytic enzymes (e.g. esterases and specifically, lipases) are often co-purified with the protein drug substance and lead to generation of free fatty acids which appear as particles in the product solution. Such challenges may be more widespread across the industry than currently appreciated and may require more attention in purification and product development. We believe that the book will be helpful in raising awareness of these issues.
Collaboration is essential in advancing research. Could you share any collaborative efforts or partnerships that have shaped your understanding of surfactants in biopharmaceutical development?
Atanas
The field has been marked by a number of collaborative initiatives that have addressed control and regulatory aspects. Some important multicompany publications have come out of these collaborations.
One of the earliest ones was Jones et al., Pharm Res., 35(8) 148, 2018 which covered the topic of use and control strategy, followed by the more recent report by Wuchner et al., J Pharm Sci 111(5) 1280, (2022) and 111(11) 2955, (2022).
We strongly believe that these collaborations have advanced both the science and raised awareness of the use of these critical materials, thus resulting in an overall improvement in the quality of the products being commercialized. This is ultimately to the benefit of the patient.
Pharma Focus Europe

Could you elaborate on the role of surfactants in the biomanufacturing process, including their impact on product yield, purity, and overall efficiency?
Surfactants (as addressed in this book) are primarily added at or after the final TFF step in the downstream purification of the drug substance. As such, they do not have a direct or significant impact on yield and overall efficiency.
Surfactants cannot be readily buffer exchanged - this aspect is expertly covered in the book. The caveats about use of well controlled raw materials applies here in that if degraded surfactants are used, the purity of the drug substance may be impacted.

Surfactant degradation is a key focus in your book. What are the main factors contributing to surfactant degradation, and how can biopharmaceutical companies mitigate these risks?
Degradation mechanisms of surfactants are complex but can be classified into oxidative and hydrolytic. Based on this understanding, appropriate measures can be introduced in the control and handling of the ingredient as well as processing and analysis. Primary route of degradation for the raw material will be oxidation – thus protection from heat, light, oxygen, and prevention of contamination with metal ions is key.
Hydrolytic mechanisms are not very active in the raw material, but may be common in the formulated product due to residual trace enzymatic activity in the drug substance (as noted above). Thus, understanding and controlling the host-cell protein profile, especially for high concentration products, is very important.
Finally, what message or key takeaways do you hope readers will gain from reading your book, and do you have any upcoming projects or initiatives related to surfactant research that you can share?

We intend the book to provide a one-stop resource into the diverse aspects of surfactants and their use -scientific as well as regulatory. The references can serve as a starting point for the readers who want to delve in-depth in specific aspects of the field, and perhaps also serve as an inspiration to make further advances, including alternative surfactants, novel analytical methods, improved control strategies etc.
Looking ahead, what do you envision as the future of surfactant research in the context of biopharmaceuticals, and are there any emerging trends or technologies that excite you?
Future research in the context of biopharmaceuticals could focus on higher levels of quality control of raw materials, improved and higher resolving analytical methods, deeper understanding of mechanisms of stabilization including molecular modeling of the interactions between various ingredients and the protective function, and better insight into degradation mechanisms.
Understanding safety aspects, especially the rare events when surfactants (in the low amounts used in biologics) cause tolerance issues, will surely benefit from further research. And of course, new surfactants which may address some of the drawbacks of the current set, remains a very exciting and active area of investigation.

In conclusion, what advice would you give to aspiring researchers or professionals interested in the field of surfactants and their application in biopharmaceutical development?
This is an important, exciting and vast field. There are many aspects that can be delved into, especially with new cutting-edge tools becoming available. While we have made a lot of progress in the last few years, the field is not saturated. There remain areas to explore and develop - both technical and regulatory. We hope that the book provides a good starting point for young professionals to advance further the current pharmaceutical knowledge and ultimately - help patients.

Thank you, Satish Kumar Singh & Atanas Koulov, for participating in this Book Interview with Pharma Focus Europe magazine!

Atanas has more than 15 years of experience in pharmaceutical drug product development from Roche/ Genentech, Novartis and Lonza. His focus areas are DP control strategies, particle contamination and control, surfactant degradation, analytical development and quality control. He has authored more than 50 scientific publications and book chapters.



Satish has long experience in the biopharma industry in product development activities and is an internationally recognized expert in biologics and vaccines. His focus areas relate to technical and regulatory challenges, including aggregation, immunogenicity and control strategy development. He has authored more than 90 peer-reviewed publications and several book chapters.

Drug products containing active biological ingredients form one of the most important and fastest-growing sectors of the pharmaceutical industry. These biologics include a wide range of large, complex molecules including protein and peptide products (such as monoclonal antibodies), through to more complex moieties including vaccines and oligonucleotides incorporated into lipid-based delivery vehicles.
Most biologics are formulated and administered to the patient in aqueous dosage forms but quite often this presents a stability challenge which results in limited shelf life, with storage requiring either frozen or refrigerated conditions. Often the only way to overcome this is to develop a dry powder formulation that is inherently more stable.
Freeze drying is the traditional process of choice for creating dry powder biologics but it suffers from several technical challenges resulting in lengthy drying processes over several days with significant energy and equipment costs. These challenges have meant that there is now a growing interest in alternative technologies for creating dry powder dosage forms.
Several experimental technologies - such as spray freeze drying, thin-film freeze drying and supercritical fluid drying – have generated interesting results but only spray drying has the existing capacity to be considered a viable option for the scale-up and manufacture of commercial-scale dry powder biologics.
There are already examples where spraydried biologics have been incorporated into an aseptic dosage form and whilst this list is relatively small, there are a considerable number of spray-dried biologics in clinical development that are expected to achieve approval in the coming years.
In a recent case study, Upperton demonstrated the ability of spray drying to stabilize a large (mwt 66kDa) soluble, globular protein recombinant human albumin (rHA). In this study, rHA was formulated and either spray-dried or freeze-dried to create dry powder products. The resulting spray dried powder was far easier to handle and was shown to have near identical physical and stability properties to the formulation that was created using freeze drying.
Spray drying is a useful technology for producing dry powder formulations not only
of proteins but also larger biological entities such as vaccines and nanoparticulate liposomal structures. This is potentially useful when considering the formulation of oligonucleotides such as mRNA which require a relatively large liposomal carrier to carry it across the target cell membrane and subsequently clear endosomal capture. Indeed in many instances, these liposomal structures cannot survive the physical effects of freezing required during freeze drying.
In a recent study, the team at Upperton investigated whether spray drying was capable of producing dry powder virosomal (liposomal based) formulations since freeze drying had been shown to cause significant damage to the delicate structures.
The delicate, waterfilled liposomal vaccines were spray dried using a range of drying temperatures and in all cases, the spray dried powders produced could be reconstituted in
water to maintain the same particle size as before spray drying.
Closer analysis of the surface antigens using HPLC and ELISA techniques confirmed that all of the influenza surface antigens and the critical P-1 and gp41 antigens remained unchanged after spray drying as well as the associated adjuvant.
Our latest white paper “Spray Drying Biologics: An Alternative To Freeze Drying” sheds more light on how spray drying offers an alternative, more cost-effective route for creating dry powder biologics with some intriguing physical advantages created by this fast-emerging process.
Explore the Upperton whitepaper to stay ahead in the industry. Scan the QR code below to access the comprehensive guide that can revolutionize your approach to drug delivery systems.


Dear Readers,
Welcome to our panel discussion on Biopharmaceuticals and Biosimilars: Market Trends and Future Prospects. Our esteemed panelists, Gillian Woollett and Christopher Conway will share their expertise on regulatory strategies, market dynamics, and innovative trends shaping the Biopharmaceuticals landscape.
Join us as we delve into the evolving world of biopharmaceuticals and biosimilars, exploring insights that promise to shape the future of Pharma Industry


Gillian Woollett
Gillian Woollett, MA, DPhil, is responsible for providing science-based regulatory strategy and policy expertise for biologics, including biosimilars, at Samsung Bioepis. She currently chairs the International Generic and Biosimilar Association’s (IGBA) Biosimilars Committee, working closely with World Health Organization (WHO) on access and affordability matters.
Christopher Conway
Chris is a seasoned business executive with 25 years of experience across aerospace, pharmaceutical/biotech, and contract research and manufacturing. He has extensive expertise in P&L leadership, sales, and marketing in both public and private equity-backed companies. Currently, Chris is the President and R&D Business Unit Head at Curia and serves as a Director on the boards of Viyash Life Sciences and the Drug, Chemical & Associated Technologies Association (DCAT).
1. How do biopharmaceuticals and biosimilars impact healthcare costs and patient affordability?

•Biologics have become mainstay treatments for many chronic and acute diseases, becoming increasingly fundamental in reducing mortality and managing multiple medical conditions. However, access to these treatments can be limited, often due to high cost of treatment or lack of necessary infrastructure.
• In the EU, biologics represented 40% of the total expenditure in 2022 which has significantly increased compared to that of 2012 (28%) and this is expected to grow due to increased utilisation of biologics as advanced established treatments, and due to the introduction of new biologics.
• In the United States, the biologics market has grown 12.5% on an annual basis from 2017 to 2021 and now comprises 46% of prescription medicine spending. As more novel biologics are introduced, the percentage of biologics spending is expected to rise over the years in the US too.
• Biosimilars, as lower cost alternatives, play an important role in alleviating the financial burden faced by healthcare systems, as well as by increasing surety of supply. In the US, the past five years’ savings due to biosimilars has been estimated to be $40 billion (compared to the anticipated spending without biosimilar competition over the same period). Similarly, estimates suggest there is up to $180 billion of potential savings from biosimilars between 2023 and 2027. In Europe, the cumulative savings from biosimilars are estimated to be over €30 billion since the introduction of the first biosimilar in 2006.
• Biosimilars also play an important role in improving the quality of care for patients. When patients do not have timely access to biologic medicines, it can significantly impact their disease progression in an irreversible manner. This is particularly important for the often debilitating, progressive, and fatal diseases treated by biologics. However, the introduction of biosimilars frequently causes higher utilisation of the molecule as lower costs offer increased access to more patients (e.g., UK with filgrastim).
• Access to quality and timely medical care will continue to be an issue for many countries around the world as more novel biologics are introduced, and biosimilars
will play an increasingly vital role in allowing earlier access to these life-enhancing biologic treatments.
2. What role do regulatory agencies play in ensuring the safety and efficacy of biopharmaceuticals and biosimilars?

Regulatory agencies play two key parts in ensuring the safety and efficacy of biopharmaceuticals and biosimilars:
1. Science based evaluation of the new proposed product, and further evaluation of any changes which occur during the lifecycle of the product
2. Initial and ongoing surveillance of the pharmaceutical supply chain, including manufacturing facilities to ensure they meet cGMP requirements
The evaluation of biosimilars is more complex than that of generic small molecules – requiring the manufacturer to be able to defend science-based questions on their product which they would not experience with small molecules.
3. What are the key differences between regulatory pathways for biosimilars and small molecule drugs?

The goal of a subsequent version of a previously approved medicine is to match the
clinical outcomes of the original through offering quality, safety and efficacy without requiring a complete, new development programme. For generic drugs this can usually be achieved based on the known molecular structure of that original medicine, but for biologics it can be more complicated because biologics are made in living systems and often represent complex mixtures. Fortunately, extensive experience has been accumulated with the originator products by the time biosimilars are developed, and often with manufacturing changes to those products (the so-called comparability exercise) which enables sponsors and regulators to used state-of-the-art technology to measure what matters most to those clinical outcomes. This is particularly true of the class of biologics known as monoclonal antibodies.
For a generic product to be approved, in the US, the sponsors must demonstrate that the active ingredient, dosage form, route of administration, and strength are the same as the reference small molecule drug. Analytical characterisation and bioequivalence test are required to demonstrate that the generic product performs in the same manner as the reference product. However, the in vivo bioequivalence studies can be waived in some cases depending on the site of action, route of delivery, dosage form, and formulation design. Such bioequivalence studies are routinely waived for injected products.
For a biosimilar, the sponsor needs to demonstrate that the biosimilar product is highly similar to the reference product and has no clinically meaningful differences in terms of safety, purity, and potency. This has, to date, entailed a lot more than bioequivalence stud-
ies and routinely involved multiyear extensive comparative clinical efficacy studies. However, we now have the opportunity to revisit the highly successful experience with biosimilars approved already that shows that analytics are the fundamental and most sensitive basis for judging biosimilarity. Plus, significant progress is being made in analytical science and its ability to detect differences, and this allows a reduction in the clinical study expectations with no change in the quality, safety and efficacy of the biologics ultimately approved. This uses the same regulatory science established with comparability by FDA in 1996 for originator biologics, as also adopted by EU in 2003, and subsequently as part of the global harmonising body ICH as the guideline ICH Q5E. ICH guidelines offer support for the quality for all medicines worldwide.
Biosimilars play an increasingly vital role in allowing earlier access to life-enhancing biologic treatments.

The generic small molecule and biosimilar pathways differ dramatically because within the small molecule world, it is possible to exactly duplicate the target compound. With biosimilars, it is not possible to exactly duplicate the target molecule, and therefore, additional studies are needed
With small molecule generics, substitutability is a given; however, with biosimilars, it is not. A specific class of interchangeable biosimilars requires additional studies and evidence to be considered directly substitutable at the pharmacy level.
Many generic small molecule products do not require clinical studies for approval; however, for biosimilars, clinical studies are a given, meaning more complexity and cost, leading to longer lead times to market versus their small molecule counterparts.
4. How do regulatory changes, such as the introduction of biosimilar naming conventions, affect market dynamics?

In its simplest form, biosimilar naming conventions impact adoption by pharmacists. The current convention involves using a nonproprietary base name (similar to the originator biologic) along with a designated suffix unique to each biosimilar. Pharmacists would be more confident to use the biosimilar interchangeably with the originator if both have the same
name. Something as seemingly simple as the naming convention has a dramatic impact on adoption, which ultimately impacts price, market share, and most significantly, competitive dynamics.
5. Are there any specific regulatory challenges in gaining approval for complex biologics and biosimilars?
 GILLIAN WOOLLETT
GILLIAN WOOLLETT
Biologics, including biosimilars, face a multitude of regulatory challenges, and the biggest issue becomes their being treated inconsistently with each other and across markets. Ultimately no patient can access a product if it is not approved for use by their country and if their health care system does not support access. Legal, regulatory and economic factors matter. The science is largely asked and answered and the same worldwide.
Economics considerations often predominate. Biosimilars stimulate market competition and lower the average price of the molecule, thereby increasing access. Further, the savings from biosimilars can be reinvested to improve quality of healthcare as well as for use of the next generation of improved medicines, including biologics.
It is estimated that 70% of originator biologics could face biosimilar competition in the future, but nearly half of them (47%) have no biosimilars in development. This illustrates the challenges to sustainability for biosimilars, and needs to be addressed with some urgency. Streamlining development, and global harmonisation can facilitate the availability of quality-assured, safe and
effective biosimilars to many more patients. There is an international regulatory initiative underway to consider this and it can greatly facilitate access by low- and middle-income countries as well as traditionally leading markets such as the EU and US. Creating regulatory predictability, through removing the expectation of comparative clinical studies that contribute no new information for regulatory decision-making purposes, could rescue some of the potential for competition. If there is not enough competition from biosimilars, it will ultimately have a negative effect on the sustainability of the biosimilar market and the viability of the biologics market overall. Lack of competition precludes access to the latest originator biologics because the older biologics will continue to consume available funds. The virtuous cycle becomes stalled and patients suffer unnecessarily.
From sponsor’s perspective, improving the efficiency of biosimilar development (reducing both cost and time) is essential, and it is already major priority in the US with the FDA’s pilot research programme funded by BsUFA III. There are also active debates ongoing between global regulators and sponsors about regulatory streamlining:
• No unnecessary clinical comparator studies (e.g., implementation of the MHRA, WHO Guideline).
• Regulatory convergence (EU Term)/ harmonization (US term) to enable one data set to be used in multiple jurisdictions, with no repeats in specific studies, when the reference product is known to be the same.
• Regulatory reliance to reflect previous reviewer evaluations enables more timely approvals as there is then no need for
repeated evaluations of the same date by each regulator in every jurisdiction
Recognition of a global comparator product when there is clear evidence that the originator biologic used as the reference is already the same in different markets so a biosimilar should be able to be too. This may include public information from regulators own websites, such as FDA and EMA that shows that the reference products themselves were approved based on the same pivotal clinical studies in both jurisdictions and therefore must be the same product.
The science supports the more efficient approach, and the regulators largely agree, so the issue is expediting the process to achieve such efficient regulation that retains the feasibility of biosimilar development for multiple sponsors in multiple jurisdictions as soon as possible. Absent regulatory predictability and science-based, consistent, regulatory decisionmaking competition is likely to stall.
6. How do market access strategies differ between developed and developing regions for biopharmaceuticals and biosimilars?
 GILLIAN WOOLLETT
GILLIAN WOOLLETT
Different countries have different health priorities, and different levels of resources to spend addressing them. While medicines, including biologics, are very important, their appropriate use depends on other infrastructure, such as access to health care providers and hospitals, as well as timely diagnosis of disease for which effective therapies are available. Consequently, different therapeutic
areas are being addressed very differently in various jurisdictions.
WHO plays an important role in helping countries access affordable essential medicines, and also in facilitating collaborative approaches to their review and approval. WHO is very involved in access to both generic and biosimilar medicines because their affordability is key to access and they represent 80-90% of the doses that ultimately reach patients.
One challenge is when a country does not have the reference medicines, can they access a biosimilar? That again entails local decisions by the country concerned.
Biosimilars sponsors would like to make their quality-assured, safe and effective medicines available as broadly as possible, but this requires market access, procurement as well as the necessary healthcare infrastructure to be available too.

Market access strategies for biopharmaceuticals and biosimilars vary significantly between developed and developing regions. Factors such as treatment rates, regulatory environments, and affordability all impact access strategies. For these reasons, companies need to tailor their go-to-market and commercial models to each individual region’s unique characteristics. This can prove to be quite challenging and often financially unsustainable.
7. What impact do intellectual property rights and patent expiration have on the biosimilars market?

Regulatory agencies ensure safety and efficacy of biopharmaceuticals through science-based evaluations and ongoing surveillance.
As with small molecule products, patent rights play an important role in determining when a biosimilar may enter the market. The Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act (BPCIA) sets forth a process whereby branded pharmaceutical companies identify relevant patents and potential competitors (biosimilar manufacturers) challenge those patents. If the challenge is successful and the patents are found to be invalid or not infringed, the biosimilar can enter the market earlier. If the patents are valid and infringement is demonstrated, then the biosimilar cannot enter the market until after the relevant patents have expired.
8. Can you discuss the role of real-world evidence and postmarket surveillance in ensuring the safety and effectiveness of biopharmaceuticals and biosimilars?
 GILLIAN WOOLLETT
GILLIAN WOOLLETT
As with any medicines approved by stringent regulatory authorities, pharmacovigilance is an important part of the life-cycle of biopharmaceuticals, including biosimilars, to ensure continuous safety and effectiveness after introduction into the market. For those countries with established PV systems, they apply to biosimilars in the same manner as any other medicine.
Biosimilars are behaving as expected, namely giving the same clinical benefit as their reference originator products, and confidence in analytics that support the approval and continued manufacturing of quality-assured biologics is increasing. No unusual or expected adverse events have been seen with biosimilars anywhere and that supports their global use. Demands for real-world evidence (RWE) and big data are increasing and global for all medicines, and data integration becoming more feasible. Nonetheless, while sponsors are ready to streamline development they need regulatory predictability to invest in more biosimilars and subsequent markets: for instance, reducing studies that offer no new information such as comparative efficacy studies, using experience and data accumulated with the same prod -
ucts in other jurisdictions, such as RWE, and facilitating regulatory reliance globally through regulatory norms such as WHO can all expedite broader access everywhere. Such approaches share the costs across more patients and make economic sense for everyone.

The science and core regulatory requirements are the same for every biosimilar irrespective of the therapeutic area, but the understanding by health care providers has to be revisited each time a new physician and patient population is given the opportunity to use them. Fortunately, leading regulators including FDA and EMA, have become more involved in education, working on educational materials, including supporting Continuing Medical Education Credits. It is an on-going challenge, because they have a lot of stakeholders to reach, and many health care professionals have little time and are already familiar with the reference product and have little incentive to change. Biosimilars sponsors also have to take on a role to ensure that all stakeholders fully understand that biosimilars will give the same clinical results as their reference products and are approved to the same quality, safety and efficacy standards as their reference products by the same regulatory authorities.

These factors do not differ too much from the factors that influence both physicians' and patients' acceptance of any prescribed product. Safety and efficacy are, of course, critical, but it does not end there. Physician prescribing habits, patient affordability, and, generally speaking, the level of knowledge all have an impact. The better we can educate, the more apt both patients and physicians will be to make informed decisions. Otherwise, other factors like lack of confidence in regulatory pathways and naming conventions will have a much greater impact.
10. How do healthcare systems balance cost savings with maintaining therapeutic options for patients through biosimilar adoption?

There are many factors that come into play here, which makes striking this balance difficult. Healthcare systems must strike a delicate balance by leveraging evidencebased practices, optimizing resources, and embracing technology to achieve cost savings without compromising patient care. The ability to achieve this balance is widely variable
11. Are there any specific therapeutic areas where biosimilars are expected to have a significant impact in the near future?
Biosimilar naming conventions impact adoption, price, market share, and competitive dynamics significantly.

While biosimilars have been widely utilised in therapeutic areas of immunology and oncology, the use of biosimilars has expanded to various therapeutic areas including ophthalmology, endocrinology, and haematology. Biosimilars are expected to have a significant impact on therapeutic areas where there was no biosimilar competition previously especially for rare diseases. Essentially a biosimilar can be made to any previously approved biologic, but the market conditions do vary.
Real-world evidence and post-market surveillance are crucial for continuous safety and effectiveness of biopharmaceuticals and biosimilars.
Across the industry, there are ongoing developments for the immunology pipeline including ustekinumab, golimumab, certolizumab pegol, and tocilizumab (just to name a few) as these medicines are expected to lose exclusivity within the next few years. There are also a number of biologics such as aflibercept, denosumab, and eculizumab that are expecting competition from multiple biosimilar companies. Commercial decisions govern once the science and regulatory issues are resolved.

Biosimilars are on track to continue their double-digit growth globally, with the market projected to reach over $30 billion by 2025 and $60 billion by the end of the decade. In order to achieve that rate of growth, they will no doubt impact a wide range of therapeutic areas including but not limited to Oncology, Diabetes, and Arthritis.
12. As newcomers to Pharma Focus Europe magazine, could you share how your contributions have enriched our understanding of biopharmaceuticals and biosimilars, and how you envision your insights benefiting our readership and the industry as a whole?

The long-term viability and sustainability of biosimilars is not guaranteed. There is a need for biosimilar awareness translated across therapeutic areas, as well as products, to increase biosimilar development and utilization more expeditiously. The goal is now and always will be to lower healthcare costs with no compromise in the quality, safety and efficacy of the biologics available to patients. Education by regulators especially, but also individual companies will continue to be important.

The majority of the population has an “outsidein” view of this world. Having been in the industry for the last 20-plus years, I am fortunate enough to have a “peek behind the curtain,” which affords me the ability to provide a unique perspective.
Thank you to our panelists for their insights on Biopharmaceuticals and Biosimilars: Market Trends and Future Prospects. We hope these discussions have provided valuable insights into the evolving Pharmaceuitical landscape.
Dates: November 12-13, 2024
Location: Pennsylvania Convention Center, Philadelphia, USA
Overview: Welcome to the Advanced Therapies Congress USA 2024, the premier gathering advancing cell and gene therapies! Join us at the Pennsylvania Convention Center in Philadelphia on November 12-13, 2024, for an unparalleled experience in the world of advanced therapies.
What to Expect: The Advanced Therapies Congress is a convergence of leaders and experts from the entire cell and gene therapy development value chain. With 8 tracks of content spread over 2 dynamic days, this event promises deep insights, networking opportunities, and access to cutting-edge solutions.
KEY FEATURES:
Exhibition: Explore offerings from 50 top solution providers covering all stages of cell and gene therapy development.
Networking: Engage with thousands of experts in 12+ hours of tailored 1-2-1 networking sessions.
Comprehensive Coverage: Delve into the entire pipeline of Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMPs) with insights from pharma, biotech, startups, researchers, clinicians, academics, HTAs, payers, and regulators.
Our Story: With a legacy of hosting Europe's largest commercially focused ATMP event for 18 years, we are excited to bring our expertise to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania's thriving cell and gene hub. Our focus is on accelerating the devel-
opment of next-generation therapies to benefit patients worldwide.
Targeted Audience: Connect with decision-makers from leading biotech and pharma companies, ensuring a valuable mix of buyers and sellers.
Start-up Village: Discover early-stage companies in our start-up village, fostering collaboration and innovation across the developmental pipeline.
Networking Excellence: Our Terrapinn Events App enhances networking opportunities, creating a dynamic environment for sponsors, speakers, and attendees.
Agenda Highlights: Explore 8 tracks of content covering manufacturing, supply chain & logistics, pricing & market access, and developments in key therapeutic areas such as cell therapy, gene therapy, gene modified cell therapy, gene editing, stem cells, regenerative medicine, and more.
Mission: Our mission is to unite global leaders in advanced therapies, foster collaboration, accelerate development, and ultimately change patient lives through next-generation medicines.
Who Should Attend: This event is tailored for leaders of ATMP developers and their senior executives driving industry advancements. Join 1,000 global executives, be inspired by 200 speakers, and engage with 50 start-ups for an unforgettable experience over 2 transformative days.
Mark your calendar for the Advanced Therapies Congress USA 2024 and be part of the innovation shaping the future of healthcare!







Date: September 16-17, 2024
Location: San Diego, CA
Overview: Join us at the 14th annual American Drug Delivery & Formulation (DDF) Summit, where the brightest minds in pharmaceuticals, biologics, and device development converge to tackle the industry's most pressing challenges. This premier event promises two days filled with innovative solutions, cutting-edge research, and unparalleled networking opportunities.
1. High-Quality Content:
The summit has built a reputation for delivering top-tier content through a packed agenda of carefully curated talks. With four parallel streams focusing on small molecules, biologics, tech & innovation, and devices & combination products, participants can tailor their experience to address specific challenges and interests.
• Small Molecules
• Biologics
• Tech & Innovation
• Devices & Combination Products
The summit features keynotes, case studies, and panel discussions by senior industry professionals from leading companies such as Sever, Hovione, GSK, Merck, and Nanoform. These sessions provide invaluable insights, knowledge, and expertise across multiple domains, fostering crossdisciplinary learning and skill development.
2. Invaluable Networking:
The DDF community is known for its inclusive and welcoming environment, offering a valuable platform for leading scientists in various fields to connect. Through numerous networking breaks, one-on-one meetings, receptions, and roundtable discussions, attendees have
ample opportunities to forge and enhance connections within the industry.
WHAT
Expand Your Network: Meet face-to-face with senior industry leaders and expand your network within the pharmaceutical and biotech sectors.
Gain Insights: Hear from experts about the latest research and solutions to the challenges you face daily.
Enhance Knowledge: Deepen your expertise while sharing your own ideas and research with like-minded individuals.
Business Growth: Engage with leading industry solutions providers who can help propel your business forward.
Featured Case Studies:
• Enabling Bioperformance Prediction Through Data Analytics
• Engineering Prodrug Therapies for Infectious Disease and Cancer Therapy
• Predictive High-Throughput Screening of Oligonucleotide Lipid Nanoparticles for Gene Silencing
• Targeted Delivery of Pharmacological Agents in the Vascular System
• The Evolving Paradigm of Post-Market Safety Reporting for Combination Products
• The Port Delivery System with Ranibizumab: A New Paradigm for Long-Acting Retinal Drug Delivery
• Current Challenges and Opportunities in Developing Combination Products
• Development of High-Volume Wearable Drug Delivery Systems
Audience Breakdown:
The American DDF Summit attracts senior pharmaceutical development and formulation scientists from both industry and academia. With many highlevel networking opportunities throughout the twoday agenda, this summit is the perfect opportunity to meet and engage with the industry's top professionals.
Don't miss this opportunity to stay ahead of the curve in drug delivery and formulation. Register now to secure your place at the forefront of pharmaceutical innovation!



Join us at BioTechX Europe, Europe’s largest pharmaceutical development and healthcare event, happening on 9-10 October 2024 at Messe Basel, Switzerland. This event is a convergence of cutting-edge technologies, visionary speakers, and industry pioneers shaping the future of biotechnology, precision medicine, and digital transformation in healthcare.
Diagnostics & Precision Medicine: Explore the latest advancements in diagnostics, precision therapies, and digital health solutions revolutionizing patient care.
Digital Transformation: Dive into digital initiatives, data legislations, and end-to-end supply chain innovations driving healthcare evolution.
AI in Drug Development: Uncover the power of AI in drug discovery, clinical trials, and data expansion strategies.
Quantum Pharma: Delve into quantum machine learning, drug discovery breakthroughs, and quantum research impacting pharmaceutical development.
Data Integration & Analytics: Learn about data privacy, AI/ML-driven clinical outcomes, industrializing AI, and FAIR data practices.
Bioinformatics & Genomics: Explore how bioinformatics, single-cell genomics, and population genomics are shaping precision medicine.
Lab Operations & Automation: Discover the latest advancements in lab quality assurance, automation, and digitalization for enhanced research outcomes.
Networking Opportunities: Connect with 3500 global executives, 400 speakers, and 50 startups in the biotech and pharmaceutical industries.
Engage in 1-2-1 networking sessions to build meaningful collaborations and explore new business opportunities.
Basel, known as the pharma hub of Europe, provides the perfect backdrop for BioTechX Europe. With a thriving ecosystem of research institutions, pharmaceutical giants, and innovative start-ups, Basel is at the forefront of healthcare innovation.
Don’t miss out on this unparalleled opportunity to be part of Europe’s premier biotechnology congress. Register now to unlock insights, forge partnerships, and shape the future of healthcare. BioTechX Europe awaits you at the forefront of innovation!

"41% of event professionals are participating on more events in 2024 than they originally planned." Don't be left behind... We are here to help!

9 - 1 0 O c t o b e r 2 0 2 4 M e s s e B a s e l , S w i t z e r l a n d
D a t a . A I . P r e c i s i o n . I n n o v a t i o n .
F o r P h a r m a , H e a l t h c a r e & P a r t n e r s


2 0 2 4 S p e a k e r s i n c l u d e : P


B O O K N O W !
U S E C O D E O C H R E 2 0 F O R 2 0 % O F F

18 – 20 June 2024|Boston, USA
https://biogatesc.com/events/va-cc-in-e/#aboutsection
About Event: The Vaccines Summit Boston is an esteemed annual event dedicated to bringing together leading experts, researchers, policymakers, industry professionals, and stakeholders from around the world to discuss and collaborate on important aspects of vaccines and immunization.
Listed Under: Research & Development
26 – 26 June 2024|Basel, Switzerland
https://digitalbiomarkers.panagorapharma.com/
About Event: Now in its seventh year hosted in partnership with Roche in Basel, the Digital Biomarkers in Clinical Trials Summit is the first and only global forum of its kind to focus on ways for pharma clinical trials to take advantage of new opportunities to collect better data and improve the patient experience; as well as how these new digital health tools (DHT) supplement existing biomarker strategies.
Listed Under: Clinical Trials
08 – 10 July 2024|Boston, MA, USA
https://cgtsummit.com/about
About Event: The inclusion of talks, poster presentation, workshops, discussions and networking events over the three days indicates a comprehensive program design to engage participants of various interactive formats. It allows the attendees to learn from experts, showcase their own research through posters, participate in workshops to gain practical insights, engage in discussions to share perspectives, and connect with professional researchers from diverse backgrounds.
Listed Under: Research & Development


29 – 31 July 2024|Boston, USA
https://mrnabased-therapeutics.com/about/aboutevent/
About Event: As the mRNA industry rapidly expands into rare and oncological disease indications, in addition to infectious diseases beyond COVID, the 4th mRNA-Based Therapeutics Summit returns with a refreshed, comprehensive program spanning every stage of drug development..
Listed Under: Research & Development
16 – 17 August 2024|Boston, USA
https://www.ipharmaexpo.com/
About Event: The expo will showcase the latest trends and technologies in pharmaceuticals, drugs, and formulations. The expo is expected to witness approx. 150 exhibitors and 15002000 visitors footfall from pharma industry & management. Direct access to highly targeted senior pharma executives, buyers, procurement managers, contract manufacturers, hospital administration, and many more Meetings with manager and business development managers who are looking for new supplies, building strategic partnerships, or entering into new ventures.
Listed Under: Manufacturing
19 – 20 September 2024|Munich, Germany
https://www.brainlinx.com/conference/GPSF-2024/ index.php
About Event: This Forum will assist with covering all the aspects of the Pharma Supply Chain & Logistics and its integration with digitization, covering Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning & Block Chain, as well as new ideas for next-level business growth and portability.
Listed Under: Strategy
09 – 10 October 2024|San Diego, USA
https://ddsswc.agilefalconsg.com/
About Event: The 16th Drug Discovery Strategic Summit (DDSS) provides a forum for innovative ideas to meet actionable implementation. DDSS guides Drug Discoveries with strategic agility, allowing you to manage evolving areas with foresight and innovation.
Listed Under: Strategy
12 – 13 November 2024|London, UK
https://aidrivendrugdevelopment.com/events/aidriven-drug-discovery-summit-usa
About Event: In recent times, a number of prominent collaborations between pharmaceutical companies and AI firms have emerged, signalling the growing importance of validating and enhancing these methodologies. As technology continues to advance, the AI Driven Drug Discovery Summit serves as a platform to showcase innovative approaches for effectively incorporating cuttingedge AI technologies into the ever-expanding realm of datasets.
Listed Under: Information Technology
18 – 19 November 2024|Zurich, Switzerland
https://automa.plus/
About Event: AUTOMA+ is a closed-door networking congress which gathers leaders and pioneers of the pharmaceutical sector. As we are all living in the digital world now, pharma professionals and corporations are focused on achieving digital maturity, exchanging experiences, sharing insights and building their own way through the digital space.
Listed Under: Information Technology
Caris Life Sciences® and COTA, Inc. have joined forces to enhance their multi-modal data services, aiming to advance biopharmaceutical drug development and improve patient care. Caris, a leading AI TechBio company in precision medicine, and COTA, an oncology real-world data (RWD) and analytics company trusted by top pharmaceutical firms, announced this collaboration to revolutionize healthcare through molecular science and AI.

The collaboration between Caris Life Sciences® and COTA, Inc. merges Caris' extensive genomic, transcriptomic, proteomic, and imaging data with COTA's meticulously curated clinical data, capturing cancer patients' treatment paths and results. This partnership creates a robust, real-world, multimodal data platform on a large scale, poised to drive advancements in cancer therapeutics.
Caris, known for its leadership in precision medicine and molecular profiling, has developed a vast molecular database derived from almost 10 million tests. This database, comprising over 60 petabytes of oncology-specific genomic, transcriptomic, proteomic, and imaging data, marks a significant milestone in the industry. Caris also pioneered the inclusion of Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) DNA coverage and Whole Transcriptome Sequencing (WTS) RNA coverage for every viable sample in the molecular diagnostic sector.
COTA's extensive data encompasses over two million cancer patients treated across 200 care sites, spanning academic medical centers to rural and urban community practices. This comprehensive dataset offers a robust representation of cancer care nationwide. By synthesizing this information, COTA provides life sciences companies with valuable insights to develop improved, personalized cancer treatments.


Scenic Biotech, a leader in modifier therapies for severe genetic disorders, revealed a new research collaboration with Bristol Myers Squibb. This partnership aims to speed up the development of Bristol Myers Squibb's drug targets by pinpointing target biology for indication selection and expansion.
The agreement includes an upfront payment for Scenic Biotech, with potential additional payments based on meeting various research, development, and commercial milestones. Financial specifics have not been disclosed.
Scenic Biotech's partnership with Bristol Myers Squibb is its second major collaboration after the genetic modifier agreement with Genentech in 2020. These collaborations harness the power of the Cell-Seq platform to uncover genetic insights crucial for discovering new therapies. While Scenic mainly uses Cell-Seq for modifier gene identification, the technology also delves into uncharted biological pathways and disease biology exploration.
Scenic Biotech is pioneering modifier therapy, a groundbreaking method for addressing genetic disorders. Unlike traditional approaches targeting the primary mutation, modifier therapy aims to restore health by targeting alternative genomic functions that counteract the disease's effects, resulting in therapeutic benefits. Utilizing their proprietary Cell-Seq platform, Scenic has developed a strong pipeline of first-in-class small molecule programs, either owned entirely or through partnerships with major pharmaceutical companies. By uncovering novel genomic pathways, Scenic is poised to create a range of modifier therapies to benefit patients.
Delphia Therapeutics, Inc., debuts with a focus on pioneering activation lethality in cancer biology. This innovative strategy targets cancer's vulnerability to oncogene overactivation. Through this approach, Delphia is developing unique targeted cancer medications with potential for substantial anti-tumor effects and long-lasting patient benefits across various cancer types. The company secured a US$67 million Series A financing round led by prominent early life sciences investors like GV (Google Ventures), Nextech Invest, Polaris Innovation Fund, and Alexandria Venture Investments.
Oncogenes drive cancer by enhancing key pathways that promote cell and tumor growth. Targeted therapies inhibit these oncogenes, initially causing a response. However, tumors are diverse, and under inhibitor therapy, drug resistance quickly arises. This resistance often amplifies pathway activity, fueling tumor growth and disease progression.
Delphia's founders have conducted groundbreaking research showing that numerous oncogenic pathways are exceptionally sensitive to overactivation. This overactivation induces stress on cellular pathways, proving lethal to cancers with mutations that drive them towards maximum pathway activity (termed 'activation lethality').
Cellular pathways have intricate regulation mechanisms to maintain optimal activity. Oncogenic mutations disrupt this regulation, leading to heightened pathway activity. However, in cells with these mutations, some regulators remain vulnerable, acting as a final defense against overactivation. These critical, vulnerable regulatory nodes present novel therapeutic targets for inducing overactivation and selectively eliminating tumor cells.
Delphia's advanced platform combines tumor genetics, innovative functional genomic methods, and investigations into inhibitor drug resistance to pinpoint targets crucial for activation lethality. Using this platform, Delphia is progressing a lineup of pioneering cancer medications designed to effectively regulate oncogenic pathways.

Eisbach Bio GmbH, a leader in cancer therapeutics using synthetic lethality, has received FDA clearance for its IND application for EIS-12656. This small molecule targets the chromatin helicase ALC1 (CHD1L) through allosteric mechanisms, preventing cancerassociated genome reorganization caused by DNA damage. Consequently, ALC1 chromatin trapping leads to the selective elimination of cancer cells.
EIS-12656 targets tumors with deficient DNA repair pathways, showing significant inhibition of tumor growth in preclinical models. It also displayed efficacy when combined with standard-of-care treatments. Its allosteric mechanism offers selectivity compared to similar synthetic lethal targets, contributing to its outstanding safety profile in preclinical studies.
An open-label study will assess the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of EIS-12656 in patients with advanced solid tumors with defined genetic profiles. The study will involve escalating doses of EIS-12656 as monotherapy, followed by dose expansion segments and assessment in patients who have progressed while on PARP inhibitor therapy.



Arecor Therapeutics plc and Medtronic plc, a healthcare technology leader, have joined forces in a research collaboration to create a new, highconcentration, thermostable insulin. This insulin will be utilized by Medtronic's Diabetes business in an advanced implantable pump system.
The innovative insulin from this collaboration could revolutionize treatment for a niche group of diabetes patients with limited options. It has the potential to reduce pump maintenance and offer doctors more versatility, ultimately leading to improved patient care and cost savings in healthcare.
Arecor Therapeutics plc is a global biopharmaceutical company that enhances existing therapies to improve patient care. Their proprietary technology platform, Arestat™, powers the development of a range of innovative products in diabetes and other areas. They collaborate with top pharmaceutical and biotech firms to deliver these therapies and maintain an extensive patent portfolio supporting the Arestat™ platform.
Arecor's diabetes-focused efforts are broadened by this collaboration, complementing their two leading clinical programs: AT278 and AT247, both ultra-rapid acting insulin candidates. These candidates aim to simplify blood glucose control for diabetes patients and could support the development of advanced miniaturized insulin delivery and closedloop artificial pancreas systems. Additionally, their recent partnership with TRx Biosciences focuses on developing an oral GLP-1 receptor agonist, offering a more convenient option for diabetes and obesity patients. Tetris Pharma, part of Arecor, commercializes Ogluo®, a glucagon prefilled autoinjector pen for severe hypoglycaemia in diabetes patients.
Ajax Therapeutics, Inc., a biopharmaceutical firm specializing in next-generation JAK inhibitors for myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), has announced FDA clearance for its Investigational New Drug (IND) application. This approval allows Ajax to commence a Phase 1 clinical trial for AJ1-11095, a pioneering Type II JAK2 inhibitor, in myelofibrosis patients.

AJ1-11095, developed by Ajax in collaboration with Schrödinger, represents a next-generation JAK2 inhibitor. Through extensive structure-based drug design and computational methods, it selectively targets the Type II conformation of the JAK2 kinase. This approach offers enhanced efficacy and disease modification compared to currently approved JAK2 inhibitors, which primarily target the Type I conformation. Additionally, preclinical studies demonstrate AJ1-11095's ability to reverse marrow fibrosis, reduce mutant allele
Myelofibrosis (MF) is a rare blood cancer affecting around 20,000 individuals in the U.S. This condition is characterized by spleen enlargement, bone marrow scarring (fibrosis), progressive anemia, and debilitating symptoms like fatigue, night sweats, itching, and abdominal discomfort, significantly impacting patients' quality of life. While Type I JAK2 inhibitors are the main treatment, they primarily address symptoms like spleen size reduction without addressing the disease's root cause. Many patients eventually discontinue Type I JAK2 inhibitor therapy due to reasons like lack of benefit, adverse effects, or disease progression, highlighting significant unmet needs in MF treatment.

FogPharma®, a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company pioneering a new class of therapies with its Helicon™ peptide platform, and ARTBIO, Inc., a clinical-stage radiopharmaceutical company specializing in 212Pb alpha radioligand therapies (ARTs), have announced a collaboration. Together, they will co-develop Helicon-enabled ARTs (HEARTs) to improve outcomes for patients with various types of cancer.
ARTBIO and FogPharma are partnering to codevelop novel Helicon-enabled ARTs (HEARTs) targeting multiple cancer types. This collaboration combines FogPharma's leading Helicon platform, which features tunable stabilized α-helical peptides, with ARTBIO's AlphaDirect™ platform, which utilizes the superior isotope 212Pb. ARTs with 212Pb are clinically advantageous due to their short halflife, delivering maximum energy to tumors while maintaining high stability and allowing imaging with SPECT/CT.
The synergy between these two advanced platforms holds great promise for creating nextgeneration ARTs designed for precise tumor targeting.
Both partners will share responsibilities equally across all phases of the collaboration, including research, development, and commercialization. Specific financial details have not been disclosed.
Verismo Therapeutics, a clinical-stage CAR T company specializing in the innovative KIR-CAR platform technology, has received FDA notification to proceed with the Phase 1 clinical trial of SynKIR™-310 for NHL investigation.
The Phase 1 trial, named CELESTIAL-301, aims to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and initial efficacy of SynKIR™-310 in patients with relapsed/refractory (r/r) B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas (B-cell NHL), including Diffuse Large B Cell lymphoma (DLBCL), Follicular Lymphoma (FL), Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL), and Marginal Zone Lymphoma (MZL). The study will include patients who have relapsed or become refractory to previous CAR T therapy, as well as those who have not received CAR T therapy before.
The CELESTIAL-301 trial aims to address significant gaps in medical care. While commercially approved CAR T cell therapies have initially shown high response rates in blood cancers, around 40-50% of patients experience relapse over time due to decreased T cell function and persistence. Patients with relapsed/ refractory (r/r) Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) face limited treatment options after failing commercial CAR T therapies. Current clinical studies have not adequately met the medical needs of these patients.
SynKIR™-310 utilizes Verismo's distinct KIR-CAR platform alongside their proprietary CD19 binder, DS191. This binder, tailored for the KIR-CAR platform, enables treatment of B-cell disorders and malignancies. SynKIR™-310, guided by DS191, targets a CD19 epitope similar to approved CAR T therapies, with the added benefit of potentially prolonging anti-tumor T cell function and persistence. Dr. Donald Siegel and Dr. Michael Milone, Verismo's co-founders, are co-inventors of DS191.
Verismo intends to commence the CELESTIAL-301 clinical trial in the latter half of 2024, marking their second study exploring the KIR-CAR platform technology. This innovative approach leverages natural NK cell receptors, aiming to redefine T cell therapies. Verismo's flagship candidate, SynKIR™-110, is presently under investigation in the Phase 1 clinical trial STAR-101 at two sites, with plans for expansion to additional sites in 2024.
