earth
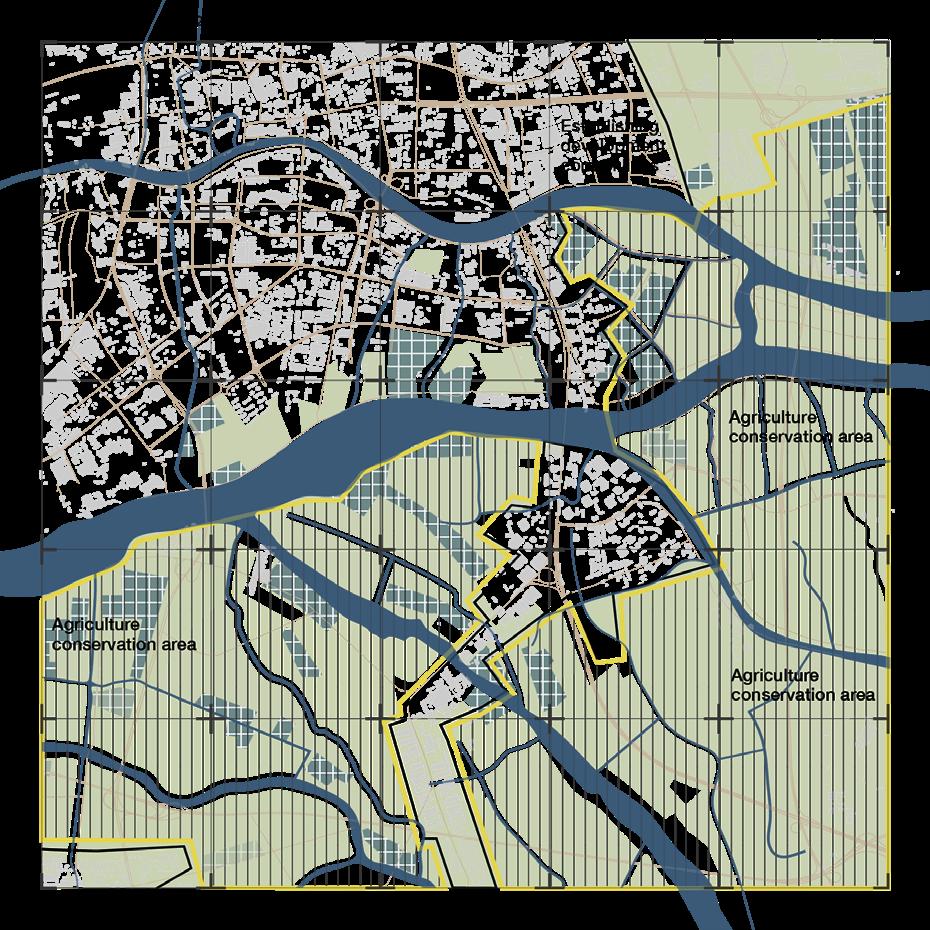
Agricultural land and urban villages How did the urbanisation impact existing tissue of the region?
Urban Centre
Second tier towns
Villages
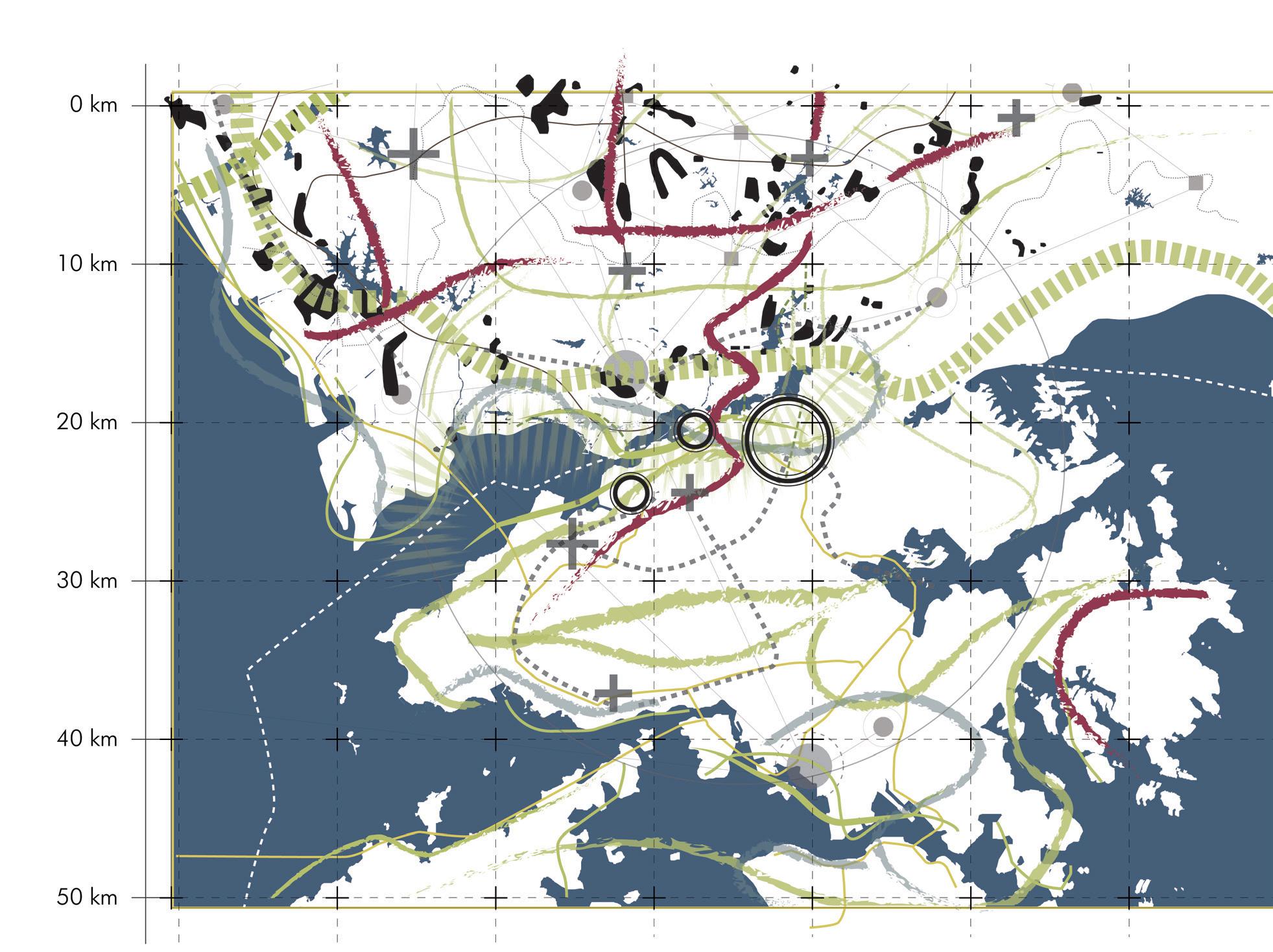
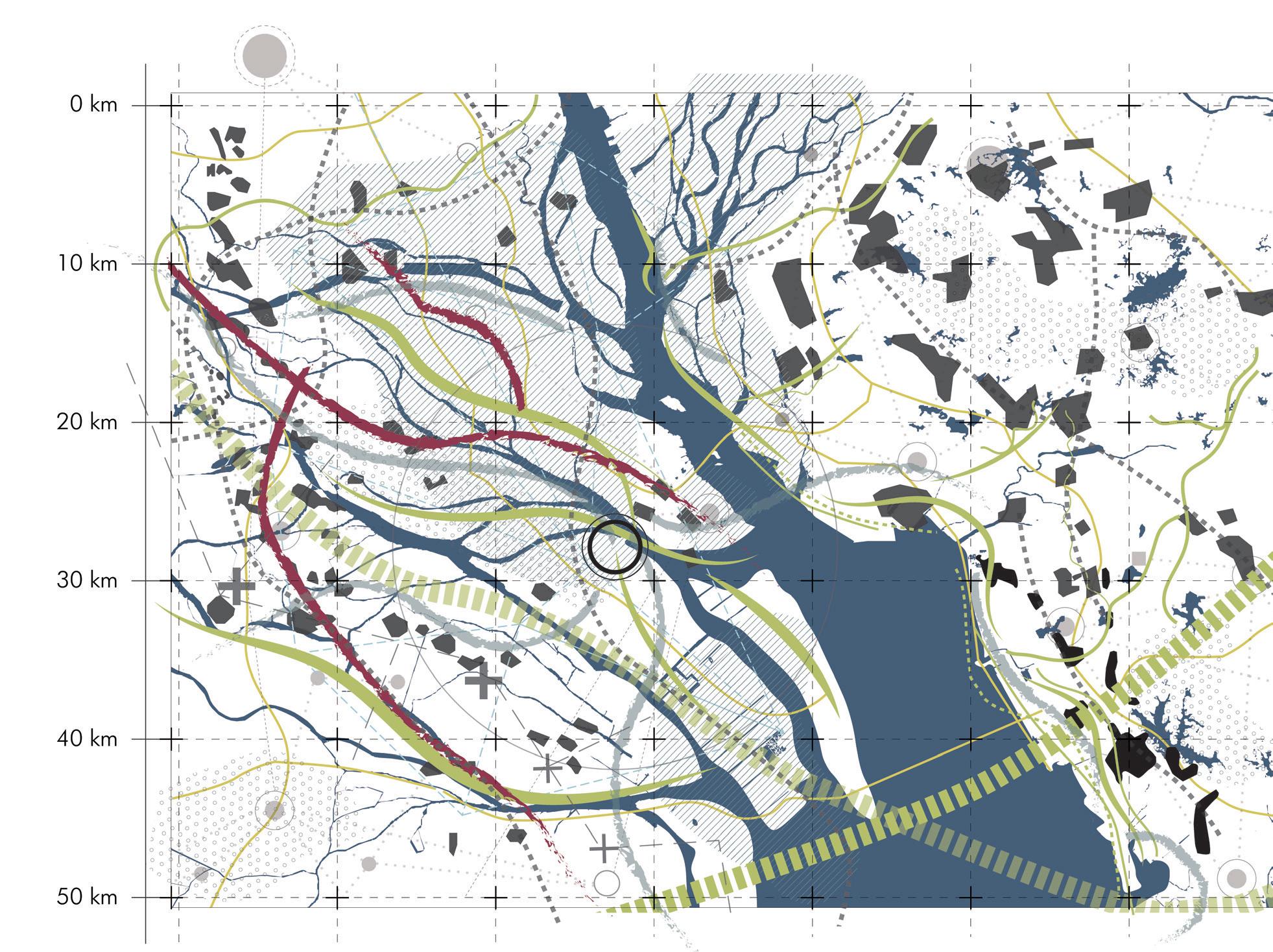
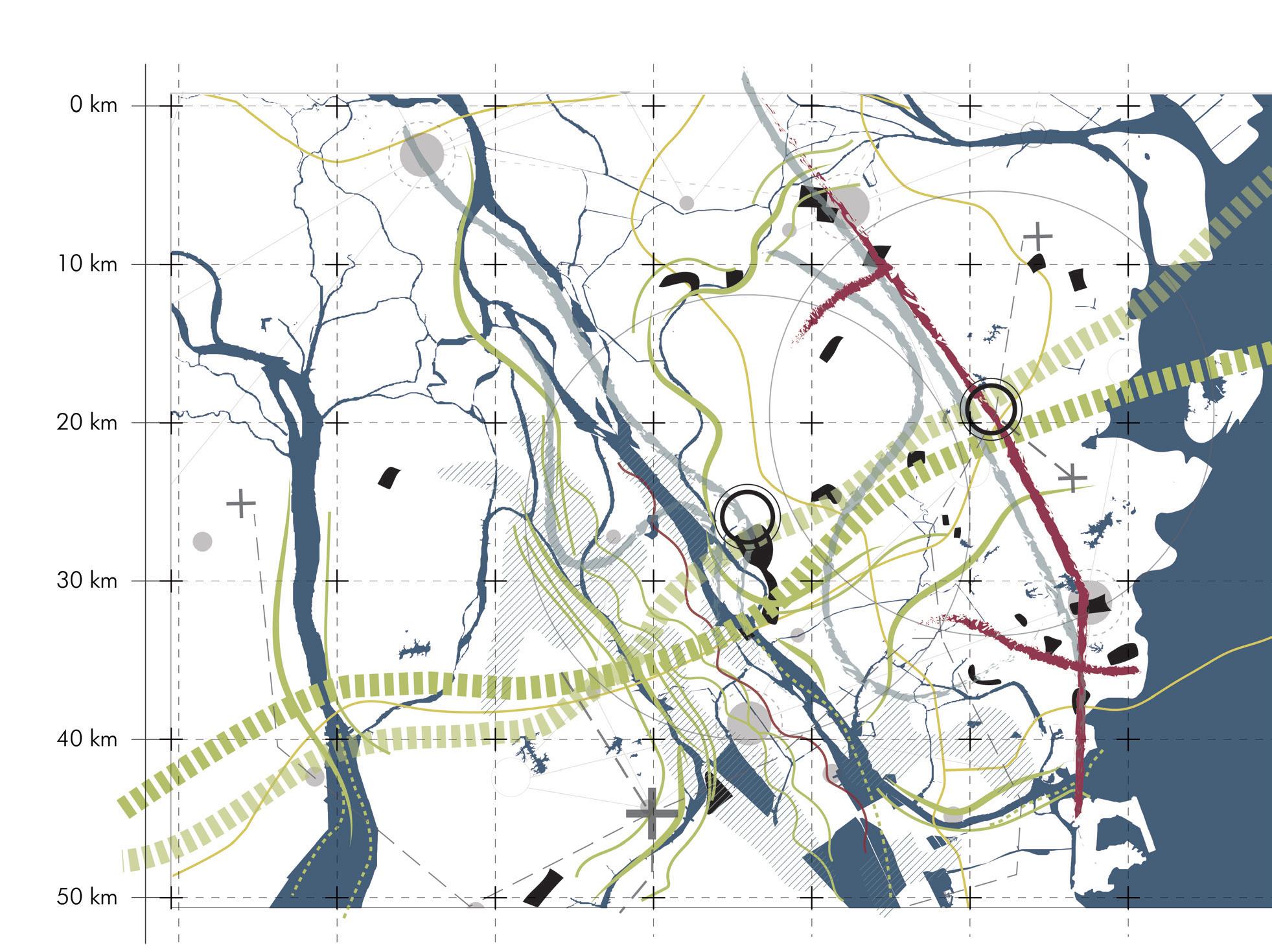
Growth pattern Urban Urban Centre Urban Centre Centre Second Second Second tier towns tier towns tier townsVillages Villages Villages Growth Growth pattern Growth pattern pattern
sion of the city encroaching andofvillages New urban centres Expansion developing of the city encroaching Existing towns structure networks New urban centers developing Existing Existing Existing structure structure structure of networks of networks of networks Expansion Expansion Expansion of the of city the ofcity encroaching the encroaching city encroaching towns towns and towns and villages and villages villages NewNew urban New urban centres urban centres developing centres developing developing towns and villages
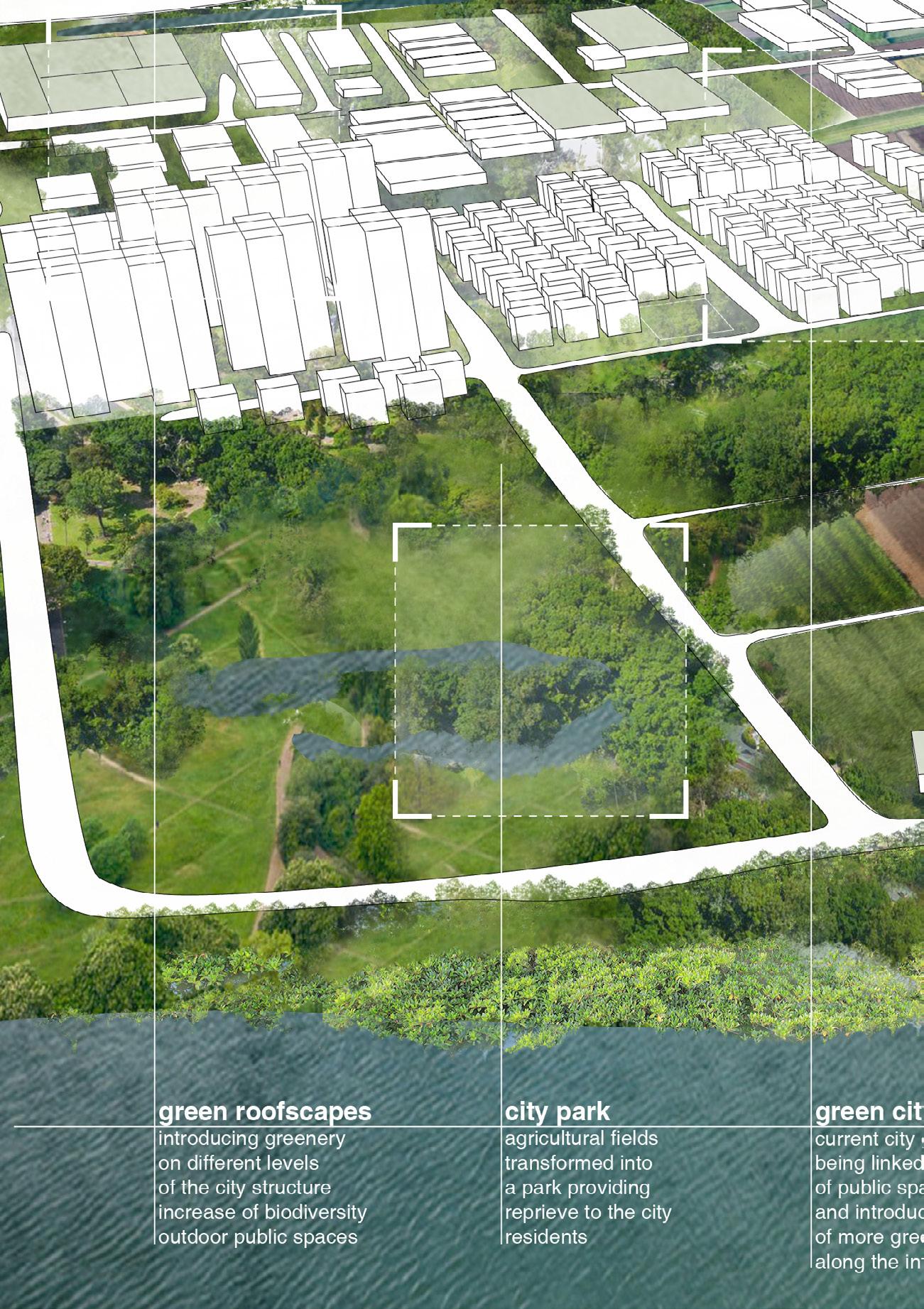
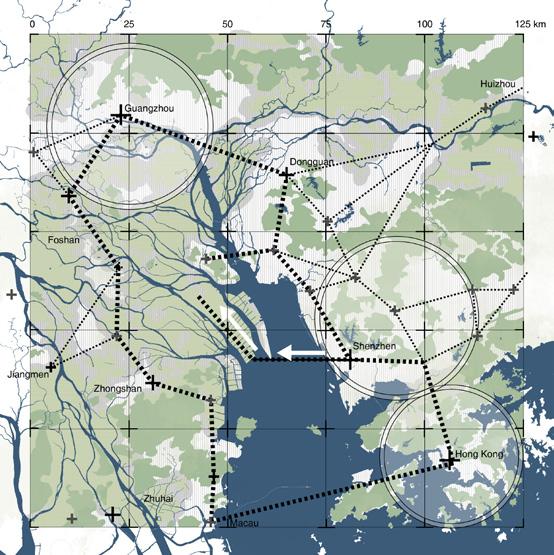
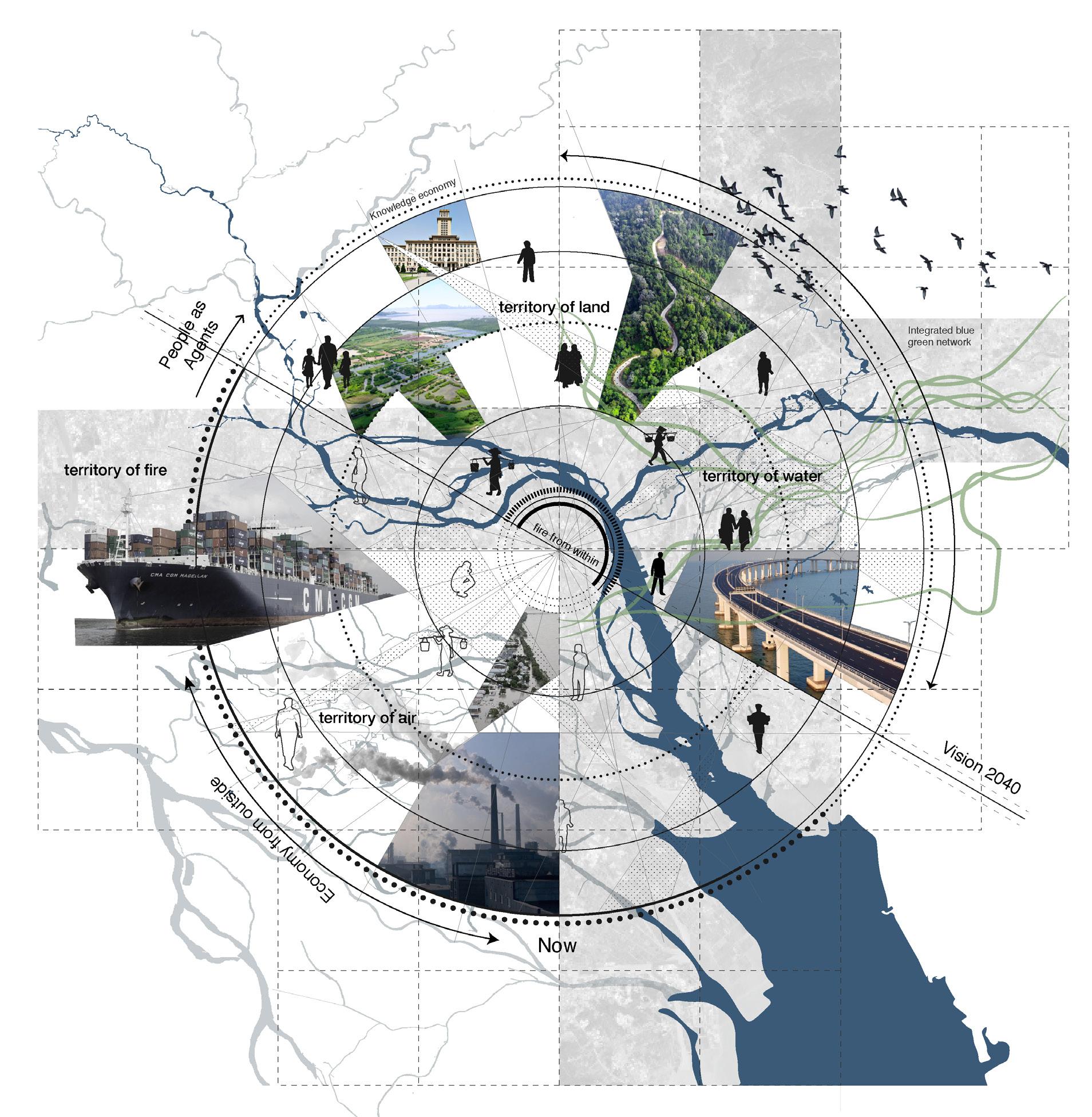
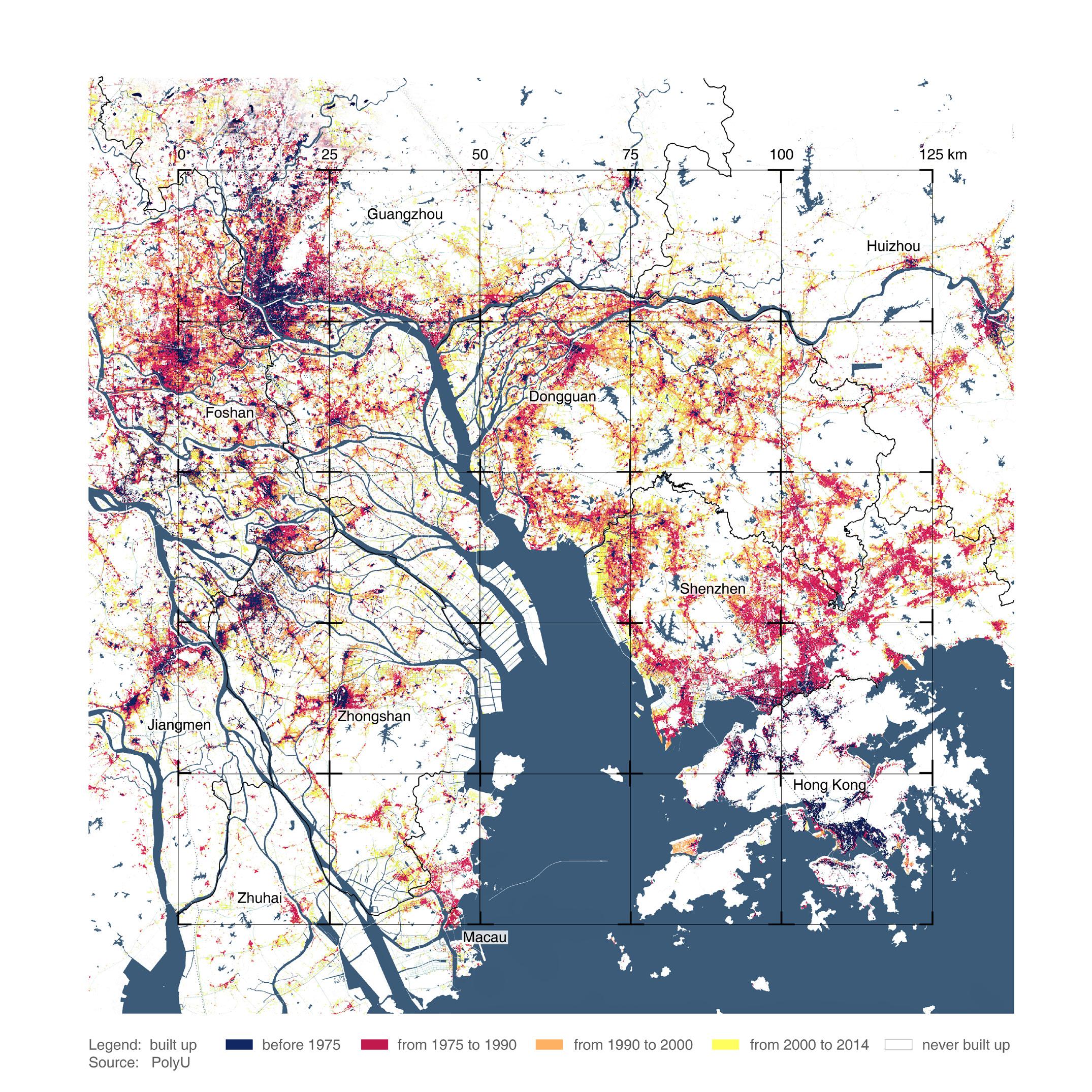
Rapidly rising economy propelled internal rural to urban migration which transformed the cities of GBA into highly populated and urbanised centres. As a result of the urbanisation, there were swift transformations to agriculture and aquaculture lands resulting in the loss of biodiversity and farmlands. With limited land availability in urban centres, large areas of agricultural land are transformed for the sake of development. The capacity of ecological systems to produce food, catchment areas for fishing
40
and the biodiversity of the grasslands and grazing areas are on the decline. Another important consequence of this growth is the creation of urban villages. The development of these cities as a part of China’s urbanisation efforts often followed the incorporation model where the urban areas engulf these villages making them ingrained into their urban fabric. They appear on the outskirts and the downtown segments of major cities of GBA including Shenzhen and Guangzhou. These villages
are usually seen as squalor, cramped spaces and unwanted side effects of urbanisation. However, they carry a cultural value and are surrounded by skyscrapers, transportation facilities and other urban systems. They are under threat to make way for further densification within the city. These patterns have created several vulnerable communities like the farmers who suffer the loss of their land, the inhabitants of the urban villages whose habitats suffer from the constant threat of gentrification.