INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA RIVISTA DELL’ icf ANNOXIV NO3 2023SUPPLEMENT www.interprogettied.com INTERNATIONAL ISSUE INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA RIVISTA DELL’ icf ANNOXIV NO3 2023SUPPLEMENT www.interprogettied.com INTERNATIONAL ISSUE POSTE ITALIANE SPA - SPED. IN ABB. POSTALE 70% - LO/MI - COSTO COPIA €10,00 normativi integrata normativi integrata INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA RIVISTA DELL’ icf ANNOXIV NO3 2023SUPPLEMENT www.interprogettied.com INTERNATIONAL ISSUE POSTE ITALIANE SPA - SPED. IN ABB. POSTALE 70% - LO/MI - COSTO COPIA €10,00

V. Cavour, 31 - 26858 Sordio (LO) - Italy - Tel. +39 Stainless steel or titanium reversible self-priming motor-driven pumps OUR PUMP WILL BE THE HEART OF YOUR PRODUCTION V. Cavour, 31 - 26858 Sordio (LO) - Italy - Tel. +39 Stainless steel or titanium reversible self-priming motor-driven pumps OUR PUMP WILL BE THE HEART OF YOUR PRODUCTION www.interprogettied.com V. Cavour, 31 - 26858 Sordio (LO) - Italy - Tel. +39 Stainless steel or titanium reversible self-priming motor-driven pumps OUR PUMP WILL BE THE HEART OF YOUR PRODUCTION 31 - 26858 Sordio (LO) Italy - Tel. +39 Stainless steel or titanium reversible self-priming motor-driven pumps WILL THE HEART OF YOUR PRODUCTION www.interprogettied.com
HRS Series


RAPID SANITARY Series




RAPID Series
RAPID VER Series
AC TITANIUM Series

info@wolhfarth.it - www.wolhfarth.it +39 02 9810153 - Fax +39 02 98260169



Austria | Belgium | Germany | Italy | Switzerland | Poland | Romania Conceptual Design Basic Engineering Detail Engineering Project Management Construction Management Qualifica secondo cGMP Procurement La via per il successo di ogni progetto. ENGINEERING FACILITIES OF THE FUTURE www.vtu.com VTU Engineering Italia Srl office.italia@vtu.com Via G. di Vittorio n. 16 39100 Bolzano (BZ) Torre Pontina, Via Ufente 20/22 04100 Latina (LT) Viale T. Edison 110 20099 Sesto San Giovanni (MI) Via della Vittoria 90/C 30035 Mirano (VE)









4 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA Summary Summary INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA icf ANNO NO SUPPLEMENT www.interprogettied.com INTERNATIONAL ISSUE INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA RIVISTA DELL’ icf 6 Editorial Two reforms to redesign the pharma market 8 Cover story Risk Management: a new Risk-Based decision-making approach 12 Trends Pharmaceutical packaging: safety is what counts 16 Trends 22 Exhibitions A hotspot for experts in mechanical processing and bulk solids 24 Exhibitions Shaping the future of the process industries 28 Environment 30 Machines Robotic solution to process small batches of single-dose PFSs for veterinary vaccines
“The new revision of the ICH (Q9) identifies Risk-Based decision-making process as the best method for ensuring the quality in medicinal, biological and biotechnological products throughout their entire life cycle.” Andrea Villa and Nicolas Livraghi, PVS Group, page 8







RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA icf 5 Summary
2023 - SUPPLEMENT 32 Plant engineering Engineering the future of life-saving drugs 36 Plant engineering Sustainability becomes a driver for chemical plant construction 42 Hygienic design 44 Energy transition The shift from CO2 50 Maintenance How to enhance compliance while creating a safer working environment 52 Traceability An intelligent and integrated ecosystem with technological innovations
Components 56 Technologies The biggest challenges in coating and their technological solutions
Insights The life science companies discovering new technologies
Advertising list Colophon NO.3 2023 - Supplement
NO.3
54
60
64
Two reforms to redesign the pharma market

Two fundamental reforms by the EU Commission, if approved, could redesign the scenario for the development, production and sale of drugs in Europe. The former concerns the review of pharmaceutical legislation and a European Council’s recommendation about antimicrobial resistance. The latter regards intellectual property, in particular the unity of the SPC (supplementary protection certificates) and the activation of compulsory licenses in the event of public health emergencies. The two reforms have various interconnections and must in any case be submitted to the scrutiny of the Parliament (which will be renewed in 2024) and the European Council. But the debate is already underway, especially among insiders, who have already expressed comments and a few criticisms through the main industrial associations, although with different positions on individual issues. One of the main objectives of the draft regulation reform is to boost a truly unique pharmaceutical market, for instance by rewarding companies that launch a new product simultaneously in all member states, thus overcoming the current fragmentation, largely due to the choice of manufacturers to focus on the most profitable markets or where there are the best conditions in terms of prices and reimbursements. The new measures, which also try to provide answers to
the needs arisen in times of pandemic, aim at speeding up the arrival of new drugs on the market, reducing the EMA evaluation times from the current aver age of 400 days to 180 and 150 in case of health emergencies. Monitoring of possible shortages of critical med icines and vulnerabilities in sup ply chains is also being pushed. The experience of the pandemic has also affected the propos als on intellectual property, with the introduction of compulsory licenses in the event of public health emergencies, which would come into play as a last resort and in a centralized way in Europe, again in the per spective of less regulatory fragmentation. Some industrial associations, while highlight ing positive aspects, underline the risks for the future of continental research and devel opment due to the reduction of the regulatory protection period, as well as the difficulty of simultaneously launching products in all EU countries. Compulsory licenses are also under scrutiny, which according to Efpia would not al low companies to choose the partners deemed most reliable. The path of reforms has therefore begun, but it promises to be certainly not with out pitfalls.

6 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
Editorial
A self-modelling gasket tape made of soft and flexible non-sintered expanded 100% PTFE. Texlon® resists chemical products with the exception of alkaline substances and is usually supplied with bi-adhesive film which facilitates application.



covers,

covers and joint covers, which are tailored with types of materials and fabrics that are suitable not to be contaminated and degraded by fluids passing inside the plant.

Clamp Texpack® gaskets are used as sealing elements between two stainless steel clamp fittings (ferules) sealed with a special collar, where no bolts are required.

Texpack® srl - unipersonale - Via Galileo Galilei, 24 - 25030 Adro (BS) Italia Tel. +39 030 7480168 - Fax +39 030 7480201 - info@texpack.it - www.texpack.it Gaskets for chemical and pharmaceutical industry
5500 Texlon® self-adhesive soft tapes autoadesive
3350-3360 Valve and flange covers Texpack® textile products include flange
valve
5700C PTFE envelope gaskets for fittings clamp
Ask for GASKETS and GLAND PACKINGS CATALOGS to our customer service
Risk Management: a new Risk-Based decision-making approach
by Andrea Villa* and Nicolas Livraghi**
On January 18th of this year (2023 ed.), the latest version of ICH Q9 was approved by the members of the ICH Assembly.
What changes from the previous version approved on November 9th, 2005?
In the new and most recent edition, a new risk-based decision-making approach is proposed, or in technical terms: Risk-Based. The Risk is defined as the combination of the probability of occurrence of damage, the detectability of damage, and the severity directly related to the damage itself.
The new revision of the ICH (Q9) identifies Risk-Based decision-making process as the best method for ensuring the quality in medicinal, biological and biotechnological products throughout their entire life cycle.
 *Validation Specialist, PVS Srl
**Senior Validation Manager, PVS Srl
*Validation Specialist, PVS Srl
**Senior Validation Manager, PVS Srl
It is therefore very important to have full knowledge of the entire process leading to the manufacture of a medicinal product, in a range from the construction of the production
8 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
The new revision of ICH Q9, which proposes a new approach for risk management capable of ensure the necessary quality levels in drug manufacturing, has been approved.
Cover story
facility to the packaging of the product. Within this wide range, it is necessary to identify what risks are associated with the production of a medicinal product both in the production of API and in the production of what will be considered the finished product.

The risk management process is mainly composed of three main macro areas:
- The first, identified as “Risk Assessment”, which includes hazard identification, risk analysis and then its evaluation;
- The second, identified as “Ri -
sk Control,” which includes the reduction and assessment of risk acceptability. Indeed, it is hardly possible to cancel a risk, but it is possible to reduce it to consider it acceptable. Through the proper execution of qualification and validation processes, the good organization of quality review, and the use of increasingly advanced control systems, it is possible to reduce the probability, severity, and detectability factors that determine residual risk;
- The third and last, identified as “Risk Review”, which includes the review of events, with the aim of being able to evaluate, with a broad and general view, whether the “Risk Control” phase has been performed efficiently.
Moreover, it remains imperative that risk management should be based on scientific principles with the goal of ensuring patient safety. So, how is it possible to carry out an accurate risk-based decision-making process?

First, it is necessary to understand the level of formality that the process requires.
Formality means the ability to document, in an exhaustive way, a certain decision-making process to support and give strength to a certain thesis. The level of formality is directly related to the degree of uncertainty in the process. The same degree of uncertainty relates to what is known in terms of danger and damage, thus their associated risk, to the degree of importance and complexity of the process under analysis.
In fact, the higher the levels of uncertainty, importance, and complexity of the process under consideration, the higher the level of formality of Risk Management must be, detailing as best as possible the approa-
NO.3 2023 - Supplement RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA icf 9
Cover story
Overview of a typical Quality Risk Management Process - “ICH Q9(R1)”
ch chosen in order to improve risk management and give depth to Risk-Based decision-making.

Secondly, it is necessary to choose the correct risk-based decision-making approach. Not all decision-making processes are characterized by high levels of structure, and not all require highly formal analysis. Indeed, if the process under consideration has a low level of uncertainty and complexity and therefore does not require a comprehensive Risk Assessment, it is possible to manage the risk through, for example, the application of comprehensive and well-structured Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), which obviously are in accordance with the relevant reference guidelines, or through Risk Assessments
that are not overly structured. However, if the process under consideration reaches high levels of complexity and uncertainty, it is necessary to identify a correct and unambiguous approach, with the goal of better shaping the decision-making. Third, but not of less importance, is the ability to minimize subjectivity in the decision-making process. This makes possible the actual assessment of hazards, the probability that an event will occur, and the severity of the damage caused by the event.
In any case, it is not possible to completely eliminate subjectivity within a decision-making process, but it can be minimized by a multidisciplinary team, basing its arguments on scientific principles and applying, if necessary, the tools that Annex I to ICH Q9 proposes.
The new ICH Q9 therefore identifies three new factors of equal importance to be addressed in Risk-Based decision-making processes to ensure the right level of quality in drug manufacturing.
Perhaps it is better to talk about three new tools: formality, proper Risk-Based decision-making approach and subjectivity management. This new ICH Q9 delivers to ensure patient safety. l

10 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
Minimizing subjectivity in decision making makes it possible to effectively assess hazards, the probability that an event will occur, and the severity of the damage caused.
Cover story
A new flavor experience
With more than 15,000 products and 45 locations in 25 countries, the OQEMA Group is one of the leading chemical distributors in Europe.
Thanks to the partnership between OQEMA Italy and Flavorchem Europe, a BRC-certified global supplier of flavors and ingredients , and the combination of research and development resources, OQEMA will expand its existing portfolio with a wide range of flavorings, extracts, ingredients and food colorings for the food market. Explore a new flavor dimension for your business.

WWW.OQEMA.IT
Pharmaceutical packaging: safety is what counts

The demand for pharmaceutical products is increasing worldwide, with more and more medications being launched onto the market in ever shorter periods of time. Last year alone, turnover in the German pharmaceutical market – the largest in Europe and the fourth largest worldwide – was around 53.6 billion euros. According to Statista, the volume has more than doubled in the last fifteen years and almost 100 billion counting units, i.e. tablets, sachets, injections, etc., were sold at last count. They all have to be packaged hygienically and safely, meeting strict legal requirements. This places high demands on packaging materials, filling processes and packaging machines.
At the latest since the pandemic, it has become clear how important protective packaging is for vaccines, medications, disinfectants and other medical products. We have seen from the example of the Corona vaccines that developing a vaccine is not enough. Numerous players along the entire supply chain had to work well together to protect millions of people from the virus. Billions of little glass vials for the vaccine were needed, as well as special cooling boxes for transport and special freezers for storage.
When the packaging world met in Düsseldorf for interpack last May, it was also about innovations in manufacturing, packaging and logistics of pharmaceutical products, including new solutions

to the problem of product piracy. The pharmaceutical industry is affected by counterfeiting like no other. The lucrative business with counterfeit medications, which in the best-case scenario only contain less active ingredient, but can also be laced with unknown substances that are harmful to health, has picked up speed again with the growing online trade. The WHO estimates that more than half of the medications bought online from illegal websites are counterfeit. The estimated market value of counterfeit medications is around 75 billion US dollars per year.
Counterfeit protection through security features
In addition, global supply chains are
12 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
When the packaging world met in Düsseldorf for interpack last May, it was also about innovations in manufacturing, packaging and logistics of pharmaceutical products, including new solutions to the problem of product piracy.
With the Pexcite software platform, users can collect, present and analyse information from all areas of the production and packaging process (photo Uhlmann PacSysteme)


becoming increasingly complex. Active ingredients are often produced in one country, processed and packaged in another and finally distributed and marketed across borders. The European legislator therefore took up the fight against counterfeit medications years ago with EU Directive 2011/62/EU. The directive, which comes into force in 2019, prescribes a number of safety features for prescription medications. For example, each package of pharmaceutical product must be labelled with a Unique Serial Code (USC) in combination with the article number (GTIN), the lot number (LOT), the expiry date (EXP) and the name of the manufacturer. All information is encoded in a 2D data matrix code, which is then printed in plain text on the packaging with a certain minimum print quality. In addition to the unique code, each package must carry tamper-evident features. Companies such as interpack exhibitor Bluhm Systeme have been developing coding and labelling solutions for pharmaceutical packaging that comply with the EU directive for counterfeit-proof packaging for years. This includes various labelling solutions such as laser or inkjet coders, thermal transfer printers, labelling systems and the appropriate software. For example, the Integra One inkjet labeller developed for drug coding prints unique identification codes,
barcodes or data matrix codes on a wide range of pharmaceutical packaging. UV laser marking is also a proven labelling solution. Domino has introduced a new UV laser system in 2022 that is suitable for marking plastics as well as current sustainable packaging materials, including recyclable, flexible mono-material films. The system can be used to mark both white and coloured substrates without compromising the barrier properties of the material. Thanks to a photochemical reaction, the new marking laser does not rely on laser-activating pigments or additives or specially prepared coding fields.
Labels: more than just stickers
Anti-counterfeiting measures can also be security labels with first opening indication and integrated overt, covert and digital anti-counterfeiting features that irreversibly indicate a tampering attempt. Void seals, which leave visible effects when the label is first removed, are ideal for outer packaging. Various security features are often combined or supplemented with additional functions. In addition, digital labels with NFC technology and track & trace systems ensure the complete traceability of a pharmaceutical product. Labels are an important component of pharmaceutical packaging and serve not only to protect against counterfeiting. Depending on the application on primary packaging such as bottles, blisters, syringes and vials or on secondary packaging such as folding boxes, they have to meet a wide variety of requirements: They carry general information, guarantee first-opening protection or can be partially detached to be pasted into patient records or vaccination cards. Multipage labels can also accommodate large amounts of information; they are often a combination of label and package insert. And for products that need to be refrigerated, temperature-resistant labels are
needed to ensure good legibility during storage and transport.
Increasingly automated
As safety is paramount for pharmaceutical products, the requirements for packaging machines are also high. Machine manufacturer R.Weiss, for example, uses modular picker lines in which Delta robots pack products at top speed. For Siemens Healthineers, the company recently developed an intelligent UniRob turnkey system for packaging diagnostic products that automates the process of manually loading folding cartons. In the process, multipacks in dif-
ferent pack sizes are now also placed in environmentally friendly cardboard inlays, which replace the plastic previously used. A six-axis robot sucks the blanks from the magazine, unfolds them and inserts them into the carrier conveyor, which can be flexibly and fully automatically adapted to the respective formats.
Multivac has introduced a new carrier system in the Healthcare sector that ensures controlled, gentle product transport from pre-filled glass or plastic syringes to the packaging machine. For this purpose, the syringes are separated in an upstream process and placed in
Trends RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA icf 13 NO.3 2023 - Supplement
an oriented position in a workpiece carrier. At the packaging machine, a robot then takes them from the carriers and places them individually or pre-grouped into the packaging cavities. The packs are checked for completeness using a vision system from Multivac Marking & Inspection. Even at high throughput, it checks whether the individual products are correctly placed in the designated cavities. If they are not, the corresponding pack is automatically ejected. The filling of liquid pharmaceuticals requires special know-how. Syntegon has developed the modular Versynta FFP (Flexible Filling Platform) for this pur-

far E is a solution for the aseptic filling of injection fluids into vials. The technology fulfils all requirements of the EU GMP guidelines for the production of sterile pharmaceutical products. Romaco is also committed to more sustainable production and the reduction of CO2 emissions: Through innovative process control, for example, production times can be decisively shortened and thus energy and material can be saved in a targeted manner. In addition, all of the manufacturer’s machines are available in a climate-neutral version and are equipped with energy monitors for sustainability reporting.

or centralised control and management of the entire production processes. The platform can be used across all digital devices in use, such as desktop devices, tablets and smartphones. “Visually appealing design, the light, friendly look and feel means above all complexity reduction for the users who use Pexcite. People have to enjoy working with our product and not be afraid of doing anything wrong or breaking anything”, says Thomas Kreutle, Director Development & Operations Digital Solutions at Uhlmann Pac-Systeme. For this, the software platform received a Red Dot Award 2022.
Sustainable pharmaceutical packaging
pose, an individually configurable machine especially for the aseptic filling of small batches. The new filling solution achieves output rates of up to 3,600 vials, syringes or cartridges per hour with simultaneous 100 percent in-process control. The platform includes several pharmaceutical handling units, each with a four-axis robot that moves the containers from one station to the next without glass-to-glass contact, thus reducing product loss.
Full-line supplier Romaco has also developed a new liquid filling line. Maco-
User-friendly software
Software solutions that collect data along the pharmaceutical supply chain also promise more security. With the Pexcite software platform from Uhlmann Pac-Systeme, users can collect, collate, display and analyse information from all areas of the production and packaging process and thus realise different tasks as required: Implementation of track & trace specifications along the entire process chain, monitoring of the productivity of machines and processes, digital tool management
The pharmaceutical industry is still reluctant to use recyclable materials. However, consumers today also expect more commitment to sustainability from this industry. Pharmaceutical packaging manufacturers are already one step ahead and have already developed numerous recyclable solutions for the primary and secondary packaging of medications. Last year, for example, the presentation of a recyclable paper blister caused a sensation and a recyclable monomaterial barrier tube in pharmaceutical quality was awarded a packaging award. Recently, a tubular film made from the bio-based polymer PLA was launched on the market that is industrially compostable and can be used as a sterile barrier system for diagnostic flow-pack applications. In the area of primary packaging, i.e. where medications are packed directly, it will probably take some time before recyclable monomaterials become established. In contrast, experts already see a trend towards recyclable solutions in secondary packaging. Körber Pharma GmbH, for example, has developed secondary packaging made from grass paper as an alternative to packaging made from recycled paper and cardboard and was awarded the Pharmapack Sustainability Initiative Award 2022 for this. l
(Source: interpack press office)
Trends 14 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
A six-axis robot erects cardboard inlays.
(photo R. Weiss)

Faster progress towards an animal-free regulatory system
Over a decade ago, the European Commission committed to ultimately replace animal testing. Yet still today, the acceptance of existing non-animal testing remains low in Europe. With the imminent revision of REACH, the question remains: how can we develop an assessment framework that reflects scientific progress and incorporates New Approach Methodologies or ‘NAMs’ into the REACH process to the greatest extent possible?
To support transition to an animal-free regulatory system, ECHA recently organised a workshop which brought together key stakeholders to discuss critical needs to enable faster progress. Improving the safety assessment of chemicals is crucial for promoting innovation in safe and sustainable products. However, there are challenges to overcome: like it is important to recognise that NAMs are not a one-to-one replacement for current testing methods, and there is also a need to build confidence in the effectiveness of NAMs-based safety assessments compared to animal testing. The ECHA workshop aimed to build a common understanding of what NAMs can achieve in the short and long term.
“We don’t believe that the protection
Olon enters in ADC market
Olon Group, a global leader in the development and production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) for CDMO and general markets, announces the start of construction of a new facility at its Rodano site (Milan, Italy) which will be entirely dedicated to managing and producing Ultra-Potent compounds, used for example as payloads and payload-linkers for antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), one of the most promising emerging cancer therapies, which combines the ef-fective killing power of small molecule cytotoxins and the highly specific targeting ability of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs).
“Actually, about 80% of the ADCs either approved or under development contains this type of payload, such as Dolastatins or Maytansnoids” said Giorgio Bertolini, SVP R&D Olon Group, “and there are also other highly strategic classes of cytotoxic payloads, such as Anthracyclines, Camptothecin and Calicheamicin.” The Italian group, with years of expertise in
HPAPIs, has invested €22 million in a new facility dedicated to these ultra-potent compounds. The ultra-high-containment production line will produce high-potency and toxic products and will therefore reach containment level OEB6 (target OEL 10 ng/m3).

The new project foresees the complete construction of a new building, within which a second “shell” will be built, containing the production facility and the quality control and research and development areas, as well as all auxiliary facilities. This complete, closed-loop system will include all steps of the process: synthesis, isolation, drying and analysis; an ultra-high-containment plant.
The first phase of the construction, to build the payload research and development area, has already begun and completion is foreseen by H1, 2024. Once completed, the company will move on to the sec-ond stage of finalizing the production line by creating the QC and GMP Production areas, with the in-stallation of
health and the environment versus no animal testing is an either / or situation. We think we can do both”, said Sharon McGuinness, Executive Director, ECHA Representing Cefic, Chantal Smulders, Global Head of Product Safety Science and Regulatory Advocacy at Shell shared industry views on how to achieve a modernised and accelerated chemical safety assessment. She presented a comprehensive fourpoint action plan to facilitate a responsible transition, increase acceptance, and foster confidence in the application of NAMs.

“The future of regulatory testing is animal free. One day soon we can get there if we put in place the right regulatory framework and support ”, commented Tilly Metz, Member of the European Parliament.
industrial production equipment. For the Italian-based contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) which has worked with highly-potent APIs (HPAPIs) – including anti-cancer drugs and cytotoxic – for over half a century, the decline of the blockbuster, high-volume model in oncology and the rise of niche therapies based on precision medicine are creating new opportunities for continued growth.
Olon is one of few suppliers in the global API market able to integrate every level of containment from the initial API development to commercial manufacturing and from a few grams to hundreds of kilo-grams.
16 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
ECHA Workshop on New Approach Methodologies (NAMs)
Trends
Evotec and Bristol Myers Squibb enter licence agreement within neuroscience partnership
Evotec SE announced that Bristol Myers Squibb Company has exercised its option to enter into an exclusive global licence agreement. The licence covers selected late-stage discovery programmes that were developed and progressed within the collaboration.
Evotec and Bristol Myers Squibb originally entered their neurodegeneration partnership in 2016. The initial partnership proved highly productive in generating a promising pipeline of discovery to clinical-stage programmes. Based on this success, Bristol Myers Squibb and Evotec have extended and expanded the partnership for an additional 8 years in March to further broaden and deepen the strategic alliance.
Under the licence agreement, Bristol Myers Squibb has selected an undisclosed number of programmes that were rapidly developed and progressed using Evotec’s precision medicine platforms for further development within the expanded collaboration. Evotec receives a $ 40 m payment and is eligible to earn performance milestone payments, as well as tiered royalties up to low double-digit percent-

ages on product sales.
Dr Cord Dohrmann, Chief Scientific Officer of Evotec, commented: “This licence agreement will further bolster our joint pipeline of programmes targeting several neurodegenerative conditions. We are confident that the strong collaboration of the experienced teams at Evotec and Bristol Myers Squibb will make novel innovative treatment options available to patients living with a broad range of neurodegenerative conditions.”
Evotec and Bristol Myers Squibb aim to identify disease-modifying treatments for a broad range of neurodegenerative diseases. Currently approved drugs only offer short-term management of patients’ symptoms and there is a significant unmet medical need for therapies that slow down or reverse disease progression in the field of neurodegenerative diseases.
This partnership pursues an innovative approach to the discovery and development of novel medicines by leveraging several of Evotec’s modality-agnostic precision medicine platforms. The partnership has already been successful in generating a pipeline of discovery and pre-clinical-stage programmes. A first programme, BMS986419 or EVT8683, targeting eIF2b, was in-licensed by Bristol Myers Squibb in September 2021, following the successful filing of an IND application with the FDA and has proceeded into the clinical Phase I.
OUR STANDARD: INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS FOR YOUR ASEPTIC PROCESS. STERILINE Srl Via Tentorio 30 - 22100 Como - Italy www.steriline.it | Trends
Nerviano Medical Sciences Announces Licensing of Linker-Payload Technology to Solve Therapeutics to Develop and Commercialize Novel Antibody-Drug Conjugates
Nerviano Medical Sciences Srl, a clinical-stage biotechnology company member of NMS Group Spa, the largest cancer research and development company in Italy, announced signing of a license agreement and right of option with Solve Therapeutics, Inc. to develop and commercialize novel antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) for up to four cancer targets selected by SolveTx.

NMS is focused on discovery and development of innovative therapies for the treatment of cancer based on proprietary kinase and ADC linker-payload platforms, with approved targeted drugs licensed to pharma companies and proprietary innovative small molecules undergoing clinical studies. The development program will leverage NMS’s proprietary innovative linker-payload platform technology and
SolveTx’s antibody-based oncology therapeutics technology. NMS’s linker-payload platform is carefully designed to generate more stable, efficacious, and safer ADCs to treat heterogenous and chemotherapy-resistant solid tumors. The licensed linker-payload includes optimized features; it can be readily conjugated to targeting antibodies, is highly active in preclinical in vitro and in vivo studies, shows bystander activity in heterogeneous tumors, promotes immune system recognition of tumor cells to induce immunogenic cell death, and demonstrates activity in chemotherapy-resistant and poorly proliferating tumors while maintaining a wide therapeutic index.
“We are excited to partner with SolveTx to extend our pipeline beyond our world-famous kinase platform and clinical assets to create
> estrusori > dosatori > componenti > trasporto pneumatico > sistemi completi
NUOVA GENERAZIONE DI DOSATORI FARMACEUTICI.
UNA CLASSE SUPERIORE.
+ Dosatori ad alta precisione per un dosaggio ottimale degli ingredienti
+ Cambio rapido tra configurazione a vite singola e a vite doppia
+ Un unico riduttore di velocità offre una gamma completa di portate per tutti i modelli
+ Ingombri ridotti ideale per sistemi multi componente



+ Inclinazione dosatore di 2 gradi per un migliore drenaggio nel WIP
+ Facile da smontare e pulire
Via Volturno, 37
20861 Brugherio (MB)
Tel: +39 039 883107
Fax: +39 039 880023
info@montenegrosrl.it
novel drugs designed to target tumors more precisely and deliver more potent anticancer agents with our next generation linker-payload technology. The SolveTx team has a proven track record of developing transformative anticancer drug candidates and we are pleased that they have selected our linker-payload system for integration into their novel ADCs.” said Hugues Dolgos, PharmD, Chief Executive Officer of NMS and NMS Group.
David Johnson, Founder and Chief Executive Officer of SolveTx, added ”SolveTx is eager to explore use of NMS’s linker-payload as components of our ADCs. We feel that the NMS technology holds promise to overcome the limitations of current linker-payload systems and look forward to rapidly advancing our ADCs to benefit cancer patients in need.”
I nuovi dosatori farmaceutici Coperion K-Tron sono ideali sia per applicazioni a batch che continue. Il concetto generale è impostato specificamente per una rapida pulizia e smontaggio, richiede solo pochi secondi disconnettere la tramoggia semisferica, l’agitatore, le viti di estrazione e la tramoggia di stoccaggio dal riduttore. www.coperion.com/it/dosatori-farmaceutici


Montenegro S.r.l.
ICF_CK-IT_Pharma-Feeders_194x121mm_it_2023.indd 1 12.01.2023 10:16:16 Trends
Process Service


37 years of expertise in fine chemical and pharmaceutical industry

Fine chemical plants
High purity products
Bulk APIs Productions
Sterile production lines (bulk, filling and lyophilizations)





Biopharmaceutical plants (fermentations, DSP, mAbs)
High Potent APIs (HP API) Productions
Utilities and clean utilities systems design
HIGH POTENT APIs (HP API) PRODUCTIONS
R&D and QC laboratories Kilolabs Small Scale High containment systems validated up to 10 nanograms/m3 YOUR PHARMA ENGINEERING PARTNER Via A. De Gasperi 111, 20017 Rho (MI) | Tel. +39 02 93909272 | Email info@process-service.it | www.process-service.it
Faravelli obtained the renewal of ISO 9001
On 5 June 2023 Giusto Faravelli Spa obtained the renewal of UNI EN ISO 9001:2015 certification. The audit was carried out by the certifying body CSQA, which confirmed compliance with the requirements. Our company operates within the framework of an Integrated Quality Management System to maintain a high and constantly increasing level of products and services, aiming at compliance with international quality


standards and close to the needs of the market and current regulations.
The renewal of the ISO 9001 certification not only makes us proud, but also confirms the company’s commitment and focus on quality. ISO 9001, the best-known and most widespread standard for quality management systems, is a tool that supports companies in achieving their objectives by making the best use of available resources.
ISO 9011 accompanies companies on a path of continuous management improvement in terms of efficiency, cost reduction, customer satisfaction and loyalty.

HQ of the Group, Giusto Faravelli Spa has been ISO 9001 certified since 1993.
CSQA has been accompanying the company’s certification process since 2016.
OQEMA and Lanxess have entered into a new partnership
OQEMA and Lanxess have entered into a new pan-European partnership for the distribution of Lanxess’ Colorant Additives. The portfolio offers customers all over the world a broad selection of high-quality colorants under the brand names Bayfast®, Bayplast®, Bayscript®, Levanox®, Levanyl®, Levascreen® and Macrolex®. André Schommer, Group Segment Manager Case at OQEMA, says: “We are very excited to begin our new partnership with Lanxess to further strengthen our specialty chemicals portfolio. Our European sales and tech-
nical teams, who have a deep understanding of the market, and our wide range of services will enable us to enhance the growth of Lanxess’ colorant additives business.” “This new relationship can only strengthen and enhance Lanxess’ position in the market place while continuing to deliver a first-class customer experience. We look forward to the growth and success that this partnership will bring”, Carl Waite, Lanxess Head of Sales Polymer Additives North/ East Europe, commented.
Innovative solutions were explored at Pharmap 2023

Presenting innovative solutions and contributing to further development of ongoing pharmaceutical trends were the main directions of Pharmaceutical Manufacturing and Packaging Congress. Pharmap 2023 gathered pharmaceutical companies, CMOs and CDMOs, governmental bodies to exchange experience in digital transformation and discuss innovative solutions and business practices. The Congress was held on June, 12-13, in Geneva, Switzerland. The first day of the Congress started with the executive opening panel, where speakers from LabWare, Optel Group, 3V Tech, GSK, PharmaLedger Association, Bushu Pharmaceuticals, Pharmazac had a discussion about new models for pharma manufacturing and packaging. Fausto Artico, Global R&D Tech Head and Director of Innovation and Data Science at GSK, shared his thoughts on how companies can innovate and introduce changes in manufacturing. Also, the speaker pointed out what com-
panies need to do to make it work not only from the tech point of view but also in terms of the leadership style with the aim to create a strategic vision for the people. The agenda of that day included the session dedicated to up-to-date topics of the pharmaceutical industry, including the sustainable future of the pharmaceutical packaging model, supply chain optimization, cost-optimization, agile pharma manufacturing, and innovative packaging solutions. One of the highlights of the second day of the Congress was the session dedicated to MES & robotics implementation driving towards Industry 4.0. Speakers shared their thoughts on MES implementation, paperless manufacturing, digital manufacturing and operational challenges, as well as transformation of pharmaceuticals with robotic solutions and AI. Speaking about robotics implementation, it begins to challenge the traditional approaches, practices, and business models for the manufacture of pharmaceuticals. The application of advanced robotics has the potential to increase the agility, efficiency, flexibility, and quality of the industrial production of medicines. The next edition of the Pharmaceutical Manufacturing and Packaging Congress 2024 is going to take place on 22-23, April, in Amsterdam, the Netherlands.
20 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
Trends




NUOVA GUSEO
MICRONIZATION PLANTS CONTAINMENT SYSTEMS HAMMER MILLS Nu ov a Gu s eo Sr l - V ia Dante 8 C a p 29010 V illa n ov a su ll’ A rd a (PC ) Italia - Te l : 0523 83714 9 For information contact us by mail: www.nuovaguseo.eu
SINCE 1900 EXPERIENCE AND RELIABILITY AT YOUR SERVICE CONE MILLS
A hotspot for experts in mechanical processing and bulk solids
Visitors from all around the world look forward to a wideranging programme at Powtech 2023 in Nuremberg. Around 600 exhibitors will showcase the latest solutions for processing solids and liquids.

tors alike can build on the sound advice provided by the inspired Powtech team. In September 2023, Powtech in Nuremberg will once again become the hotspot for process engineers and technicians from Europe and many other international markets. In the exhibition halls, more than 600 exhibitors will present their innovations for the handling, manufacture and processing of powders, bulk solids and liquids. Hands-on exhibits and experts with sound experience and the latest knowhow provide the perfect backdrop for developing detailed practical solutions, customised services and integrated processes in conjunction with and for visitors.
European trade fair with international pulling power
From 26 to 28 September 2023, numerous international experts in mechanical processing, bulk solids and conveying technology will once again gather at Powtech. The extensive supporting programme with new offerings from forums and special shows offers visitors
even more wide-ranging sources of inspiration. This year, the parallel Partec scientific congress with more than 400 participants will once again be a special highlight of the event. The planning for the exhibition, congress and many accompanying attractions is currently in full swing. New and established exhibi-
Heike Slotta, Executive Director Exhibitions, is confident: “Not only are we going to welcome numerous visitors from Europe, Powtech also has enormous pulling power in the world’s key processing markets like the USA, China, Brazil and Japan. We expect an excellent calibre of visitors in decision-mak-
Exhibitions 22 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
ing roles, as well as industry experts, which goes hand in hand with a significant increase in visitor numbers”. Both the exhibitor and visitor numbers at Powtech can be relied on, as they are verified by the FKM (Society for Voluntary Control of Fair and Exhibition Statistics) in a process that many trade fair organisers voluntarily take part in. Only registered visitors appearing on site per trade fair day are counted, irrespective of the halls visited or the numbers passing through the turnstiles. Exhibitor’s stand personnel are also not included. Partec: particle technology at the highest level of research.
This year too, the Partec congress, which takes place parallel to Powtech at Exhibition Centre Nuremberg, will also boost visitor numbers. The international scientific congress for particle technology, sponsored by the VDI Association of Process and Chemical Engineering (GVC), ensures regular dialogue between researchers, graduates and development engineers - while giving Powtech a special flair and an extra, exclusive audience. Because quite a few of the 400 or so congress participants and young professionals in attendance also make a point of visiting the stands of specific exhibiting companies.
Special shows, pavilions and other events complete the package
Another Powtech drawcard is its attractive supporting programme, including the following features:
• the VDMA Special Show on process engineering and air purity with solutions and technologies for dust removal, drying and processing and other bulk solids handling processes
• the APV Pharma Pavilion focusing on fill and finish and lyophilisation (freeze drying)
• the Startup@POWTECH Pavilion, where young companies from Germany showcase their inventions

• the International Start-up Area for
“newcomers” from all around the world
• and the Campus Pavilion, where universities, colleges and other institutions present information about themselves, their research areas and services.
Expert forum “Stage Talks” and “Virtual Talks” ahead of fair
This year too, exhibitors will also get the chance to present their solutions and services for particularly innovative topics to visitors in the form of 20-minute presentations followed by discussion rounds at the expert forum ‘Stage Talks’. This year, the platform will be devoted to the topics: New Food, Perfection in the Supply Chain, Sustainabili-
have been expressly included in the Industry Guide. The phones have not stopped ringing for the Powtech team, which is in the middle of allocating space in the exhibition halls and constantly seeking the best option for each client. As Marianny Eisenhofer, Director Powtech, says: “At the moment we are getting a lot of inquiries from companies that want to exhibit at Powtech for the first time. We are offering these companies especially in-depth advice, but of course our established exhibitors also have one or two questions in the light of the current challenges. We strive to satisfy everyone and find a helpful solution”. With its excellent value for money, Powtech has long been regarded as
ty and Safety, Process Optimisation and Industry 4.0, Fluids meet Solids, and Future Energies. In the run-up to the trade fair, the regular Powtech Virtual Talks webinars will familiarise visitors with these topics (Attendance is free of charge.
Preparations in full swing for all participants
Accordingly, there are plenty of good arguments in favour of a visit to Powtech in the autumn, and for the last exhibitors to register. For the application areas of batteries and cosmetics, suitable solutions will also be on display at Powtech, so these topics

a sustainable event. Increasingly, the issue of sustainability is also becoming more important for the operation of the trade fair. The focus is on the UN’s 17 sustainability goals. As well as energy-saving measures like waste separation and recycling, this is also reflected among other things in the promotion of reusable stand construction. Of course, this is where exhibitors also need to do their part. However, visitors can also make a major contribution to sustainability, e.g., by opting for a climate-friendly mode of travel using trains and subways. That is also a way of starting off a visit to Powtech in
relaxed frame of mind. l
RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA icf 23 NO.3 2023 - Supplement Exhibitions
a
Photo by NürnbergMesse / Thomas Geiger
Shaping the future of the process industries
From 10 to 14 June 2024, Achema will once again be the place to go for the entire range of technologies and services for the process industries. With five innovation themes and the Special Show Hydrogen, the world’s leading trade show for process technology will focus on the key challenges facing the industry in 2024.

The process industries are a driver of innovation and growth in the global economy – and simultaneously undergoing a transformation themselves. The “green” transformation is by far the most challenging project in the history of the
process industry, with hydrogen potentially becoming a game changer. In many places, digitalisation is seen as the key to innovation across the industry – from plant engineering to the laboratory sector. In addition, fluctuations in supply chains and geopolitical divisions are driv-
ing the need for flexible and regional plant projects. That is why Achema 2024 will present concrete solutions with five Innovation Themes, the associated Innovation Stages and the Special Show Hydrogen. “The Achema Innovation Stages are located in the immediate vicinity of the exhibition and directly in the halls, according to the respective topics covered,” says Dr Björn Mathes, CEO of Dechema Ausstellungs-GmbH, explaining the concept. “Each Innovation Stage will feature keynotes, expert panel discussions and case study presentations from both users and solution providers.”
Process Innovation: making plants future-proof
Innovations in process technology are at the heart of Achema. Process technology today is at a crossroads: while new investments in “green technologies” are growing at an unprecedented pace, it is becoming increasingly complex to maintain operations and keep existing plants in the market. This is where the Process In-
Exhibitions
novation Stage comes in, with topics such as electrification, making chemical processes more flexible and efficient, and contributions on smart technology, equipment, analytics and operations.
Pharma Innovation: experience the latest in pharmaceutical technology

Pharma technology is the fastest-growing community at Achema, and the pharmaceutical industry has never been more exciting. As new research and production methods are developed and new sites are established around the world, existing processes must meet increasingly stringent requirements and standards. In addition to numerous other Pharma Innovation topics, biopharmaceutical production will be a particular focus of discussion in 2024.
Green Innovation: on the path to sustainable transformation
Production-integrated environmental protection, efficient industrial water management and the integration of molecular and industrial biotechnology have already become hallmarks of Achema. But Green Innovation by now also means solving the challenge of carbon-neutral production in the process industry, as well as addressing issues around the circular economy, ESG and sustainable investment. As the biggest transformation challenge the chemical industry has ever faced,
carbon-neutral production requires a technological leap forward in apparatus and plant engineering.
Lab Innovation: where value creation begins
The laboratory is the birthplace of world-changing innovations and the traditional guardian of product quality. Success in the lab is determined more than ever by the technologies used there and the interfaces with engineering and production. In addition to lab design, planning, construction and management, advanced bioanalytics and pharmaceutical applications will be examined in depth. At Achema 2024, the Lab Innovation Stage will be coupled with an Action Area dedicated to the digitalised, miniaturised and automated laboratory of the future.
Digital Innovation: advancing the digital transformation
Digitalisation and the resulting innovations such as advanced analytics or Industry 4.0 technologies continue to be a perennial topic. The complexity of the issues is increasing rather than decreasing: IT vs. OT, connectivity vs. security or smart vs. smart enough –the challenge for operators is to find exactly the right configuration for their business. With this in mind, the Digital Innovation Stage will cover numerous topics around key enablers of innovation today.
Hydrogen Innovation and Special Show Hydrogen
Hyperscaling hydrogen production and infrastructure is one of the key enablers for a clean energy transition and achieving climate goals. Only Achema offers so many solutions for producing, handling, transporting and storing hydrogen. The Hydrogen Innovation Stage covers all aspects relevant to the process indus-
try: rapid scaling of production and infrastructure, power-to-X, industrial applications and sector coupling and many more.
The special show hydrogen presents the previous milestones and future challenges of the hydrogen economy. Experience the latest technologies and innovations for global and regional hydrogen projects in one place and gain insights into pre-competitive collaboration to solve hydrogen challenges.

“Achema is the showcase for process technology worldwide. It is precisely in the field of hydrogen that the central role of the Achema community becomes evident, with its many technologically mature innovations paving the way to the hydrogen economy,” says Björn Mathes. “With its technological diversity, Achema will once again be the central hub in the global innovation network in 2024 and thus the basis for setting the course for the future in the process industries and far beyond.” l

RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA icf 25 NO.3 2023 - Supplement
Exhibitions
Ilmac 2023 inspires the future of chemistry and life sciences
Around 400 leading suppliers in the industry will come together in Basel to present their solutions, innovations and new products to the around 10,000 expected trade visitors from Switzerland, Austria and Germany.

Ilmac is bringing the chemical and life science industries together once again at the key location of Basel from 26-28 September 2023. Trade visitors from Switzerland, Austria and Germany can expect to touch base with reputable companies from over 20 countries. At this year’s event, the most important industry meeting place will present promising new live formats and enhanced digital offerings.
This autumn, leading suppliers in the industry, such as Agilent, Endress+Hauser, Integra, Mettler Toledo, Metrohm, Siemens and Skan, as well as innovative start-ups, will come together at Ilmac in Basel to present their solutions, innovations and new products to the around 10,000 expected trade visitors from Switzerland, Austria and Germany. The organizers expect around 400 exhibitors to attend. New additions such as the Startup Area, the “Lab of the Future”, the “Job Connect” area and the Speakers’ Corner will complement well-established formats such as the Ilmac Conference and Pharma Logistics Days, which are taking place in parallel for the third time, making Ilmac a highly efficient knowledge and networking platform for the chemical and life science industry. “Basel is a world-leading hub for the life sciences. Our aim is to actively contribute to the growth and advancement of the location by offering the

industrial sector the Ilmac platform, which will generate the necessary inspiration to improve and continuously innovate the healthcare ecosystem,” says Roman Imgrüth, CEO of MCH Exhibition & Events.
Ilmac Conference – the latest research and business insights

The program of the scientifically driven “Ilmac Conference” will help prepare participants for the future. The three-day congress facilitates efficient knowledge sharing, covers a wide variety of topics and boasts top-class speakers.
This year’s focus lies on important industry topics such as “Lab Digitisation”, “Chemical Technologies” and “New Biotech Methods”. The “Ilmac Conference” is organised in cooperation with the Swiss Chemical Society, the Swiss Biotech Association and the Swiss Association of Graduate Chemists FH (SVC). “As a partner of Ilmac, SCS has been accompanying and supporting the event for over 60 years. The city of Basel, a key location for laboratory-based research in Switzerland, offers the ideal conditions for a successful trade fair,” says David Spichiger, Executive Director of the Swiss Chemical Society.
Smart and sustainable: the laboratory of the future
Laboratory facilities are in a phase of transformation. In light of increasing digitisation, various processes and structures of the future laboratory will be subject to comprehensive re-examination. The Lab of the Future allows Il-
mac participants to interactively experience a future laboratory, using augmented and virtual reality. “As a partner of Ilmac, we’re letting this year’s participants delve into the laboratory of the future. Inspired by the collaboration in the Basel Life Science Cluster, we’re showing the benefits, technological advances and sustainability of a digital, integrated laboratory,” says Dr Sadiya Raja, Arcondis. Laboratory buildings consume up to 10 times more energy than other buildings. Green Lab, a cluster run by the Green Building Schweiz association, initiates and moderates the collaboration between all participants and supports the dissemination of technical innovations as well as the use of new or little-known business models for Green Labs which are safe, sustainable and competitive. The Green Lab Symposium is the only laboratory symposium in Switzerland. It hosts workshops that let participants exchange best-practice examples, bring together experts from a wide variety of disciplines and help search for solutions in individual projects.
The pulse of pharmaceutical logistics
The chemical and life science industry has very high and very specific demands when it comes to the transport of goods. At the Pharma Logistics Days in Hall 2.0, companies can find trends, innovations and the right partners for their transport challenges. Over the course of two days, around 40 of the leading logistics service providers will present new solutions and innovative services.
Exhibitions
26 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA

World Forum and Leading Show for the Process Industries 10 – 14 June 2024 Frankfurt am Main, Germany www.achema.de
Solvay to produce green hydrogen for its Peroxides activity in Rosignano
Ilham Kadri, CEO of Solvay

Solvay and Sapio are partnering in the joint development of the Hydrogen Valley Rosignano Project, a largescale hydrogen production plant with locally-sourced green energy in Rosignano, Italy. Led by two technology leaders in the hydrogen economy, this project will further enable the decarbonisation of Solvay’s activities in Rosignano, leading to a
15% reduction of CO2 emissions for Peroxides related operations. The green hydrogen production plant will be built by mid-2026 on a former industrial area within Solvay’s Rosignano facility and will be powered by green electricity through the construction of a dedicated 9.5 MW photovoltaic installation.
It will have a capacity of 756 tons of green hydrogen per year, which will be used for the production of peroxides on site.
“We are very proud of this project at
our Rosignano facility. Hydrogen is a key enabler for a modern, resource-efficient and competitive economy, and we are proud to be one of the first players to take on this opportunity. It will help us reach our important ambition towards carbon neutrality before 2050,” said Ilham Kadri, CEO of Solvay. “This project is the first example of green hydrogen peroxide production at such a scale in Europe. Moreover, this investment will be an important stimulus to the local and regional economy.”
Forerunner and innovator for the national circular economy for 60 years
Itelyum, a group specialised in the management, recycling and valorisation of industrial waste, controlled by Stirling Square and owned by DBAG, celebrated 60 years in business and results as a sustainability game changer.
“Six decades of activity as an absolute forerunner of the times, always at the forefront of the circular economy and sustainable development,” said Itelyum CEO Marco Codognola. “Every year Itelyum takes a step forward on the road to decarbonisation, also thanks to the range of regenerated products that allow significant savings in CO2 emissions. And also: one million eight hundred thousand tonnes of special waste per year treated, achieving circularity indices close to 85%, through the regeneration of exhausted oils, the purification of solvents and the all-round management of special waste, both hazardous and not, also growing in the port sector and in water treatment”.
This morning at Villa Necchi Campiglio, in Milan, after the speeches by Deputy Minister Vannia Gava and Lombardy Region Environment Councillor Giorgio Maione, the years that have built a company history characterised by a pioneering and visionary spirit were retraced: from the beginnings at Viscolube onwards, it has always looked ahead, with the ability to produce change in regenerative processes.
“We have consolidated a business based,” says Itelyum President Antonio Lazzarinetti, “on offering sustainable solutions that generate economic, social and environmental value for our people, our customers and the territories in which we operate. Our story began in 1963 in via Tavernelle in Pieve Fissiraga with 50 employees and today continues with Itelyum present throughout the country, gen-
erating 600 million in revenues, through 32 operating sites, 1,300 people and highly specialised technology, unique in Italy”.
Today, the Itelyum Group brings with it, through its Research and Development activities, a further step towards the evolution of material processing as a response to non-renewable sources and the protection of the natural heritage.
Projects that herald an epochal change in the sector:
1) Rare earths. A multifunctional pilot plant for the recovery of WEEE of various types is in operation.
2) Silver recovery from photovoltaic panels. If the efficiency of the panels is greater than 20%, they are regenerated and sent for reuse, while the fraction of panels that does not pass this test is sent for recycling. In the latter case, they are disassembled for aluminium recovery and through a state-of-the-art process the crushed residual fraction is obtained, which is rich in silicon and silver.
3) Plasbreaker: lubricating bases from mixed waste plastics (plasmix). The aim of Plasbreaker is to convert plasmix into value-added products such as lubricants and hydrogen. This treatment also involves the use of used oil that cannot be regenerated and therefore cannot otherwise be recycled, with a consequent additional environmental benefit.
4) Biolubricants from used vegetable oils and the vegetable fraction of used mineral oil. The aim of this project, called BIOLUBE Itelyum, is an innovative process that is able to obtain biolubricants from waste materials such as used vegetable oils (UCO) and the soaps contained in bitumen residues from the regeneration of used mineral oils.
Environment 28 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
Bormioli Pharma reaffirms its commitment to environmental and social sustainability
Pharma, a leading international manufacturer of pharmaceutical packaging and medical devices, presented the second edition of its Sustainability Report. This edition aims to reaffirm and consolidate the company’s commitment to environmental and social responsibility, protecting the wellbeing of people and the environment, in line with its mission to “Make health a positive practice, accessible to everyone, kind to the planet’”.
Of the main targets, the 30% CO2 reduction by 2030 (compared to the 2021 baseline) has been confirmed, and new ones
have been introduced, such as the commitment to carry out an initial LCA analysis on a glass product by the end of this year and to complete the assessment of “Scope 3” emissions - i.e. those related to but not directly attributable to the Group’s business, such as those arising from employee mobility, supply chain operations and the use of manufactured goods - by 2025. The “50in5” target of increasing the share of sustainable raw materials in production processes has also been confirmed: this is a goal that the company has already come a long way towards, reaching 39% in 2022,
versus a target of 50% by 2025. The goal of reducing water consumption, to be achieved by 2030, has been made more challenging and raised from -30% to -41% compared to the consumption recorded in 2021, demonstrating how the company has already embarked on a virtuous path and wants to commit itself further in this direction. This revision is in fact supported by already achieving a 35% reduction in 2022.
“From the war in Ukraine to rising energy prices, 2022 was a year marked by a series of huge geopolitical and macroeconomic events. Despite this, Bormioli
Pharma has always guaranteed production continuity, confirming its solid position as a partner of excellence for the international pharmaceutical industry”, commented Andrea Lodetti, CEO of Bormioli Pharma.


Continuous Process Monitoring of TOC

This Compact Version is ideal for installations in common mounting spaces on water puri cation or distribution skids. Clearly arranged components and menu-based operation via transmitter makes the analyzer fast and straightforward to handle. Removable stainless steel cover available.
Swan Analytical Instruments ∙ CH-8340 Hinwil www.swaninstruments.ch · swan@swan.ch















Environment Pharmaceutical
AMI LineTOC Compact
Robotic solution to process small batches of single-dose PFSs for veterinary vaccines
Steriline delivered to FATRO an extremely compact robotic filling machine, to produce small batches of veterinary vaccines in single-dose pre-filled syringes.
Steriline, an Italian manufacturer of robotic and standard fill/ finish lines for the aseptic processing of injectable drugs, delivered to FATRO an extremely compact robotic filling machine, to produce small batches of veterinary vaccines in single-dose pre-filled syringes (PFSs).
FATRO, founded in 1947 by the pharmacist and veterinarian Gualtiero Zaini and his son Corrado Zaini (a chemist), develops and produces medicines and vaccines for animals. Today, it is a flagship of the Italian Veterinary Pharmaceutical Industry, exporting its products to more than 90 countries according to an internation-
al expansion plan that adapts the strategies to the different local realities. In order to enter into the veterinary segment market that requires single-dose formats, FATRO decided to introduce into its fleet of machines a lean solution, equipped with only a few components, that processes small batches of single-dose PFSs. The machine was supposed to occupy as little space as possible, to reduce the management costs of the grade B area the equipment would have to be housed in.
Steriline proposed an extremely compact and flexible filling solution: a Robotic Nest Filling Machine (RNFM2) designed to manage 0.5 ml PFSs with a production capacity of up to 2,900 pieces/ hour.

With two manual loading and unloading stations, where an operator inserts tubs previously peeled under a Laminar Air Flow, the stand-alone solution is equipped with a robotic arm that picks up the nest in the tub containing the empty PFSs and positions it under the two filling heads connected to peristaltic pumps. Simultaneously to the filling process, two stoppering heads seal
the filled PFSs. Once both processes are completed, the robotic arm repositions the nest in the tub at the exit station, ready for the operator to withdraw and transfer to the secondary packaging process. The whole process therefore requires a very small action area, which translates into the very limited machine footprint (1.250 m x 1.250 m) under the open Restricted Access Barrier System (oRABS).
“We are very happy to have acquired this machine from a company we have been partners with for a decade. Thanks to the Robotic Nest Filling Machine, we can now satisfy market demands and be closer to our customers’ needs,” says Dr Francesco Meliota, FATRO Vice President.
The whole project, from the order to the product set-up, took one year. The Factory Acceptance Test (FAT) was completed in September 2022 without requiring any customer service intervention.
Filippo Parini, Area Sales Manager at Steriline, states: “I am happy that FATRO chose Steriline expertise and competences despite the many competitors in the Bologna area. Fatro was really satisfied with Steriline capabilities and technologies and invited us to propose our solutions for other applications. I am convinced that this is the
beginning of an even stronger partnership.”
Complete lines for the aseptic processing of injectable products
Steriline is a well-established European manufacturer, highly specialised in the production of complete lines for the aseptic processing of injectable products, supplying pharmaceutical companies worldwide.
Steriline was founded in 1989 in the Lake Como area (Italy), where its headquarters and manufacturing facilities are still based. With operations in over 50 countries around the world, Steriline has a network of over 220 people, including direct employees and external partners, in addition to 40 local sales representatives. Exports represent more than 90% of Steriline’s turnover, with over 1,800 machines installed throughout Asia, Europe and the U.S.A.

Machines
30 icf
RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
Steriline Robotic Nest Filling Machine (RNFM2)
Detail of Steriline RNFM2

Improve Asset Performance with HxGN EAM! Industry-leading Enterprise Asset Management Software to Extend Asset Lifecycles and Improve Productivity | Learn more on www.eam.hexagon.com
Engineering the future of life-saving drugs
In Austria, efforts by one biotech player to expand production of key protein- and DNA-based ingredients for tomorrow’s drugs are moving into high gear. In just 25 months from initial concept development, Biomay has started up its new, state-of-the-art CDMO plant in Vienna. Thanks to all engineering partners, and the innovative design of the 4,000 m2 high-tech facility, Biomay now operates a flexible manufacturing platform for a wide range of bioproducts of virtually any batch size.




“Every day, when I walk into this building, I feel so proud to see how we are scaling up and making a difference for so many people –enabling innovative and truly life-saving medicines for our customers’ patients all over the world,” says Dr. Hans Huber, Chief Executive Officer at Biomay. “With our new facility, we can massively increase production volume while responding much faster to changing market demands – so we can make an even bigger impact.”
“Life-saving medicine” is certainly no exaggeration. In 2021, for example, the company announced its partnership with BioNTech SE to support the supply chain for manufacturing of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 mRNA vaccine.
Overcoming early growing pains Hans Huber may be feeling relaxed and confident these days, but life
32 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
engineering
Plant
hasn’t always been so easy. A few years ago, the company began to hit some growth constraints. To begin with, requests for batch sizes and types were increasingly varied and frequent – sometimes even requests for personalized products. Some larger customers also wanted more plasmid DNA as starting material for mRNA, since the production of COVID vaccines simply couldn’t wait.
As a biopharmaceutical contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO), the customers include a diverse mix of international biotech companies. However, with a maximum bioreactor capacity of just 40 liters, there were limits to what could be delivered from the older facility.
“The volume of requests was just crazy,” recalls Hans Huber. “We reached a stage where we had to make a critical decision about what kind of a company we wanted to be in the future. It became clear that we needed to rethink, reimagine, and rein-
vest to move to the next level as a CDMO,” he recalls. “Our ambition is to be a leading one-stop supplier of GMP services with a unique position of providing DNA plasmids, messenger RNA and recombinant proteins for breakthrough drugs”.
Growing together with VTU Engineering
In 2018, finding themselves at a crossroads, Hans Huber and his team decided that Biomay needed to scale up and build a larger facility to support their ambitious plans. To help guide them on this journey, they turned to VTU Engineering, an international technology group with extensive experience in executing large CAPEX projects in the life science industry in Europe.
“I remember our initial meeting vividly,” recalls Alexander Asbäck, Managing Director and Chief Operating Officer of VTU Group GmbH. “We met up in a residential neighborhood of Vienna where their technicians were huddle in a lab doing magical things with molecules. It was so obvious to me that they really needed and deserved a new, state-of-the-art manufacturing facility.”
“We chose VTU not only because of their experience in EPCMv projects but also because of their will-
ingness to work on flexible design solutions within a very tight budget frame,” said Hans Huber. “They listened, worked closely with our team to develop innovative solutions, and were flexible enough to accommodate our needs and collaborate with other partners.”

In its role as EPCMv contractor, VTU was responsible for bringing the project together, gathering all the necessary expertise for the required speed of execution. The next question was where to build, what to build and how fast?
A holistic, sustainable approach Biomay secured a site and building permits in Aspern Seestadt, a northeastern suburb of Vienna. Aspern Seestadt is one of Europe’s largest urban development projects, known for its “green”, eco-friendly profile. In addition to providing cutting-edge technology, sustainable design is a key part of the district’s profile. And indeed, the facility is equipped with a groundwater heat pump for cooling and heating the entire building as well as solar panels for fossil-free electricity supply.
Building a future-proof CDMO facility
“One early engineering challenge was defining the specifications to be
Biomay is a world-leading, one-stop supplier of GMP services, providing DNA plasmids, messenger RNA and other cellular materials for demanding international customers

RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA icf 33 NO.3 2023 - Supplement
Hans Huber, CEO Biomay AG:
“With our new facility, we can massively increase production volume while responding much faster to changing market demands”
Plant engineering
flexible enough to handle multiple process steps, support a future-proof design, be GMP compliant and meet a tight budget – all at once,” says Alexander Asbäck. “Flexibility was our guiding star for everything.”
The two-storey, multi-purpose facility is deceptively simple, stylish and has everything required for being a next-generation manufacturing plant. The classic GMP production setup follows an “upstream-downstream” seed-train flow with one key difference – there is a dedicated area for innovative, personalized (patient-specific) batches. Upstream, by starting with a 750-liter stainless steel fermentation tank, Biomay boosted its capacity by a factor of
ten with respect to batch size and volume. Gross bioreactor sizes are now 5L, 50L, 150L and 750L. The upstream layout, which is divided into multiple clean room areas, includes a central media supply as well as separation, cell disruption via homogenization or chemical lysis and sedimentation. Downstream, purification steps include chromatography followed by ultrafiltration skids that
ized medicine for cancer patients in GMP quality within just a few weeks,” Hans Huber says. Together with its customers, Biomay is now providing DNA plasmids for patient-specific tumor-antigens, known as “neoantigens,” as a promising new solution to cure cancer patients. “This places tough challenges on us to be innovative and creative, to meet short time frames while remaining cost-effective,” he says.
Building during a pandemic
The construction and planning of the plant, which took 25 months and began in end 2019, was finalized in January of 2022. One of the big challenges was that planning and construction took place during waves of the covid pandemic, requiring Biomay, VTU and the other partners to meet up virtually for much of the development work.

“On top of everything else, securing a safe and healthy workplace and adhering to a Zero Accidents policy
Alexander Asbäck, Chief Operating Officer, VTU Engineering: “One early engineering challenge was defining the specifications to be flexible enough to handle multiple process steps, support a future-proof design, be GMP compliant and meet a tight budget – all at once.”
can be flexibly configured via panels and mobile tanks. The aseptic filling section is designed as its own separate clean room.

VTU was involved in everything from feasibility to design, procurement, and construction, including documentation and validation.
Patient-specific treatments
One unique aspect of the design is Biomay’s ability to supply personalized batches for patient-specific drugs. “Imagine creating personal-
for all parties was our highest priority,” says Thomas Miklautsch, Managing Director of VTU Engineering who was deeply involved in the project. Since the project was crucial to overall public health, vaccinations were administered early on, and physical meetings kept to a minimum.
“It’s ironic that we were constructing a factory for covid vaccines in the middle of the pandemic,” says Thomas Miklautsch.
“In the end, we provided the complete package from A to Z – guid-
34 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
Upstream production in the GMP clean room area
Quality in the details
Plant engineering
ing them from initial concept to final certification,” says Miklautsch. “We did this on time, on budget and by applying the most modern planning tools. ”He notes that key success factors included bringing in a wide range of competencies, using advanced engineering planning tools, and thinking out of the box.
Digital engineering platform
Another process expert who was involved in the project was Gloria Galindo-Peitbuchner, Senior Process Engineer at VTU. For her, working virtually was a novel twist that took some getting used to. Equally challenging was “working smart” to set efficient engineering standards that did not yet exist at Biomay due to its rapid growth and mid-tier size.
“The digital engineering platform we used was also helpful in keeping everything on track,” she says. “This was critical since it provided the structure needed to move quickly and get GMP and other key certifications.”
Using standardized manufacturing processes
To avoid “overdesigning” and waiting for approvals for every small process design modification, Bio -
may adhered to standardized biotech manufacturing processes. This also meant sticking to standard stainless-steel equipment, versus single-use equipment with disposables, which the staff was familiar with in terms o cleaning-in-place (CIP) and steaming-in-place (SIP) sterilization. Also, instead of using a “ballroom concept” the facility was divided into smaller rooms to keep production changeover times to a minimum.
“There are always tradeoffs,” says Hans Huber, ”but I now feel we’ve got a next-generation facility that that will allow for strategic growth
and offer our customers attractive manufacturing capabilities.” Looking ahead and considering ongoing waves of the pandemic globally, he expects that some higher production scale will be required, even for Phase 3 clinical studies or for bringing new products to market. Not only can Biomay meet this need by also implementing single-use equipment, if re-
quired, but it also owns a plot of land behind the facility for potential future expansion.
Success through teamwork
“To sum up, what made this project a success is the very good teamwork and communication with VTU and all the other contractors who brought their experience and tools to the table. Thanks to the efforts of many, we now have a sustainable and cost-optimized process facility that offers a higher degree of flexibility and can be quickly adapted to new market requirements,” concludes Hans Huber. l
and other equipment are placed on wheels to allow for flexible batch configurations and cleaning


RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA icf 35 NO.3 2023 - Supplement
Bioreactors
Modern bioreactor with real-time digital monitoring
Plant engineering
Sustainability becomes a driver for chemical plant construction

These are the birth pangs of a new economy: the increasing demand for chemical products is bringing growth to the industry, which at the same time has to cope with the necessary transformation towards climate neutrality. For chemical plant construction, both of these factors mean a lot of work in the coming years.
by Armin Scheuermann
The energy crisis resulting from the Russian war of aggression on Ukraine has sent shock waves through the global chemical industry in 2022. Germany and chemical nations
in Europe, which have few energy resources of their own, have been hit hard by the rapid rise in gas prices. As a result, the pressure for more efficient processes and new energy sources has increased significantly. But a rethink of the raw material and energy base was already underway. This is
because chemical nations and global chemical companies have long been working towards the goal of “Net Zero” and want to end greenhouse gas emissions by 2070 (India), 2060 (China and Russia) or already by 2050 (all other chemical nations).
The project is ambitious: in Europe
36 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
engineering
Plant
alone, the chemical industry will have to invest 1 trillion euros for this purpose, according to estimates by the consulting firms Accenture and Nexant ECA. 400 to 600 billion euros will be spent on modifying and building new production plants for the eight most important chemicals: ammonia, ethene, propene, nitric acid, carbon black, caprolactam, soda ash and fluorochemicals. In the USA and China, investments will be much higher. Chemical plant construction has a key role to play here: the mammoth task is to scale up new technologies to largescale production in the shortest possible time - actually the industry’s paradigm discipline.
Decarbonisation picks up speed
For several years now, companies in the plant engineering sector have been registering growing interest among their customers for solutions to decarbonise chemical value chains. In view of the high prices for natural gas and other energy sources, the development has gained significant momentum in 2022. Across the board, global chemical plant suppliers re-


port an increasing share of orders for sustainable solutions in their latest annual reports. But the market has changed significantly compared to the Corona years of 2020 and 2021: the traditional oil and gas business is also humming. Increased prices for crude oil and natural gas have led to a revival of upstream activities in 2022. With projects worth over 2 trillion US dollars, oil and gas industry investments reached a new record high in 2022. And because the largest chemi-
cal plant construction companies usually also have a foothold in the oil and gas business, plant construction capacity is becoming scarce. The demand for plant engineering solutions is also intensified by politics: it is estimated that the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) passed by the US government in 2022 alone could lead to investments of 369 billion US dollars in the area of energy security and climate neutrality by 2030. The EU Commission is planning on a similar scale with its REPowerEU programme, and Japan also wants to invest massively as part of its Green Transformation programme.
Multinational suppliers such as Fluor, Worley, Technip and Samsung Engineering have recently reported not only a significant increase in incoming orders, but also spectacular decarbonisation projects by their customers. In December 2022, for example, the start of construction for a new steam cracker in the port of Antwerp caused a stir: the British petrochemical group Ineos is building an ethane cracker there under the title “Project One”, which, after commissioning in 2026, is to emit around 50% less greenhouse gas than the most efficient plants of this kind to
Chemical nations and global chemical companies have long been working towards the goal of "Net Zero" and want to end greenhouse gas emissions by 2070 (India), 2060 (China and Russia) or already by 2050 (all other chemical nations)
RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA icf 37 NO.3 2023 - Supplement
Plant engineering
(Photo from Achema 2022)
date. At 3.5 billion euros, it is the largest investment project in the European chemical industry in the past 25 years. The contract for the technology licence and the front-end engineering and design (FEED) has been secured by Technip Energies. Only formed in 2021 from the French Technip FMC, the plant engineering company focuses on engineering and technology solutions for energy transformation.
Intensive cooperation between chemistry and plant engineering

The spectacular project is just one of many: almost all chemical companies that operate steam crackers are now working on climate-friendly solutions for the cracking furnaces - because ethene is the starting point for many plastics and basic chemicals, and to date almost 700 kilograms of carbon dioxide are produced per tonne of ethene. The project is so huge that it requires new cooperative ventures between plant builders and operators - and even cross-competitive ones: BASF, Sabic and Linde are currently jointly developing an electrically
heated cracking furnace. At the same time, Dow and Shell, together with researchers from the Dutch TNO, are pushing ahead with the electrification of steam crackers. Together with the plant manufacturer Fluor, Dow wants to build a steam cracker with net zero CO2 emissions in Fort Saskatchewan, Canada. The Brazilian chemical company Braskem wants to electrify its crackers together with the Finnish technology and plant engineering company Coolbrook. And time is pressing: because largescale chemical plants in particular will be operated for several decades, projects planned today must be net-zero-capable with a view to 2050. Promising new processes such as methane pyrolysis or methanol synthesis from biomass or electrolysis hydrogen are not yet available for large-scale use. As soon as the processes have been developed in the laboratory, plant engineering will have the task of scaling up these “first-of-a-kind” solutions from the laboratory to the industrial scale. A key role is therefore played – at least as a bridging technology – by
the capture and storage of CO2, known as Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS). Dow and Ineos, for example, are relying on this approach in their current cracker projects, but the net zero target can also be achieved for other chemical processes such as ammonia production. In March 2023, the first ship transport of carbon dioxide captured in an Ineos chemical plant in Antwerp caused a sensation: this marked the start of the cross-border Greensand project, in which up to 8 million tonnes of CO2 are to be stored annually in a depleted oil field off the Danish North Sea coast. In addition to Ineos, the energy company Wintershall DEA and the engineering company Aker Carbon Capture are involved in the project. Also in Antwerp, the chemical company BASF is developing a CCS project with the plant engineering and industrial gases specialist Air Liquide. The Global CCS Institute has researched 200 commercial CCS projects in 2022, a total capacity of 244 million tonnes per year. But this is just the beginning: the United Nations IPCC estimates that at least 4 gigatonnes of CO2 will have to be saved annually by 2050 via carbon management and removal technologies in order to reach the 1.5 degree target. For this to become a reality, intensive cooperation between chemical companies that supply technologies and chemicals for CO2 capture and plant engineering companies with scale-up expertise is necessary.
CCS also has what it takes to massively accelerate the transition to a climate-neutral hydrogen economy: because water electrolysis from sustainably generated electricity will not deliver the quantities of green hydrogen needed by industry and the chemical sector for a long time yet, blue hydrogen is a climate-friendly option that is available very quickly: in this process, hydrogen continues to be produced from natural gas, but the carbon dioxide produced in the process is captured and stored.
38 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
(Photo from Achema 2022)
s
Plant engineering
ITELYUM: il nome dell’economia circolare.

Tecnologia, esperienza e innovazione per la rigenerazione degli oli lubrificanti, la purificazione dei solventi e i servizi ambientali per l’industria.
29 siti operativi e più di 1.200 persone: soluzioni sostenibili per circa 35.000 clienti in più di 60 Paesi nel mondo.
Univisual.com
The focus on a value contribution to solving the climate problem and sustainable management is also important for plant engineering for another reason: attracting talent through employer branding (Photo © shutterstock Gorodenkoff, by Achema Press Office)

Mammoth task of decarbonisation changes chemical plant engineering
However, it is clear that the mammoth task of decarbonisation is also changing chemical plant construction itself. In recent years, the flood of projects and rising prices have already led to a paradigm shift in contract design. While clients were able to commit their contractors to fixed-price contracts a few years ago, the wind has now shifted in favour of EPC providers: chemical plant builder Worley, for example, reports that the share of fixedprice contracts (lump sum turn key) in turnover has fallen to 1%. The company now bills 80% of its contracts on a reimbursable basis.
In the future market of hydrogen, manufacturers of electrolysis plants are planning to massively expand their capacities. The chemical plant construction sector will be investing
massively in its own technology and corporate development in the coming years.

And because investors are increasingly attaching importance to sustainable business models, companies in the chemical plant engineering sector must themselves operate according to ESG criteria. This is why almost every annual report in the industry recently contains a reference to progress in the areas of environmental, social and responsible corporate governance. The focus on a value contribution to solving the climate problem and sustainable management is also important for plant engineering for another reason: attracting talent through employer branding. After all, one of the biggest challenges currently facing the industry is the lack of qualified specialists.

Automation of the engineering processes and the construction site
Because not only personnel but also other resources important for chem ical plant construction will remain scarce in the coming years, the in dustry is focusing on increasing pro ductivity: digitalisation and auto mation of engineering processes and artificial intelligence are just some of the levers with which the industry is tackling the issue. Conclusion: with its solutions ex pertise, the global chemical plant engineering industry is an impor tant enabler for the decarbonisation of chemistry and the energy trans formation of the economy. The industry is tackling the chal lenge of scarce human and engi neering resources through digital isation and investment in its own business.
40 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
Plant engineering s











Less is More
An innovative rotating cleaning nozzle with a special flat fan design developed by Lechler, saves time and money through uniform coverage when cleaning tanks. In a series of tests, it was capable of reducing the cleaning time by 40% and fresh water consumption by 30% in comparison to conventional spray balls.
re are mechanics, chemistry, time and temperature (Sinner Circle).
Predictable return on investment
The cost associated with this nozzle is paid off quickly, especially when you compare the significant reduction in lower operating costs. More efficient cleaning systems will also
Reliable cleaning processes reduce the risk of claims



Hygiene is absolutely essential to ensure the quality and uniformity of goods that are manufactured, filled and packaged. Industrial cleaning processes such as Cleaning in Place (CIP) provide a long-term contribution in maintaining the required hygiene levels and protecting manufacturers against expensive claims which can damage their reputation. The required cleaning jobs must be performed quickly and more or less in between production. Longer downtimes result in higher costs.
With modern cleaning processes, the focus is no longer on effectiveness but efficiency. Optimally matched factors achieve the desired cleaning result with the economical use of resources. The main four factors he-


become increasing important in production plant as well in the future. The goal is to show how the cleaning result is affected by gradually increasing the operating pressure and the size of the tank. The results will be used by Lechler for further optimization of the rotating cleaning nozzle. In order to increase process reliability even further, the rotating cleaning nozzle can also be optionally combined with a rotation monitoring sensor.
Renowned plant manufacturers have placed their trust in the nozzle technology and know-how of Lechler company for many years now. Reduction in the costs for energy, natural resources and additives is an important argument in the industry.
Lechler never focuses on just the individual nozzles but always on the overall process.

Hygienic Design www.lechleritalia.com
Different type of materials, certifications, flow rates, diameters of coverage, impact forces and efficiency classes. Lechler’s tank cleaning satisfy all needs of processes.



Discover yourself advantages.




Function video Scan the QR Code or go to: https://www.lechler.com/mediateca ENGINEERING YOUR SPRAY SOLUTION Lechler Spray Technology S.r.l. Via Don Dossetti, 2 - 20074 Carpiano (MI), Italia Telefono +39 0298859027 - info@lechleritalia.com www.lechleritalia.com
A WIDE RANGE OF STATIC AND ROTATING TANK CLEANING NOZZLE TO SOLVE ANY CLEANING PROBLEMS
The shift from CO2
For the chemical industry, the energy transformation is a significant challenge that must be dealt with as rapidly as possible. The shift to renewable raw materials and energy sources thus calls for extensive changes to existing processes. But it also opens up avenues for avoiding, capturing and storing CO2.
by Florian Kraftschik* and Frederik Effenberger**
The energy transformation has a clear goal in the industrial sector: shifting the energy supply to a sustainable basis through renewable sources. The idea is to reduce or completely do away with anthropogenic CO2 emissions created by fossil
energy sources. Many of the technologies for industrial decarbonization place high and very specific demands on process measurement technology. This article offers an overview of how Endress+Hauser can make a contribution as a partner for the process industry.

The chemical industry must deal the energy transformation as rapidly as possible
For the chemical industry, the energy transformation is a significant challenge that must be dealt with as rapidly as possible. The complexity of this task stems from the fact
44 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA Energy transition
*Sales Marketing Manager Communication, Endress+Hauser Germany **Industry Manager Decarbonization, Endress+Hauser Germany
that while fossil-based raw materials must be replaced since they are the underlying cause of carbon dioxide emissions that are harmful to our climate, CO2 is a necessary raw material for diverse processes in the chemical industry. To date, however, CO2 has been generated as a byproduct, which in a future decarbonized world will no longer be possible in a conventional way.
The shift to renewable raw materials and energy sources thus calls for extensive changes to existing processes. But it also opens up avenues for avoiding, capturing and storing CO2. In order to provide a better description of the various strategies and approaches for reaching the climate goals, and to discuss the corresponding challenges and solutions, this article breaks them down into three main issues:
The first issue is the electrification of processes to avoid emissions and increase the efficiency of existing
plants with the aim of reducing emissions wherever they are (still) unavoidable.
The second issue relates to the shift to alternative energy sources, particularly green hydrogen. As well as the manufacture, transport, utilization and storage of H2, other topics that fall into this category include power-to-chemical (P2C) approaches or green steel.
The third area revolves around CO2 as a raw material, which should be viewed as an emission or as a captured product. This topic also includes key terms such as carbon capture (CC) or direct air capture (DAC), as well as the issue of CO2 storage and transport.
Electrification of processes and efficiency improvements
The first promising measure, where implementation is possible, is to convert the chemical industry processes directly to renewable, ze-
ro-emission electricity generated from wind, water and solar sources. This is certainly one of the biggest and likely easiest adjustments in the process industry. In many cases these adjustments can be made without drastically impacting processes. One example is steam generation, which can be easily electrified and where no changes to the heat network or the instrumentation for measuring and balancing the generation, distribution and consumption of heat are necessary.
For processes that cannot immediately be converted to zero-emission sources, there is often greater potential for emissions savings that can be realized by optimizing and improving plant efficiency. The optimization measures require measurement and balancing of energy consumption. This can be accomplished with Endress+Hauser’s broad field instrument portfolio, which can be used to monitor all parameters in the
A close-meshed network of measuring instruments and energy computers records the quantities of heat flowing through the Endress+Hauser steam lines

RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA icf 45 NO.3 2023 - Supplement
Energy transition
core processes, as well as in auxiliary systems such as steam, cooling or CIP/SIP. The portfolio features a wide range of measurement parameters such as pressure, flow, material moisture, liquid analysis, level, optical analysis, system components and temperature. As well as services for monitoring CO2 emissions, Endress+Hauser offers digitalization services through Netilion, an IIoT ecosystem that creates transparency in terms of plant assets and provides a basis for plant optimization.
Hydrogen as a storage medium
The second issue related to industrial decarbonization is the conversion to alternative energy sources. Sufficient availability of renewable energy is crucial for reducing emissions through electrification. The sun does not shine everywhere, nor at all times, to the same extent. And wind energy is also subject to large fluctuations. While regenerative energy is the foundation of electrification, a key factor for a successful energy transformation is storage technologies that can balance out these fluctuations. One medium that can store excess solar and wind energy is hydrogen. The conversion of electricity to hydrogen loses some energy, but hydrogen stores well and can be converted back to electricity with relative ease if required. Storing energy in hydrogen is known by the term power-to-chemicals (P2C).
In chemical plants, however, there are processes that require so much energy in total that their energy requirements cannot be fully covered by regularly feeding the grid with renewable electricity. These processes can be completely converted to hydrogen, which is delivered to the plant via a transport network.

Endress+Hauser: measurement technology for the energy transformation
Measurement devices and solutions play an important role in the overall energy transformation. Today, core processes and auxiliary systems such as heating, cooling and CIP/SIP systems are already equipped with a close-meshed network of measurement instruments in order to capture measurement values and other data for process monitoring and control and to communicate the information to the control system. For the energy transformation, plant operators will also require precise measurement values regarding energy input and usage, the exact distribution and the energy balance across the entire plant. The level of CO2 emitted into the environment must be precisely tracked as well. Given that
the exact amount of energy has to be reliably monitored, the demands on the instrumentation are high in terms of measurement accuracy and long-term stability.
After all, only those who know where the energy is being used are in a position to affect energy savings or shift to other sources.
The demands on the instrumentation are unique, however, particularly when the devices come into direct contact with hydrogen. For measuring pressure in electrolyzers, for example, Endress+Hauser offers a pressure measurement cell with a gold-coated membrane that provides effective protection against the diffusion of the very small H2 molecules through the membrane. If the gas
Energy transition 46 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
s
Using Direct Air Capture from Endress+Hauser, CO2 is filtered directly from the air and stored for further use
APIs? NOW WE CAN!
BEHIND GREAT
SATISFACTION ARE ALWAYS GREAT
AGENTI FILMANTI - DISGREGANTI - LUBRIFICANTI - GLIDANTI
- LEGANTI - DILUENTI - OPACIZZANTI - AMIDI E DERIVATI -
POLIALCOLI - ZUCCHERI - DOLCIFICANTI - VISCOSIZZANTICONSERVANTI - CORRETTORI DI PH - ANTIAGGLOMERANTI
- PRINCIPI ATTIVI - PLASTICIZZANTI

Gli eccipienti e le materie prime distribuite da Faravelli ti aiutano a raggiungere la formulazione farmaceutica perfetta, proprio quella che stai cercando: funzionale, sicura, efficace, performante.

La formula che rende ogni cliente soddisfatto e felice.
“Accompagniamo con competenza globale e sensibilità locale i nostri partner verso scelte innovative, per formulare il futuro con ingredienti e soluzioni affidabili e sostenibili”.
VIA MEDARDO ROSSO, 8 - 20159 MILANO - WWW.FARAVELLI.IT - PHARMA@FARAVELLI.IT
RAW MATERIALS #FaravelliPharmaDivision
diffuses through a membrane made with conventional materials, it can lead to instrument failure. In some instances, systems and instruments that come into contact with hydrogen must withstand extraordinarily high pressures and low temperatures and cover corresponding measurement ranges. The qualitative measurement of the H2 as a byproduct of the electrolyzer also places special demands on the instrumentation. With the OXY5500 oxygen analyzer, Endress+Hauser offers a reliable method of determining the amount of residual oxygen in hydrogen in real time. In addition, the J22 TDLAS gas analyzer (tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy) can measure traces of moisture in burnable gases in real time, which also gives an indication of the quality and calorific value of gases.
Blending H2 in fuel gases to reduce emissions
Even if it were already technologically feasible to partially or completely convert plants to hydrogen today, it’s worth pointing out that the industry finds itself in a phase in which hydrogen is still not available in sufficient quantities, to say nothing of the aforementioned green hydrogen from renewable sources. Nonetheless, even if the conversion to H2 cannot be carried out immediately and completely in one fell swoop, emissions can be partially reduced by blending H2 with other fuels. Considering that the precise composition of the gas has to be measured, the instrumentation plays a crucial role here. Let’s take a look at a gas turbine fed by a hydrogen blend as an example. In this scenario, flow measurement and optical analysis technology from Endress+Hauser can be used to determine the natural gas and H2 mixture and retrofit
the plant step-by-step for pure hydrogen operation. Another application that follows this approach is the use of a hydrogen blend to fuel hot blast furnaces, which is also known as green steel.
CO2 as a raw material: active capture emission technologies
For processes that have not yet been converted to renewable energies, or for those in which conversion is not possible, the third point of this article offers a solution: active carbon capture technologies (CC). This approach captures the CO2 before it’s released into the atmosphere where it has a harmful impact on our climate. Direct air capture (DAC) captures CO2 directly in the surrounding air. This involves processes such as amine scrubbing, which are already frequently used to capture CO2 from process gases, exhausts or from natural ventilation.
To precisely measure the concentration of CO2 in the outlet gases, Endress+Hauser relies on proven tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) technology to ensure that the process can be reliably and efficiently controlled. One example in which CC is already being used is the cement industry. Although CO2 cannot be completely avoided in this environment, it’s nevertheless captured through CC technology and other measures. While these measures help prevent further CO2 from being released into the atmosphere, active capture devices can also be used to filter CO2 from the surrounding air through the use of renewable energy
CO2 as a source material for derivative products
Although the focus of the CO2 transformation is on avoidance and capture, carbon dioxide plays an impor-
tant role in industry as a raw material in production. To cite one example, CO2 is used in greenhouses to increase the rate of photosynthesis and stimulate plant growth, which then boosts harvest yields with the same sized area. Even in the food industry, CO2 is required for more than just carbonating beverages and is also used by beer breweries during the bottling process. CO2 is also used as a raw material in the chemical industry, where it will be lacking if processes are converted over to zero-emission energy sources and no replacement is created. This impacts the production of methanol as an example. As absurd as it initially sounds, a new CO2 supply infrastructure, such as a pipeline network, might even be necessary in this case. For every one of these storage, transport and input processes, plant operators will need precise measurement data for process control, monitoring and documentation, for which Endress+Hauser offers various instruments, solutions and services.
Full-scale measurement concept for the energy transformation
A successful CO2 transformation will require a combination of numerous measures and various technology approaches. Endress+Hauser offers a broad spectrum of instruments and solutions for managing the process of converting the chemical industry to zero-emission technologies. These include instruments designed especially for hydrogen applications that take into account the material properties of the molecules or extreme process conditions. Endress+Hauser is also setting benchmarks in the field of optical gas analysis with TDLAS, QF and Raman sensors that help users precisely determine the composition of gases, liquids and solids. l
Energy transition 48 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
s



Information - Advertising - Digital services For over 30 years leader in b2b magazines via Roggia Borromea, 16 - 22060 Carugo (CO) Tel/fax: +39 031 3665163 vendite@interprogettied.com - www.interprogettied.com
How to enhance compliance while creating a safer working environment
Chemical companies are poised for significant growth over the next year as the industry rebounds from the losses experienced during the global COVID-19 pandemic. At the same time, the chemical industry is facing a wave of new regulations and increasing pressure to meet strict global compliance requirements —
a rise in national, local, and industry regulations covering everything from emissions to safe waste treatment. To meet these increasing compliance requirements, chemical companies must overcome key challenges surrounding gathering, managing, and reporting data. For organizations that do enhance their compliance processes, the benefits are immense —

particularly in relation to safety. Let’s take a look at how companies are using technology to overcome key compliance challenges resulting in safer working environments.
The challenge of achieving compliance
Chemical companies face an immensely complex and detailed ar-
Maintenance
HxGN EAM enables chemical companies to achieve a safer and more sustainable working environment by gaining complete visibility into assets and control of maintenance to reduce costs and downtime while increasing productivity.
ray of compliance requirements in their own country and are often required to adhere to strict global regulations.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has strict guidelines that chemical manufacturers must comply with to protect the safety of workers interacting with chemical products. And, globally, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) regulates chemical organizations’ processes, and the United Nations (UN) addresses global environmental and human safety concerns. Each of these organizations — and many other local and regional governing bodies — implement a strict set of regulations and compliance requirements on chemical companies. An integral part of meeting these requirements revolves around the following:
• Inspections
• Checklists
• Standards of performance
• Laboratory testing
• Reporting
The management of such critical information for multiple assets and large numbers of employees can quickly become chaotic. In the past, much of the process of meeting compliance requirements was manual. This, in turn, made the process error-prone and time-consuming.
Compliance creates a safer working environment
From the proper disposal of toxic waste to operational procedures surrounding equipment usage, meeting compliance requirements isn’t simply about checking off a box. Chemical companies that are enhancing their ability to meet both internal and external compliance and regu-
latory requirements are benefiting from increased safety in the workplace.
Chemical workers have long held some of the most dangerous jobs in the world. Exposure to toxic chemicals and working around potentially hazardous equipment has continually put chemical manufacturers’ greatest asset — their people — in danger. Manual processes for maintenance and tedious processes surrounding inspections and testing have led to a high risk of human error.
Now, through improved, automated processes and enterprise asset management solutions, chemical companies are poised to create a future in which meeting compliance requirements is simplified and workplace safety is elevated.

This safety translates not only directly to an organization’s own employees but also to surrounding communities and, ultimately, the greater global population.
How technology is helping chemical companies achieve compliance
Technology simplifies and streamlines processes surrounding compliance. From document management to scheduling service calls to maintenance prevention and logging of results, new automated technology solutions are empowering chemical companies to lead the way in meeting compliance requirements. With the use of advanced and connected technology solutions, chemical manufacturers are also increasing their trust in the accuracy of their data. Much of this progress is happening through embedded automation across the lifecycle of plant operations. Automation is allowing chemical companies to reach new levels of efficiency, quality, and op-
erational integrity.
Technology is enhancing compliance by improving data governance, as well. What was once scattered, siloed information is being transformed into actionable insights that empower chemical companies to meet local and global compliance regulations and mitigate employee risks. This, in turn, is resulting in enhanced safety across the chemical industry.
Enabling enhanced compliance for chemical companies
HxGN EAM enables chemical companies to achieve a safer and more sustainable working environment by gaining complete visibility into assets and control of maintenance to reduce costs and downtime while increasing productivity. Additionally, HxGN EAM allows organizations to align to REACH to ensure products are safe and reliable, allowing them to meet both internal and external compliance and regulatory requirements. If you are interested in learning more about how Hexagon technology solutions can help your organization achieve compliance in efficient and effective ways, contact Hexagon team: https://hexagonppm.com/contact. l
The chemical industry is facing a wave of new regulations and increasing pressure to meet strict global compliance requirements
RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA icf 51 NO.3 2023 - Supplement
Maintenance
Antares Vision Group, a technology partner in the digitalization of products and supply chains for companies and institutions and a leader in traceability and inspection, introduced Diamind, the most intelligent and integrated ecosystem of solutions that simplifies the technology environment, at Interpack, the leading processing and packaging trade fair, in Düsseldorf from 4 to 10 May.
The Diamind ecosystem fosters business growth and enables a data-driven, tailored journey to digital innovation. All of its solutions and innovations are aimed at guaranteeing the quality, safety, efficiency, and sustainability of products and supply chains in all the business areas in which the Group is active.

An intelligent and integrated ecosystem with technological innovations
Life science: traceability, quality control, and data management, from the product to the supply chain
Diamind Line is a suite that manages inspection systems and machines for packaging and production lines to control the quality of products, packaging, containers, and labelling, and track and trace machines and systems for digital identity management through serialization and aggregation on production lines.
• Traceability: Advanced solutions for serialization and aggregation (of bottles and cartons)
• Traceability, quality control, and product authentication: A “digital fingerprint” solution born from the partnership with Edgyn, integrated with traceability and weight control
• Blister quality control: A combination of laser technology and traditional vision systems; performs three-dimen-
sional inspection, powered with Artificial Intelligence
• Stick pack quality control
• Weight control: A checkweigher for small, medium, and large cartons, a first for Antares Vision Group in the Life Science business area
• Automatic visual inspection & high voltage leak detection
• Automatic visual inspection for liquids in glass vials

• Automatic visual inspection for prefilled syringes (conference)
• Automatic visual inspection for blowfill-seal (BFS) cards (conference).
Diamind Factory is a software suite that manages the entire production site.
• Monitoring and optimizing processes
• Production efficiency and quality improvement
• Optimizing planning and factory maintenance
• Enabling sustainability
52 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
The Diamind ecosystem is created by synergy among the technologies, experiences and skills of all companies within the Antares Vision Group.
In the photo above: automatic Visual Inspection & High Voltage Leak Detection Machine
Traceability
• Line clearance: Digitization of line clearance procedures, enhanced with Artificial Intelligence.
Diamind Enterprise and Diamind Supply Chain: Respectively, these are software suites that address regulatory compliance management at the enterprise level, including track and trace management of serialized and non-serialized products and assets, and end-toend supply chain visibility and management, from raw materials through trading partners to the end user.
• Quality: Collecting of inspection and quality control data
• Efficiency: Data analysis to improve production processes
• Sustainability: Collecting of data relating to the environmental impact at all stages of supply chain
• Regulatory compliance: Ongoing compliance with current and emerging regulations
• Visibility: A global view of the entire product lifecycle, from raw materials to the patient.
Food & beverage: product quality and consumer safety with the best inspection technologies
Antares Vision Group provides solutions
products and packaging and consum er safety.
Diamind Line:
• Detection of foreign bodies in pack aged foods and beverages with mi crowave technology: A new techno logical application that revolutioniz es inspection for quality control by overcoming the limitations of current technologies (e.g., X-rays and metal detectors)
• IR spectroscopy for leak checks (food industry): On the line, checks 100% of production for the presence of mi cro-holes in packaging and seals
• Check for the presence of micro-holes, foreign bodies, weight control, seals, and labels: A standalone machine combining several inspections to en sure product quality and safety


• Inspection of tethered caps.
Diamind Factory:
• Monitoring and optimizing processes
• Production efficiency and quality improvement
• Optimizing planning and factory maintenance
• Enabling sustainability.
Diamind Enterprise and Diamind Supply Chain
Sustainability: Collecting of data re lating to the environmental impact at all stages of supply chain
• Regulatory compliance: Ongoing compliance with current and emerging regulations
• Visibility: A global view of the entire product lifecycle, from raw materials to the final consumer.
Cosmetics: unique digital identities for traceability to fight parallel markets and counterfeits and to foster customer engagement
Antares Vision Group offers the cosmetics industry complete hardware and software solutions designed to ensure the quality and integrity of products from production to market, to help fight counterfeits and deter parallel markets, and to protect consumers.
• End-to-end traceability of products: Advanced solutions for serialization and aggregation
• Creation of a unique digital identity for each product: In line with the Digital Product Passport proposed by the European Commission
• Digitization of the supply chain
• Customer engagement. l
RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA icf 53 NO.3 2023 - Supplement
Components
The specialized know-how gained over the years of experience in solid handling, together with the innovative spirit, allows CO.RA. to provide its experience far beyond the supply of a simple plant.
During almost 40 years of experience in terms of pharmaceutical, chemical and cosmetics processes, the attention of CO.RA. to taking care of the details of each component or plant considers as a strong point the presence of technical support and specific consultancy for its customers, of which CO.RA. can boast.
The company takes care of the production process by listening to customer needs, the heart of the development of an effective technical solution, the goal is to contribute to the achievement of your production objectives, for this reason CO.RA. is interested in knowing the characteristics of customer products, carrying out the tests to verify the behavior of the product in contact with CO.RA. machines and customize them to such an extent as to make them perfectly suited to production needs.
On each systems designed and manufacturer inside the production site, it’s possible to use all kind of CO.RA. valves thanks to the versatilities of the range of products.
An example of an integrated System is the Drum Dosing System that can be divided in two categories: Continuous Liner Discharging System and Inflatable / Deflatable ring Dosing System. The operating cycle of the sys-

tem is divided into two distinct phases: gross dosing and small dosing. During the first phase the butterfly opens to allow the quick discharge of 95% of the product to be dosed until the heavy weight limit is reached.
The Continuous Liner Discharging System allows the operator to create a polyethylene continuous liner bag inside a container for the continuous discharging of a product. The product is discharged into the polyethylene liner bag and once the necessary weight is reached, the system allows the operator to cut and pack the bags in a closed cycle.
An empty container is placed on the base of the scale, the liner is pulled until it touches the bottom of the container and the end is closed by means of a clip in order to form the “bag bottom”. At this point it is necessary to push the start button on the dosing terminal, and once the product has been discharged, a clip is placed to close the bag and another clip 10 cm above that one in order to create the necessary space to cut the bag. Finally, it is necessary to remove the container from the base and repeat the cycle described above.
The Inflatable / Deflatable ring Dosing System allows the operator to lock the bag (already placed inside the container)
and to perform the unloading of the product as long as the weight is not reached. Once the weight is reached the operator by the control panel unlocks the bag and the operator can proceed to close it. The working cycle of this system is similar to the Continuous Liner Discharging System, but the closing of the bag is done manually by the operator once it has finished unloading. On this type of system, a dust suction system can be installed which further reduces operator contact with the product.
The terminal of CO.RA. systems are provided with a high tech digital devices on which possible also customize software to control process in relation to customer’s process needs. Inside Control panel, CO.RA. usually supplies in default a module for a remote assistance thanks to which is possible connect the system installed on customer site, directly to the software engineer, in order to have assistance.
Linked to the supply CO.RA. also offers a 360° support which consists of a wide range of services such as:
• Analysis and Verification of P&ID and Customer Technical Specifications;
• Meeting and technical inspections to define the project;
• Design and proposal of a Customized Technical Solution;
• Drafting of Specifications and Documents necessary for the realization of the project;
• Carrying out of Checks and Tests at CO.RA. Technology Center with customer products;
• Project validation (DQ), FAT at CO.RA. or in Smart Services;
• Installation and SAT at the customer’s site;
• IQ, OQ and PQ validation tests, Use and Maintenance Manuals complete with certifications;
• Process and systems engineering;
• Possibility of issuing GAMP5 (title CFR 21 part 11);
• Technical Training for staff training on site or in SMART mode;
• Modification of modification requirements;
• Technical support for drafting SOP;
• Technical assistance on site or in SMART mode;
• Scheduled maintenance;
• Revamping of CO.RA. products;
• Management of complaints and reports of anomalies.
54 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
Almost 40 years of experience in solid handling
Components
Single use system for filtration of HPAPI

Valex-Potent System is a compact Sigle-Use system specifically designed by BEA Technologies to conduct critical filtration and purification of HPAPI and other hazardous substances used in pharmaceutical facilities.
New healthcare challenges and an increasingly ageing population will deeply influence the expectations on the healthcare industry in the coming century. Countless patients worldwide will require the most effective drugs and best medical care. They put their trust not only in the improvement of the healthcare system but also in the industry that supports it and provides the latest pharmacological innovations. BEA Technologies responds to this challenge with constant vigilance, innovation and determination. The goal is to supply the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industry with the best items and tools to support the research and production of new drugs that patients will re-
quire in the coming years. The introduction of highly potent APIs incurs new manufacturing problems and challenges. The production of HPAPIs using hormones and cytostatic drugs can have carcinogenic or mutagenic effects to exposed operators. They should therefore be handled with specific precautions in respect to: operator safety cross contamination between products; environmental protection.
To comply with current best practice, it has been necessary to develop up-graded engineering design for filtration technologies involved in the purification of HP drugs. This requirement to take into account the toxicity and potency implications of the substances involved.
BEA Technologies has evaluated the challenges and has developed a range of filter and separation equipment for the safe production of HPAPI products, which carefully consider handling and containment.
The combined expertise in polymer science and capsule engineering have cooperated to develop a line of housings and disposable capsules safe designed to be used for the purification of Highly potent API’s.
Unique solution - double barrier Valex-Potent System is a compact Single - Use system specifically designed to conduct critical filtration and purification of HPAPI and other hazardous substances used in pharmaceutical facilities. This unique solution Valex-Potent System, provides a “double barrier” and has been recently supplied to CMO production sites. It can accelerate the process of filtration and purification of compounds requiring high level of protection for operators before final release.
BEA Technologies is studying more efficient ways to target drug production of small batches to provide effective, high levels of protection from the effect of toxic, mutagenic or irritant drugs which pose significant challenges to the pharmaceutical industry.

The inspiring philosophy of the system is to satisfy precise requirements of processes using up-to-date technology and to be at the same time easy to handle in full safety conditions for operators.
To manage the required flow, the inlet and outlet connections of the single modules of the system are located to the top of the fil-
ter module with “TC” PP fittings; then the single modules are connected in parallel to a header of incoming product (tank) and to the header of the filtered product. The Filter modules are consisting of internal filter element contained in a plastic capsule fully sealed except for the inlet and outlet connections. This solution is preventing the leakage of any substance filtered. Moreover to guarantee the “Double containment” the capsule containing the filter is further mounted inside a S.S. 316 external housing, that will collect any eventual leakage of substance in case that should be an “hammer stroke” which might damage the capsule PP housing. The system allows to install many different filter capsules inside the same S.S. external housings, to provide the maximum flexibility to filter different products. The heart of the system is a filter capsule which, depending on the particular filter media incorporated, can retain particle contaminants or bacteria and microorganisms. The Valex Potent System is designed to be customized to specific applications or quantities of product to be purified.
RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA icf 55 NO.3 2023 - Supplement
The biggest challenges in coating and their technological solutions
by Oscar Benedi, Laboratory Manager, Romaco Tecpharm
Coating is nowadays an integral part of pharmaceutical tablet and pellet production. Nevertheless, there are some problem areas that have not been adequately solved so far, some of which are nearly accepted, al-
though they have an impact on almost every coating process and entail economic losses. To a certain extent, this is due to a presumed lack of possible solutions – but they do exist and are promising. In particular, a new generation of tablet coaters is
addressing these challenges in an innovative way.
When talking about challenges in coating, there are basically three areas involved: the quality of the coating result, i.e. the quality of the products, the productivity of the coating process and the flexibility of the tablet coater, thus of the process itself.
Quality – How can high-quality coating results be ensured on a continuous basis?
One of the first things that comes to mind when thinking about product quality is the prevention of defects –aesthetic ones such as discoloration, tablet-to-tablet color variability or logo bridging and functional ones such as film cracking, tablet breakage and tablet edge or surface erosion. While the purely aesthetic defects can sometimes be tolerated, the entire batch is at risk if a functional coating is compromised. Depending on the product, this can mean losses in the six-figure range. It is therefore not surprising that this area is the one that all com-

56 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
Is coating as efficient and economical as it could be? there are some problem areas that have not been adequately solved so far. A new generation of tablet coaters is addressing these challenges in an innovative way.
Technologies
panies producing for the pharmaceutical industry are grappling with and that each has implemented its own procedures to do so. As differentiated as these approaches may be in detail, it is always a matter of stabilizing the coating process by regularly checking parameters and adjusting them if necessary. The common method for increasing and simplifying this process control is currently to improve the technical feedback – i.e. how well and quickly the technical systems give the operator feedback on process and product quality. After that, it is the operator’s responsibility to react accordingly. This is definitely a solution that works, but is it enough to achieve real process stability?

Reality is that this approach leaves a relatively large risk for errors and inaccuracies, because the regulation and control of the coating process is absolutely dependent on the expertise, experience and capability of the operator. What if there is no suitably skilled operator available due to the shortage of trained workers in the labor market? What if the expert retires or simply is
on vacation and there is no appropriate replacement? And if a fitting operator is available, what happens with long coating processes that require 20 or more hours and hence include shift rotations? All this and similar scenarios aside, even for the most experienced operator it is not always easy to get the ideal coating settings and keep track of all the parameters, especially with batch size changes, complex coating processes or demanding products that are, for example, very sensitive to humidity or temperature. The solution to this systemic uncertainty is to automate the coating process to a larger extent, including not only the control of the relevant parameters and feedback to the operator, but also their fully automatic adjustment where required. The new TPR Optima perforated coating pan from Romaco Tecpharm is capable of doing so. It monitors parameters such as temperature, humidity, flow rate, bed tablet level and much more, sets up the predefined optimal coating conditions for the specific product and thus minimizes the risk of losing parts of
or entire batches. One could say the TPR Optima tablet coater creates the absolutely reproducible coating process – irrespective of the complexity. Of course, the expertise of the operators is still needed and they can intervene manually, if they choose to. But the possibility of almost complete automation ensures that you no longer have to be an expert to achieve consistently high product quality with this technology. It is somewhat like having an autopilot. But what does this automatic self-regulation look like? This can be exemplified very well in the context of the second main problem area, where automation is also the means of choice for optimization.

Productivity – How can the coating process become more resource and cost efficient as well as sustainable?
The deficiencies in the productivity of the coating process were and are partly accepted as a given. An example is the amount of “wasted” suspension that is widely tolerated. It is currently common to plan for 50 per cent more suspension than is theoretically needed to coat a product, because a
Technologies
A new generation of tablet coaters –the TP R Optima from Romaco Tecpharm
RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA icf 57 NO.3 2023 - Supplement
loss of up to 40 per cent is considered normal. With “standard” coatings, this may not mean any major financial losses, but with functional coatings, for example coatings with API or controlled release coatings, the situation is quite different. But even with standard coatings there are hidden costs in the form of cleaning and disposal expenses, not to mention logistical expenses, because if more suspension is needed, more must be transported and stored. On top of all that, this form of “resource wastage” and “environmental impact” is no longer an option in the long run, given the global change in awareness of sustainability and the corresponding legal regulations. Producing companies must react now or they will fall behind.
Here, automation is the answer as well, and to be more precise, especially the automatic adjustment of the suspension application and drying. Technically, this is implemented in the TPR Optima as follows: Using sonar technology, acoustic wave sensors continuously measure the distance between the spray nozzles and the tablet bed, which may vary depending on the process that is conducted. If modifications are required regarding the ideal spray distance or the set spray angle, the intelligent system carries them out by means of a nozzle arm with a three point extension mechanism during the ongoing process – the machine does not have to be paused for this purpose. An automatic set of air exhaust flaps, which can be opened individually and continuously, allows absolutely precise regulation of the path taken by the air flow through the tablet bed, ensuring maximum drying efficiency. A suspension application without losses is at present not yet possible, but with the new technical possibilities of the coating technology from Romaco Tecpharm only 10 to 15 percent more coating medium is needed instead of 40 percent. And that makes a significant difference. But the “sus-
tainability factor” of the automation solution does not end with the reduction of spray loss and water consumption during cleaning. The associated more efficient drying and the possibility to make adjustments without interrupting the coating process reduce process times by hours. And prior to the actual coating, time is additionally saved in the fine-tuning and preparation of a new batch, as the TPR Optima virtually adjusts itself to the recipe and the associated parameters. It also offers the option of taking product samples while the process is running. In doing so, regulatory requirements can be met without sacrificing time. All this combined results in substantially lower energy usage. Another special feature of this technological adaptability is immense batch size variability within a single machine, which not only increases productivity, but above all brings flexibility – and that leads to the third main problem area.

Flexibility – How can companies be best prepared for trends, altering market conditions and changing customer requirements?
Almost everyone who realizes coatings has to deal with scale-up and scale-down procedures in some form or another sooner or later – for example:

- when producing for various countries, as Multi Nationals do on a daily basis, and batch sizes have to be adapted to the different market requirements
- when validations have to be carried out and about 10 per cent of the subsequent batch sizes have to be manufactured for this purpose
- when producing under contract, where a wide range of batch sizes must be processed
- when the switch from laboratory to production scale is pending
Technologies 58 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
Automatic extendable spray arm with self-adjusting movable spray nozzles allows for variable batch sizes from 10 to 100% The batch volume and the tablet bed inclination are measured continuously using sonar technology
- or when market demands simply change over time. This aspect is often not taken into account when investing in coating systems and other machines, although it is very important. After all, life cycles of more than 20 years are not uncommon for high-quality production equipment, and the market requirements almost inevitably change over such a long period. Therefore, the ability to scale batch sizes is basically about future-proofing for all coating providers.
But why is scaling up and down a challenge? Firstly, it means that companies currently need at least two machines, one for producing smaller batch sizes and one for larger batch sizes, as most coaters do not have a large enough batch size variability. Usually they can only go down to 40 per cent of the maximum batch size at the most. The resulting need for several machines is associated with very high investment costs, energy expenditure and space requirements. In addition, the parameters cannot simply be transferred from one machine to another – not even if they are the same type and brand. Consequently, a relatively large number of manual adjustments have to be made, and here again the problem of ensuring high quality and uniformity across all products, regardless of the machine or batch size, arises. Not to forget, of course, the time and work that goes hand in hand with manual adjustments. The automated adaptability of the TPR Optima also represents an approach to improvement here. With the ability to monitor and adjust to batch sizes, the tablet coater achieves a batch size range from true 10 to 100 per cent filling volume with the same drum. This eliminates the need for multiple machines just because of different volume requirements, the time and manpower it takes to set up the right parameters for different systems and the
risk of errors and imprecisions. What is more, this not only applies to validations and batches of different sizes, but also to volume changes within a single coating process, such as coatings with multiple layers. It could be argued that coaters with this range have been around for a while, and that is true, but the batch size variability of these technological solutions necessitated drum changes and manual adjustments, which removed the problem of purchasing multiple machines, but not the risks of manual intervention. Moreover, the drum changes created extra labor and cleaning efforts, including for different batches with the same active ingredient. This also becomes largely obsolete with the use of only one drum.
A final aspect of flexibility in coating is the possibility to change the coating medium itself without major technical alterations. There are several reasons why this could be required. For example, a reformulation may be a necessity due to imminent and acute bans on formulation components, as in the case of dioxide titanium, which is already banned in food production in the EU. An adequate substitute is presently being sought, also for pharmaceutical production. Trends towards more natural ingredients such as the departure from alcohol in favor of water-based suspensions may also call for recipe modifications. Again, automated parameter adjustment provides advantages. In the demanding search for new recipes, the experts can concentrate on the formulation and leave the rest to the machine. Apart from that, process times are shorter, which further facilitates R&D activities as more formulation trials can be implemented in a given period of time. Saving time is also the big issue with water-based suspensions, which have longer drying phases. Due to more efficient drying with
the “full” automation of the TPR Optima, this does not have the same impact as with previous technologies. As a matter of fact, the best possible drying is particularly important in this case, as too much humidity is one of the main factors for product defects.
Conclusion and outlook
As illustrated, there is significant optimization potential in coating that can be exploited through a higher degree of automation. Shorter process times, continuously high product quality, time and cost savings and resource conservation are just some of the gains. Tablet coaters like the TPR Optima with these technological capabilities will certainly represent the future of coating and are already supporting innovation: Finding new active ingredients is a very long-term task, which is why many new products will be developed in the next few years through the recombination of known APIs or new forms of drug delivery. Coating will play a central part in this endeavor. There will be more products with active ingredients in the coating layers and coated products that have not typically been coated in the past. The precondition for these new developments are and will be automation technologies that stabilize the coating process, make it more efficient and sustainable. l
Continuously opening flaps control the air flow and path and thus enable precise coating and drying processes according to the respective batch size

RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA icf 59 NO.3 2023 - Supplement
Technologies
The life science companies discovering new technologies
The underlying growth of the life sciences sector (pharmaceutical, biotech, and medtech) is strong at a combined US$2.83T. While growth has recently remained strong through increased demand and throughout the pandemic response (particularly with COVID-19 vaccines), we are seeing life sciences companies shifting their portfolio strategies with the hope of continuing this growth trajectory by any combination of acquisitions, divestitures of assets deemed not core to growth; investments in R&D and an accelerated embracing of digital; and data technologies which are finally beginning to scale in their adoption. Significant challenges remain though, such as the increasingly competitive mar-
ket, the changing and evolving regulatory landscape, increasing pricing and reimbursement pressures, and growing demands from patients and health care providers for more effective medications and experiences as they manage health and well-being. All of this also while in the face of broader geopolitical and economic uncertainty.
To maintain their historical and expected growth, life sciences companies are focusing on innovation and collaboration for value creation. They are investing in bringing and expanding platforms like gene and cell therapies, new platforms like mRNA, expanding indications of existing and known biologics platforms, developing novel medicines like antibody drug conjugates (ADCs), and devel-
oping novel approaches to make existing medicines even more effective (whether through better diagnostics or exploring different routes of administration). And they increasingly realize they can’t do it alone – they are more willing to collaborate with other stakeholders in the health care ecosystem to share knowledge, expertise, and resources. Digital technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), automation, and blockchain are scaling and creating efficiencies that will lower development and manufacturing costs and accelerate drug research and development efforts. At the same time, national and local governments around the world are tightening regulations and seeking greater transparency for drug reviews, approvals, pricing, and reim-

60 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA Insights
The life sciences sector is growing: what has had forward momentum is mainly R&D and new technologies that were still in the planning stages in 2020 and now are an integral part of many companies.
bursement. Amid the volatility of the pandemic and geopolitical conflicts affecting shipping and logistics, biotechnology, pharmaceutical and medical device companies see the need to increase flexibility, streamline manufacturing processes, and enhance real-time tracking. As a result, they are shifting away from planning for inflexible accuracy to designing agile supply chains that can flex and adapt quickly to changing conditions – and multiple scenarios.
Meanwhile, patients and health care providers are demanding more innovative and effective treatments. Patients increasingly want more personalized care that meets their individualized needs allowing them to access information and care at times and locations that fit their schedule. Meeting these demands requires more than just new technologies and processes. It also requires a stronger focus on patient-centricity and an advancement of value-based care.
R&D
Innovation is fundamental to the global life sciences sector, even as pricing pressures, growing market share for generic drugs, and looming patent expirations remain significant challenges. In the coming year, life sciences companies will continue to build on advances such as translational medicine, big data analytics, and digital innovations in research and development. In addition, other advanced technologies will emerge to improve research and development (R&D) efficiencies, boost long-term returns, and enhance the patient outcomes and experiences. R&D innovation is one of the top actions that 91% of life sciences organizations plan to invest in more heavily during 2023, according to a Deloitte survey of 60 senior life sciences executives from
Source: Deloitte analysis, 2022.
Please note: 2013-2019 data includes the 15 companies of the combined cohort; 2020-2022 data includes the results of the top 20 companies by 2019 R&D spend. See appendix 1 for the data of each cohort. Compared to last year’s report 2020 and 2021 figures have been restated to include the top 20 companies by R&D spend as of 2020.
Return on late-stage pipeline, 2013-22. Please note: 2013-2019 data includes the 15 companies of the combined cohort; 2020-2022 data includes the results of the top 20 companies by 2019 R&D spend. Compared to last year’s report 2020 and 2021 figures have been restated to include the top 20 companies by R&D spend as of 2020
Life sciences R&D organizations are under increasing pressure to generate sustainable returns on investment given shifts in the market, regulation, and reimbursement practices. While the industry has recently produced groundbreaking innovation such as mRNA vaccines and platform technology, which have the potential to truly transform global health, scaling the impact will require reinventing and realigning traditional R&D models.
Real-world evidence (RWE), new approaches to clinical trials and partnerships, and artificial intelligence (AI) have the potential to transform R&D—from drug discovery and development to regulatory approval.
The growing benefits of RWE
with a year earlier. This increase was largely because of increased clinical cycle times, which were compressed during the pandemic.
• The average forecast peak sales per pipeline asset fell to US$389 million from US$500 million in 2021 because of the successful commercialization of high-value assets.
RWE refers to clinical findings about the use and potential benefits or risks of medical products based on analysis of data such as patients’ health status or the delivery of care. RWE helps life sciences organizations better understand disease progression, monitor patient safety, and assess clinical and cost effectiveness. RWE also can help organizations adjust instructions for how medications may be used, administered, or labeled.3
During the COVID-19 pandemic, RWE enabled the sector to innovate faster by understanding the incidence and severity of the virus and its variants for vaccine and drug development. RWE helped vaccine developers predict global hotspots, collect better data from diverse racial and ethnic groups, and understand vaccine effectiveness across age, gender, race, and ethnicity to determine the need for boosters.
biopharmaceutical and medical device manufacturers with revenue of more than US$500 million. Almost half (48%) of the executives in the same survey said they are cautiously optimistic about the sector’s outlook in the coming year. R&D investments in composition, drug pipelines, clinical trials, and processes for regulatory approval of new assets will play a critical role in the industry’s success, but the financial challenges on achieving a return are significant.
Deloitte’s analysis of the top 20 pharma companies found that:
Increasingly, RWE is playing an expanded role in R&D in helping life sciences organizations design clinical trials, understand the heterogeneity of treatment effects, and inform price and forecasting assumptions.
Though life sciences organizations lagged other sectors in adopting RWE, it now is a growing part of the decision-making process. Companies are getting faster at collecting and analyzing RWE. Ninety percent of the biopharma executives surveyed by the Deloitte US Center for Health Solutions said their organizations are using RWE to speed product life cycles and design synthetic control arms and adaptive trials. These processes are expected to increase in the next two to three years.4
• Internal rates of return (IRR) for late-stage assets fell to 1.2% from 6.8% a year earlier. Indeed, IRRs have resumed a downward trend that began in 2014, slipping below the 1.5 rate achieved in 2019.
• R&D spending among the 20 biggest companies fell to US$139 billion in 2022 from US$141 billion in 2021 (though it remains higher than it was in 2020).
• Average asset development costs increased in 2022 by US$298 million, to US$2.28 billion, compared
Life sciences R&D organizations are under increasing pressure to generate sustainable returns on investment given shifts in the market, regulation, and reimbursement practices. While the industry has recently produced groundbreaking innovation such as mRNA vaccines and platform technology, which have the potential to truly transform global health, scaling the impact will require reinventing and realigning traditional R&D models. Real-world evidence (RWE), new approaches to clinical trials and partnerships, and artificial intelligence (AI) have the potential to transform R&D—from drug discovery and development to regulatory approval.
RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA icf 61 NO.3 2023 - Supplement
11
Figure 1. Return on late-stage pipeline, 2013-22
30 25 20 15 10 5 0 -5 -10 -15 -20 -25 6.5 7.2 6.1 5.5 5.4 3.6 1.5 2.3 6.8 1.2 Top performer Bottom performer Mean Median First quartile Third quartile 201320142015201620172018 Static IRR (%) 2019202020212022
Insights
The post-COVID outlook
The response to the COVID-19 pandemic has created new opportunities for innovation in the life sciences sector. In the coming years, it should continue to explore and embrace these new approaches, such as identifying programs with a high probability of success and ensuring they progress seamlessly from one phase of development to the next.
innovation and both real-time and remote monitoring tools and diagnostics. Organizations also may develop extensive data and intelligent workflow to support improved decision-making.
Pharma companies are now facing up to the need to frame their patient-centric strategies for operating in a new customercentered, digital ecosystem
Other benefits from the pandemic response include expanding dialogue with regulators to accelerate development of urgently needed therapies, streamline trial protocols to avoid deviations, speed development time and strive for greater diversity in clinical trials to ensure subjects match the prevalence of diseases across racial and ethnic groups.
COVID-19 has highlighted the vulnerability of R&D to the traditional, site-based clinical trial system.
Deloitte surveyed R&D and commercial leaders at both large and small biopharma companies, most of whom said they expect the shift to decentralized, patient-centric trials to continue for the long term. They also anticipate more reliance on
Organizations that can continue to capitalize on the momentum gained by accelerating digital transformation programs, strategic shifts, and commercial reorganization before or during the pandemic, will be well-positioned to benefit from the more agile post-COVID market in 2023.
Supply Chain management
Global life sciences companies are trying new approaches to respond to hidden risks within supply chains. Supply chain management has long relied on static assumptions. In this deterministic view, organizations create forecasts using historical data to design specific scenarios likely to result from familiar circumstances. For enterprises using an array of suppliers for a particular product, the deterministic view dictates that the business can absorb a shock if one of its suppliers abruptly halts production – with the understanding that another provider can take up the slack. When unanticipated emergencies arises, such as a massive breakdown of supply and distribution channels, having a range of suppliers might not be enough to overcome the disruption. Amid the volatility of the pandemic, geopolitical unrest affecting shipping and logistics, and inflation at a four-decade high, an alternate view on supply chains is emerging in the global life sciences industry. This model, known as the probabilistic approach, aims to increase flexibility, streamline manufacturing processes, and enhance real-time tracking. Within this framework, biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies
are shifting away from planning for inflexible accuracy to designing agile supply chains that can bend and adapt quickly to changing conditions – and multiple scenarios. This complex picture includes a rapidly diversifying portfolio of next-generation treatments such as personalized cell and gene therapies that require specialized manufacturing facilities, ultra-low temperature requirements, and last-mile delivery to treatment centers and patients.
Patient centricity

Habits, capabilities, and data have all changed significantly in the last year. Three-fourths of people around the world now have experience with at-home tests for a global virus, and companies are increasingly able to access, interpret, and act on the billions of patient data points. And patient expectations and their ability to voice them have risen. The conditions for true(r) patient centricity are here.
On a given day, people actively participate in their own medical plans, treatment, and disease research across millions of touchpoints in the patient journey. There are more than 435,000 active clinical trials underway across the globe, and more than two million different types of devices spanning more than 7,000 groups of instruments, machines, and software used for medical purposes. To help capture the increasing amount of data from these inputs, devices such as fitness trackers provide around-theclock monitoring. Together, these insights are propelling life sciences enterprises toward the next frontier of patient-centricity: the deployment of decentralized diagnostics and direct-to-consumer channels and solutions, the gathering of real-world information from wearables and sensors, and the creation of new digi-
Decentralized diagnostics
62 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
2023 Global Life Sciences Outlook | Patient centricity
virtual checkups and smartphone-enabled diagnostic tools — and with COVID pandemic habits now increasingly fewer patients are visiting centralized care sites. Instead, life sciences companies can collect data through devices from the comfort of a patient’s home. In China, where 95% of the population is covered by social health
Pharma companies are now facing up to the need to frame their patient-centric strategies for operating in a new customer-centered, digital ecosystem. analysis
tal alliances to achieve optimal patient outcomes. With the connected health care ecosystem, life sciences companies can expand their patient-centric ambitions beyond drug and medical device manufacturing. Increasingly, pharmaceutical companies and medical technology developers are collaborating with third parties to create more digitally interoperable systems and thus getting closer to 3600 of patient understanding and experience. In building a strategy to enhance their understanding of patients, companies are making targeted investments in technology that can tailor product offerings and navigate complex rules as they learn what patients are experiencing – and what they’ll need in the future.
Digital transformation
COVID-19 has had a profound impact on the life sciences sector, including the digital transformation that it ushered into the sector at scale and in some cases overnight. Before the pandemic, life sciences organizations, which include biopharma and medtech companies, lagged other industries in digital innovation. However, as COVID-19 spread, they quickly embraced a variety of technologies that allowed them to run their businesses remotely or virtually.1 Innovation projects that had been on the books for years received funding and advanced rapidly. Now three years later, we can see the impact of this digital transformation: what works, what is still in progress, and what remains elusive. During the pandemic, cloud technologies and platforms gave organizations the scale and flexibility to enable employees to work remotely and collaborate, which includes storing and sharing data across third-party networks and enabled by artificial in-
Which of the following best describes your experience with each digital innovation technology within your organization?
However, not all technology has been adopted equally. Biopharma more than the Internet of Things (IoT) or blockchain (Figure 1). Nevertheless, companies view digital solutions, and those companies that continue
Figure 1. Biopharma’s experience with digital technologies
Which of the following best describes your experience with each
However, not all technology has been adopted equally. Biopharma companies have embraced cloud platforms, AI, and wearables more than the Internet of Things (IoT) or blockchain (Figure 1). Nevertheless, the pandemic has fundamentally changed how these companies view digital solutions, and those companies that continue to embrace innovation will gain a competitive advantage in
Source: Deloitte’s Biopharma Digital Innovation Survey 2021
Source: Deloitte’s Biopharma Digital Innovation Survey 2021
Among leading biopharma and medical technology companies, digital CIOs, are becoming vital to business operations. Life sciences organizations how it’s integrated into the business.
Among leading biopharma and medical technology companies, digital solutions that were once seen as long-term CIOs, are becoming vital to business operations. Life sciences organizations are now focused not on the technology how it’s integrated into the business.
Innovation tightly integrated into operations has worked that see really gain traction are the ones that are farther away from
‘‘Innovation tightly integrated into operations has worked that best,” Hersch says. “The things that we’re still see really gain traction are the ones that are farther away from operations. 5
Biopharma’s experience with digital technologies is highest in cloud, AI, and wearables


For example, biopharma companies are using data to improve site chains, both of which have been effective. Technology further removed safety, have been slower to advance.
For example, biopharma companies are using data to improve site selection for clinical trials and the oversight of chains, both of which have been effective. Technology further removed from operations, such as applications for safety, have been slower to advance.
Source: Deloitte’s Biopharma Digital Innovation Survey 2021
Nevertheless, the pandemic has fundamentally changed how these compa-
for patient safety, have been slower to advance. l
Among leading biopharma and medical technology companies, digital solutions that were once seen as long-term projects for CIOs, are becoming vital to business operations. Life sciences organizations are now focused not on the technology itself, but how it’s integrated into the business.
Innovation tightly integrated into operations has worked that best,” Hersch says. “The things that we’re still waiting to see really gain traction are the ones that are farther away from operations. 5
RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA icf 63 NO.3 2023 - Supplement
‘‘ ‘‘
‘‘
36
In this issue, we spoke about...
INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
MANAGING DIRECTOR: Simone Ghioldi
EDITORIAL BOARD: Alessandro Bignami (a.bignami@interprogettied.com), Eva De Vecchis (e.devecchis@interprogettied.com)
GRAPHIC LAYOUT: Studio Grafico Page Vincenzo De Rosa, Rossella Rossi - www.studiopage.it
COLLABORATORS: Oscar Benedi, Frederik Effenberger, Florian Kraftschik, Nicolas Livraghi, Andrea Villa
INTERPROGETTI EDITORI S.R.L. via Roggia Borromea, 16 - 22060 Carugo (CO)
Editorial, sales and subscription offices Tel./fax +39 031 3665163 www.interprogettied.com
SALES DIRECTOR: Marika Poltresi
SALES: Simone Ghioldi (vendite@interprogettied.com)
ADMINISTRATION: amministrazione@interprogettied.com
SALES OFFICE: Raffaella Sepe (raffaella@interprogettied.com)
© Copyright Interprogetti Editori Srl
The columns and news are realised by the editorial team. All rights reserved – All reproduction, even partial, of published material without the publisher’s consent is strictly prohibited.
SUBSCRIPTION RATES:
Italy: ordinary mail delivery EUR 45.00, COD delivery EUR 48.00
International: ordinary mail delivery EUR 60.00, express delivery within Europe EUR 70.00
Express delivery to Africa, America, Asia: EUR 85.00
Express delivery to Oceania: EUR 100.00
Single copy: EUR 10.00
The VAT on subscription prices as well as on the price of single copies is paid by the publisher pursuant to article 74, sub-section 1, point C of the Italian DPR n. 633 of 26th Oct 1972 and subsequent amendments and additions. It is therefore not possible to issue invoices.
Registered at the Court of Milan on 7 May 2010 no. 259
Managing Director: Simone Ghioldi
Printed on 27th July 2023 at Aziende Grafiche Printing S.r.l.
Via Milano, 5 - 20068 Peschiera Borromeo (MI)
Information to be given to the data subject - art. 13, legislative decree 30th June 2003, no. 196. Personal data are processed, with or without the help of electronic means, by Interprogetti Editori S.r.l. - via Roggia Borromea, 1622060 Carugo (CO), Italy, to send you the magazine requested and for the operations connected. The processing of data will be carried out by the persons who have been committed by the controller the task of performing the processing operations connected with recording, modification, processing of personal data and printing, fulfilment and delivery of magazines, commercial and fiscal issues, accounting and call center activity. With reference to art. 7, Italian legislative decree 196/2003, you have the right to access to your data, modify, update or cancel data or to object to their processing for direct marketing purposes, by writing to the controller, and ask for the list of data processors.
Publisher’s information to public – art. 13, legislative decree 30th June 2003, no. 196. With reference to Italian Personal Data Protection Code and art. 2, point 2 of Code of Conduct for the processing of personal data in the exercise of journalistic activities, Interprogetti Editori S.r.l. informs that the place where personal data, images and photos are kept is Carugo (Italy). Data can be used by journalists, free-lance journalists, persons in the role of trainee journalists and persons who carry out processing for the publication or occasional circulation of essays, articles and other intellectual works for the purpose of the exercise of their journalistic or similar activities. The processing of data will be carried out by the persons mentioned above and by persons in charge of printing and publishing activities. With reference to art. 7, Italian legislative decree 196/2003, you have the right of access to your data, modify, update or cancel data or to object to their, by writing to Interprogetti Srl, and ask for the list of data processors. It is understood that the provisions concerning professional secrecy in the journalistic profession shall be left unprejudiced as related to the source of the information if a data subject requests to be informed of the source of the personal data processed by journalists.
64 icf RIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA
RIVISTA DELL’ icf YEARXIV SUPPLEMENT ISSUE NO.3 2023
ACHEMA 24, 27, 36 ANTARES VISION GROUP ........................ 2nd COVER, 52 BEA TECHNOLOGIES ................................ 54, 3rd COVER BIOMAY 32 BORMIOLI PHARMA.................................................... 29 BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB ............................................. 17 BRUNO WOLHFARTH ........................ FRONT COVER FLAP CO.RA. ................................................ 54, BACK COVER COPERION ................................................................ 18 CSV LIFE SCIENCE GROUP .........................................2-3 DELOITTE.................................................................. 60 ECHA ....................................................................... 16 EFFEBI ..................................................................... 15 ENDRESS+HAUSER...................................................... 44 EVOTEC..................................................................... 17 FLUORTECNO ..................................................... INSERT GIUSTO FARAVELLI ............................................. 20, 47 HEXAGON .......................................................... 31, 50 ILMAC 26 INTERPACK ............................................................... 12 ITELYUM ............................................................ 28, 39 LANXESS 20 LECHLER ............................................................. 42-43 MONTENEGRO........................................................... 18 NERVIANO MEDICAL SCIENCES 18 NUOVA GUSEO .......................................................... 21 OLON GROUP ............................................................. 16 OQEMA .............................................................. 11, 20 PHARMAP 2023 20 POWTECH ................................................................. 22 PRECISION FLUID CONTROLS ..................................... 41 PROCESS SERVICE ..................................................... 19 PVS GROUP ..................................................... COVER, 8 ROMACO 56 SOLVAY 28 SOLVE THERAPEUTICS ................................................. 18 STERILINE.......................................................... 17, 30 SWAN ANALITICA ..................................................... 29 TEXPACK .................................................................... 7 VTU ENGINEERING ................................................ 1, 32














NO.3 2023Supplement ICFRIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA Interprogetti Editori S.r.l. NO.3 2023Supplement ICFRIVISTA DELL’INDUSTRIA CHIMICA E FARMACEUTICA Interprogetti Editori S.r.l.
ULTRA GUAFLON


sealing materials ™
4.0
GUAFLON™ ULTRA
Ultimate certified sealing solution for flanged couplings that require electric conductivity.

Advantages
This unique PTFE (poly-tetra-fluoro-ethylene) matrix allows electrostatic charges to freely move from the inner white layer in GUAFLON SB TM to the outer layer in GUAFLON EXD TM thus avoiding the creation of sparks.
GUAFLON ULTRA TM avoids the need of expensive and hassling earthings for piping and equipment; still, this special seal segregates the process fluid from any contamination of black particles.
Characteristics
• Inner white core in GUAFLON SBTM (PTFE charged with Barium Sulphate - modified and stabilized formula). Approvals and certifications FDA 177.15.1550 and UE 10/2011.
Outstanding chemical resistance:
• Suitable for all chemicals within the range PH 0 - 14
• Suitable for use in Food&Pharma environments
• Outer reinforcement in black, conductive and antistatic GUAFLON EXDTM
V
Suitability
• Chemical, Food and Pharmaceutical Industries.



• Water treatment.
• Handling of solvents, gasses and fluids at high speed.
• Permeating chemicals such as chloridric acid, Bromine and other similar chemicals

FOOD INDUSTRIES
HEATING AND COOLING EQUIPMENT
CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES
STEAM BOILERS VALVES

DRINKING WATER SYSTEMS
PAPER MILLS
4.0 sealing materials
PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRIES
GAS DISTRIBUTION
OIL & GAS
PUMPS AND COMPRESSORS
HIGHLY AGGRESSIVE ACIDS AND BASES

CFR 21 part. 177. 1550
Materials Science and Technology
Electrostatic charges
IEC 60093
 28091 - 3 TF CZ OO
TA LUFT 2440
28091 - 3 TF CZ OO
TA LUFT 2440
Empa
GUAFLON™ ULTRA physical properties
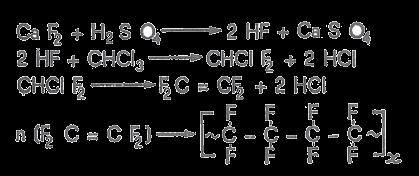

Cod.
JBED
PTFE with Barium sulfate & special conductive filler
PROPERTIES
EXCELENT
VERY GOOD
-200°C +250°C (205°C) 11> 40 34,7 Does not stand flames Not favoring 30 ÷ 130
MY (PSI) 2 2,5 80
Warning
Sealing granted in all circumstances
Sealing effectiveness relies on type of fluid, type of flange and thickness
Contact Fluortecno technical office
MECHANICAL RESISTANCE Maximum pressure bar Creep relaxation % Recovery % Tensile strength N/ mm2 Fire point Bacterial growth Superficial resistivity Ω White black
All data present in this brochure are based on laboratory trials. Properties and applications listed in this brochure are standard. Singular, peculiar applications cannot be extracted from the listed data without conducting specific analysis and evaluations.
In presence of steam and/or particularly aggressive fluids, maximum operating temperature must include a 25% safety margin. We therefore encourage to contact Fluortecno technical office for further clarifications.
SEALABILITY PERFORMANCE THERMAL RESISTANCE CHEMICAL RESISTANCE ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY
SUPERIOR
GOOD MODERATE Colour Composition Mix-Max Temperature (continuos)
Mechanical properties



The exclusive isostatic and simultaneous moulding of the two materials provides the seal with a natural, multidirectional stability thus granting an excellent sustainability of thermal cycles and a superior resistance to permeation due to the barrier effect of the double sinterization.


Tests
Mechanical traction tests
Pic. A shows the perfect multidirectional sinterization of the two materials.

In all traction trials the eventual rupture does not take place along the sinterization surface.
Compression tests
(200 Nm for 1hr. at 250°C)
BEFORE AFTER GUAFLONTM ULTRA BEFORE AFTER CONVENTIONAL MULTIDIRECTIONAL GASKET
4.0 sealing materials
Pic. “A1”
Pic. “A2”
Electrical Properties
All laboratory trials have shown that GUAFLON ULTRATM gaskets, when compressed with variable clamping, possess a superficial resistivity of 30 - 130 Ohms thus granting the equipotentiality of the two ends.





TEST REPORTS
SUBJECT: determination of electrical resistance on a gasket tightened in a flanged coupling at increasing tightening loads
Electric resistance (flange tightening load 5 kN)
Electric resistance (flange tightening load 10 kN)
Electric resistance (flange tightening load 15 kN)
Electric resistance (flange tightening load 20 kN)
Supply conditions
Flange gaskets from ND 15 to ND 300 (1/2” - 12” ANSI) and above
Standard thickness 2 mm. Optional 3 mm
Different shapes and form factors are available upon request at our Bergamo Fluortecno facility
Ω Ω Ω Ω 130 60 40 30 im 606/2016 im 606/2016 im 606/2016 im 606/2016
GUALFON ULTRATM Cod. JBED DN50 TEST METHODS
SAMPLE
Contact us: Tel. +39 035 48.74.077 FT@guastallo.com www.guastallo.com www.guaflon.com 4.0 sealing materials V


FLUORTECNO srl Via delle Imprese 34/36 - 24041 Brembate (BG) - Tel. 035 48.74.077 www.guastallo.com - E-mail: FT@guastallo.com EXPERIENCE App “Guastallo”





































 *Validation Specialist, PVS Srl
**Senior Validation Manager, PVS Srl
*Validation Specialist, PVS Srl
**Senior Validation Manager, PVS Srl



















































































































































 28091 - 3 TF CZ OO
TA LUFT 2440
28091 - 3 TF CZ OO
TA LUFT 2440