Lean Management System ◾ 135
should analyze their work and have the latitude to determine how it would best meet the needs of stakeholders. With standard work, the employees doing the work are key players in developing the standard work process. That’s why it is important to deploy the concept of standard work and other tools not in isolation, but in the context of a lean culture. This makes it imperative for healthcare employees to learn to analyze their processes, identify waste and other non-value-added activities, and prevent mistakes. Standard work becomes an opportunity to help employees do a better job. Rather than learning by mistakes, new healthcare employees can quickly learn to use the best practices of those who developed the standard work. If standard work is efficiently developed, it should allow virtually anyone to perform the work without variances in the desired output. Work can be described as standardized if the sequence of job elements has been efficiently organized and is repeatedly followed by the staff. Each step in the process should be defined and must be performed repeatedly in the same manner. Any variations in the process will most likely increase cycle time and cause quality issues. Standardized work typically describes how a process should consistently be executed and documents current best practices. It also provides a baseline from which a better approach can be developed, allowing continuous improvement methods to leverage learning.
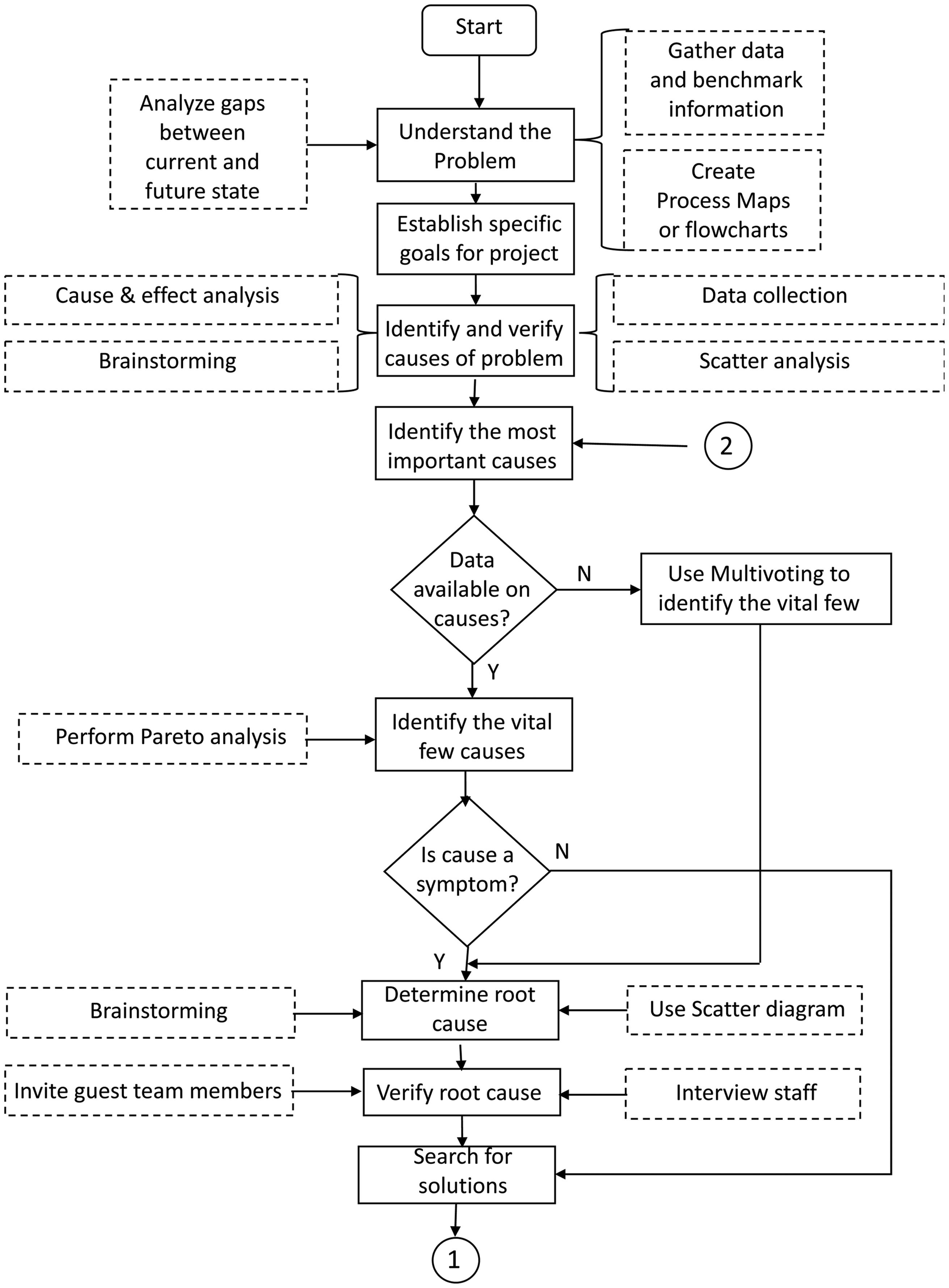
The Process The process begins with the team obtaining the answers to the following questions: ◾◾ Who operates the process? ◾◾ Where is the process located? ◾◾ What specific steps are required to execute the process? Are the steps consistent with evidence-based practice? Are there sequence requirements for the steps? ◾◾ What are the special characteristics of the workspace (storage, work cells, tool storage, etc.)? Is the layout of the work area compatible with the goals of the process? ◾◾ How many people are required to operate the process? ◾◾ What are the prerequisite knowledge, licensure, and skills required to execute the process? Do the process operators possess the prerequisite knowledge, licensure, and skills?