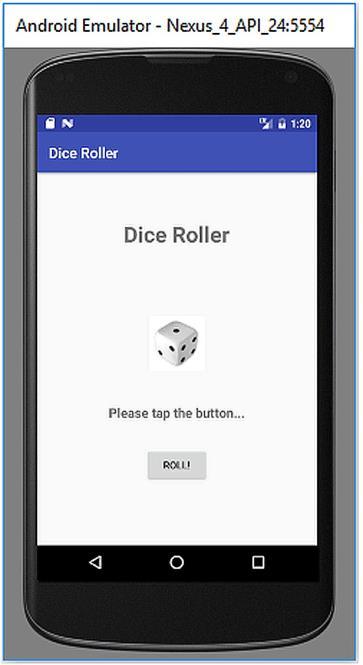
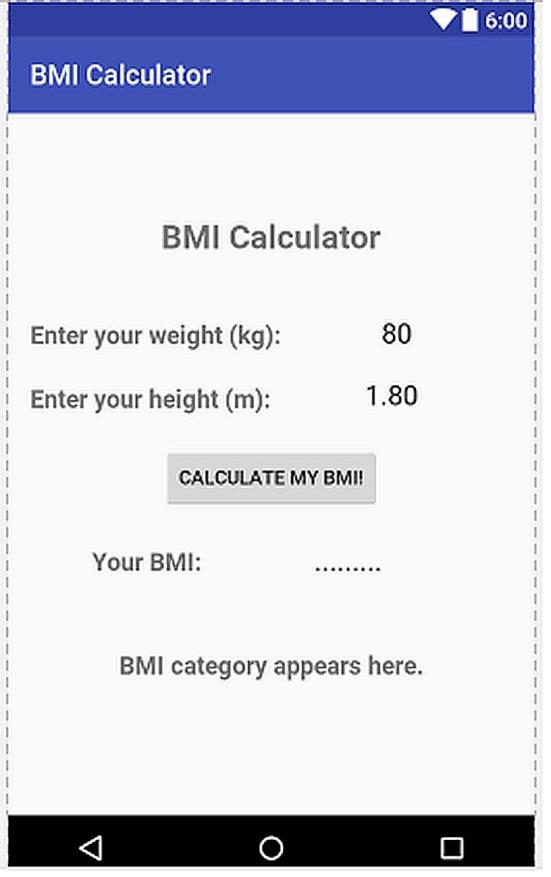
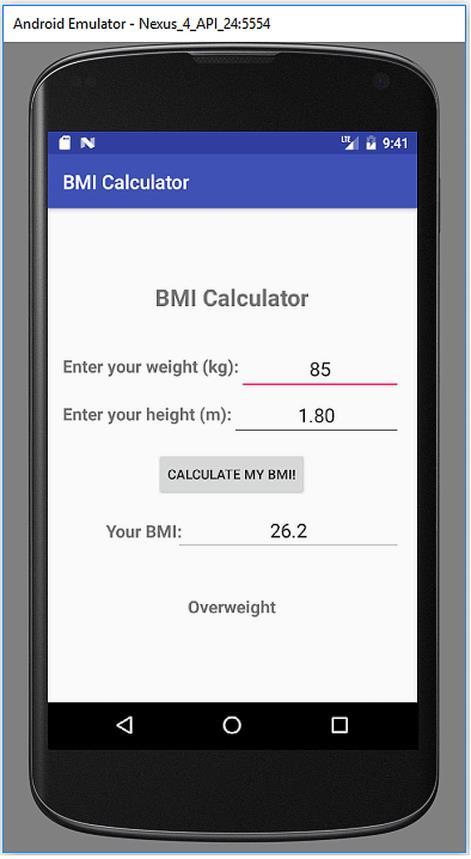
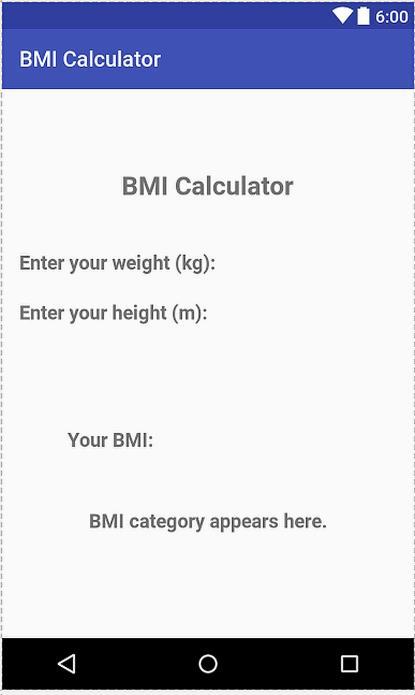
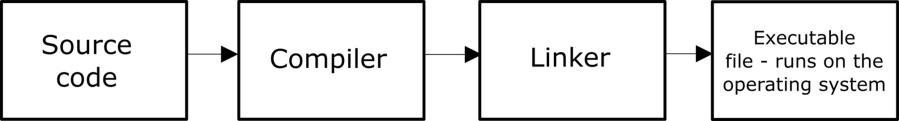
BEGINNER’S GUIDE TO MOBILE APP DEVELOPMENT IN ANDRIOD STUDIO
8. Publishing the app on Google Play (optional).
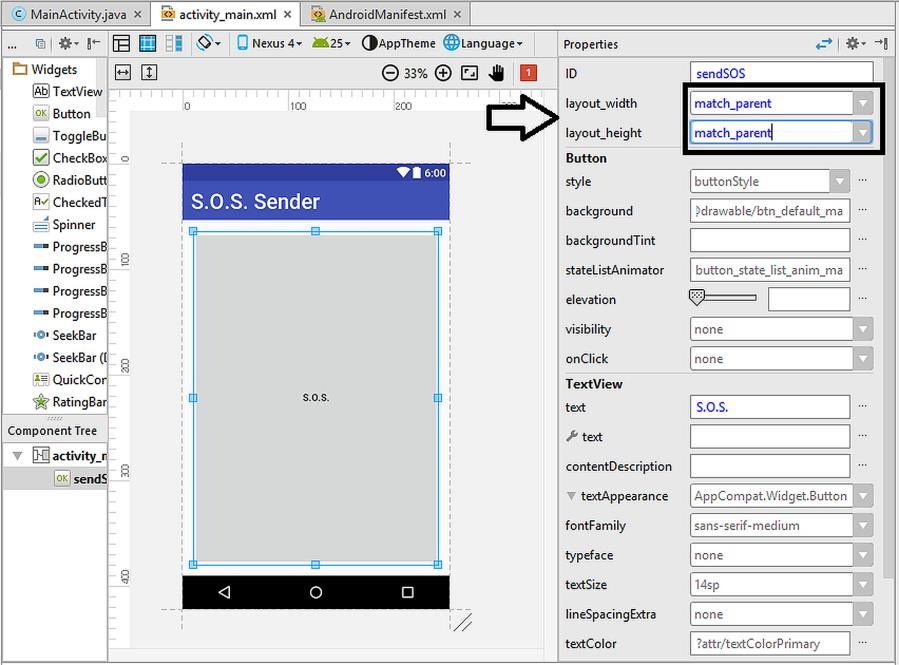
3.2. Creating a New Android Studio Project When we run Android Studio for the first time, we are presented by the dialog shown in Figure 3.1 where several options are available: i) Start a new Android Project, ii) Open an existing project, iii) Check out a project from a version control website (like GitHub), iv) Import a project created in a different development environment (like Eclipse) or v) Import an Android code sample (where code samples are downloaded from version control websites). We‟ll develop our first Android project therefore please select the first option shown by the arrow in Figure 3.1.
Figure 3.1. Creating a new Android Studio project for our first app After selecting to create a new project, a dialog box for entering the project settings will appear as in Figure 3.2. In the first textbox (shown by “1” in the figure), we are required to enter the project name, which will also be the name of the app. I entered “Hello World” but you can enter another name as you wish. The company domain is given in the next textbox shown by “2”. This is a string similar to a web address that is used to distinguish among developers in the Google Play market. You can use any unique domain here. If you won‟t upload your app to Google Play (as in this example where we‟re just developing for learning the 24