CHAPTER 4. JAVA BASICS
Our next subsection is about the logical decision making structures in Java, let‟s have a coffee break and then continue with if-else and switchcase statements.
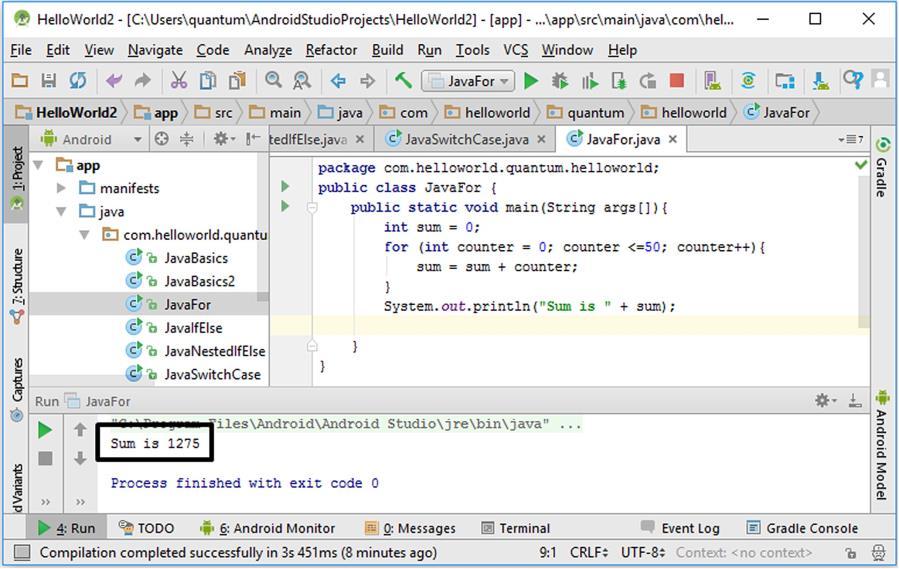
4.4. Logical Decision Making Statements in Java Decision making is a widely in programming as in daily life problems. We frequently make logical decisions in daily life such as: - “If their coffee is tasty I‟ll get another one, else I‟ll grab a tea”. - “If it‟s rainy I‟ll take my umbrella, else I‟ll not”. In a programming language, decision making statements controls if a condition is met or not as in real life. There are two decision making statements in Java: if–else and switch–case blocks. If–else structure: In this conditional, if the condition is satisfied, the code inside the if block is executed. If the condition isn‟t satisfied, then the code in the else block is executed. Hence, if we need tell the rainy – not rainy example using an if–else block, we do it as follows: if it‟s rainy { I‟ll take my umbrella. } else { I‟ll not take my umbrella. } Let‟s see how we can check if two numbers are equal in Java using an if-else statement: package com.helloworld.quantum.helloworld; public class JavaIfElse { public static void main(String args[]){ int a = 4; int b = 4; if (a == b){ 65